[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
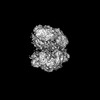
Yorodumi- PDB-8ui9: Cryo-EM map of human clamp-clamp loader ATAD5-RFC-cracked PCNA co... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ui9 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM map of human clamp-clamp loader ATAD5-RFC-cracked PCNA complex in intermediate state 2 | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / AAA ATPase / Clamp unloader | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDNA clamp unloader activity / positive regulation of cell cycle G2/M phase transition / Elg1 RFC-like complex / nuclear DNA replication / DNA replication factor C complex / Ctf18 RFC-like complex / positive regulation of deoxyribonuclease activity / dinucleotide insertion or deletion binding / PCNA-p21 complex / mitotic telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication ...DNA clamp unloader activity / positive regulation of cell cycle G2/M phase transition / Elg1 RFC-like complex / nuclear DNA replication / DNA replication factor C complex / Ctf18 RFC-like complex / positive regulation of deoxyribonuclease activity / dinucleotide insertion or deletion binding / PCNA-p21 complex / mitotic telomere maintenance via semi-conservative replication / positive regulation of isotype switching to IgG isotypes / purine-specific mismatch base pair DNA N-glycosylase activity / DNA clamp loader activity / nuclear lamina / positive regulation of DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / Polymerase switching / MutLalpha complex binding / Processive synthesis on the lagging strand / PCNA complex / Telomere C-strand (Lagging Strand) Synthesis / Removal of the Flap Intermediate / isotype switching / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH3 (MutSbeta) / Mismatch repair (MMR) directed by MSH2:MSH6 (MutSalpha) / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by DREAM complex / Polymerase switching on the C-strand of the telomere / replisome / Processive synthesis on the C-strand of the telomere / response to L-glutamate / Removal of the Flap Intermediate from the C-strand / regulation of mitotic cell cycle phase transition / HDR through Single Strand Annealing (SSA) / DNA strand elongation involved in DNA replication / negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / response to dexamethasone / DNA synthesis involved in DNA repair / histone acetyltransferase binding / Impaired BRCA2 binding to RAD51 / DNA polymerase processivity factor activity / G1/S-Specific Transcription / leading strand elongation / nuclear replication fork / replication fork processing / SUMOylation of DNA replication proteins / Presynaptic phase of homologous DNA pairing and strand exchange / signal transduction in response to DNA damage / PCNA-Dependent Long Patch Base Excision Repair / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / response to cadmium ion / ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA / translesion synthesis / estrous cycle / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / mismatch repair / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / base-excision repair, gap-filling / DNA polymerase binding / positive regulation of B cell proliferation / epithelial cell differentiation / liver regeneration / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G2 Cell Cycle Arrest / positive regulation of DNA repair / positive regulation of DNA replication / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / Translesion synthesis by POLK / replication fork / Translesion synthesis by POLI / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / male germ cell nucleus / Termination of translesion DNA synthesis / Recognition of DNA damage by PCNA-containing replication complex / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / receptor tyrosine kinase binding / HDR through Homologous Recombination (HRR) / DNA-templated DNA replication / Dual Incision in GG-NER / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / cellular response to hydrogen peroxide / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / cellular response to UV / response to estradiol / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / heart development / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / damaged DNA binding / DNA replication / chromosome, telomeric region / cell population proliferation / nuclear body / DNA repair / chromatin binding / centrosome / chromatin / protein-containing complex binding / enzyme binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, F. / He, Q. / Li, H. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024Title: The human ATAD5 has evolved unique structural elements to function exclusively as a PCNA unloader. Authors: Feng Wang / Qing He / Nina Y Yao / Michael E O'Donnell / Huilin Li /  Abstract: Humans have three different proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) clamp-loading complexes: RFC and CTF18-RFC load PCNA onto DNA, but ATAD5-RFC can only unload PCNA from DNA. The underlying ...Humans have three different proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) clamp-loading complexes: RFC and CTF18-RFC load PCNA onto DNA, but ATAD5-RFC can only unload PCNA from DNA. The underlying structural basis of ATAD5-RFC unloading is unknown. We show here that ATAD5 has two unique locking loops that appear to tie the complex into a rigid structure, and together with a domain that plugs the DNA-binding chamber, prevent conformation changes required for DNA binding, likely explaining why ATAD5-RFC is exclusively a PCNA unloader. These features are conserved in the yeast PCNA unloader Elg1-RFC. We observe intermediates in which PCNA bound to ATAD5-RFC exists as a closed planar ring, a cracked spiral or a gapped spiral. Surprisingly, ATAD5-RFC can open a PCNA gap between PCNA protomers 2 and 3, different from the PCNA protomers 1 and 3 gap observed in all previously characterized clamp loaders. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ui9.cif.gz 8ui9.cif.gz | 559.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ui9.ent.gz pdb8ui9.ent.gz | 442.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ui9.json.gz 8ui9.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8ui9_validation.pdf.gz 8ui9_validation.pdf.gz | 1.7 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8ui9_full_validation.pdf.gz 8ui9_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.7 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8ui9_validation.xml.gz 8ui9_validation.xml.gz | 87.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8ui9_validation.cif.gz 8ui9_validation.cif.gz | 128.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ui/8ui9 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ui/8ui9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ui/8ui9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ui/8ui9 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 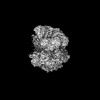 42289MC 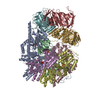 8ui7C  8ui8C  8uiiC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 4 molecules AFGH
| #1: Protein | Mass: 116421.094 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ATAD5 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ATAD5Production host: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) References: UniProt: Q96QE3 |
|---|---|
| #6: Protein | Mass: 28795.752 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PCNA Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PCNAProduction host: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) References: UniProt: P12004 |
-Replication factor C subunit ... , 4 types, 4 molecules BCDE
| #2: Protein | Mass: 39203.207 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC2 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC2Production host: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) References: UniProt: P35250 |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 38545.512 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC5 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC5Production host: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) References: UniProt: P40937 |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 39735.711 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC4 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC4Production host: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) References: UniProt: P35249 |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 40614.332 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC3 Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RFC3Production host: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) References: UniProt: P40938 |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 9 molecules 




| #7: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #8: Chemical | ChemComp-AGS / #9: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: ATAD5-RFC-cracked PCNA / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#6 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.32 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism: Insect cell expression vector pTIE1 (others) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: DIFFRACTION / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 112347 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj





















