[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8ti9: CryoEM structure of octamer assembly of Shedu nuclease domain fro... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ti9 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | CryoEM structure of octamer assembly of Shedu nuclease domain from Bacillus cereus | ||||||
 Components Components | Shedu protein SduA | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN / Shedu / DUF4263 / Bacterial defense systems / Nuclease / Anti-plasmid defense system / PD-(D/E)XK nuclease / Whirly domain / Two-component signaling | ||||||
| Function / homology | Protein of unknown function DUF4263 / : / Shedu protein SduA, C-terminal / Shedu protein SduA, N-terminal / nuclease activity / defense response to virus / Shedu protein SduA Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.19 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Gu, Y. / Corbett, K. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2025 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2025Title: Bacterial Shedu immune nucleases share a common enzymatic core regulated by diverse sensor domains. Authors: Yajie Gu / Huan Li / Amar Deep / Eray Enustun / Dapeng Zhang / Kevin D Corbett /  Abstract: Prokaryotes possess diverse anti-bacteriophage immune systems, including the single-protein Shedu nuclease. Here, we reveal the structural basis for activation of Bacillus cereus Shedu. Two ...Prokaryotes possess diverse anti-bacteriophage immune systems, including the single-protein Shedu nuclease. Here, we reveal the structural basis for activation of Bacillus cereus Shedu. Two cryoelectron microscopy structures of Shedu show that it switches between inactive and active states through conformational changes affecting active-site architecture, which are controlled by the protein's N-terminal domain (NTD). We find that B. cereus Shedu cleaves near DNA ends with a 3' single-stranded overhang, likely enabling it to specifically degrade the DNA injected by certain bacteriophages. Bioinformatic analysis of Shedu homologs reveals a conserved nuclease domain with remarkably diverse N-terminal regulatory domains: we identify 79 distinct NTD types falling into eight broad classes, including those with predicted nucleic acid binding, enzymatic, and other activities. Together, these data reveal Shedu as a broad family of immune nucleases with a common nuclease core regulated by diverse NTDs that likely respond to a range of signals. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ti9.cif.gz 8ti9.cif.gz | 309.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ti9.ent.gz pdb8ti9.ent.gz | 252.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ti9.json.gz 8ti9.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8ti9_validation.pdf.gz 8ti9_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8ti9_full_validation.pdf.gz 8ti9_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8ti9_validation.xml.gz 8ti9_validation.xml.gz | 57.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8ti9_validation.cif.gz 8ti9_validation.cif.gz | 84.3 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ti/8ti9 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ti/8ti9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ti/8ti9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ti/8ti9 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  41282MC  8ti8C  8tiaC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 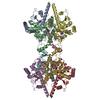
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 26236.760 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Mutation: E264A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Bacillus cereus Shedu delta_NL octamer / Type: COMPLEX Details: Octamer assembly of Bacillus cereus Shedu nuclease domain, which truncates the N-terminal and linker region. Glutamic acid 264 is mutated to Alanine. Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.216 MDa / Experimental value: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 Details: Prepared using deionized water and filtered strelized. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: Freshly collected from size-exclusion column | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 55 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.19 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 138326 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Source name: AlphaFold / Type: in silico model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj