+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: PDB / ID: 8smv | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | GPR161 Gs heterotrimer | ||||||
 要素 要素 |
| ||||||
 キーワード キーワード | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / GPCR / orphan / active / Hedgehog | ||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway involved in dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning / ciliary membrane / PKA activation in glucagon signalling / developmental growth / hair follicle placode formation / D1 dopamine receptor binding / intracellular transport / vascular endothelial cell response to laminar fluid shear stress / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / renal water homeostasis ...negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway involved in dorsal/ventral neural tube patterning / ciliary membrane / PKA activation in glucagon signalling / developmental growth / hair follicle placode formation / D1 dopamine receptor binding / intracellular transport / vascular endothelial cell response to laminar fluid shear stress / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / renal water homeostasis / Hedgehog 'off' state / adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway / cellular response to glucagon stimulus / regulation of insulin secretion / adenylate cyclase activator activity / trans-Golgi network membrane / Hedgehog 'on' state / negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus / G protein-coupled receptor activity / bone development / recycling endosome / platelet aggregation / G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding / Olfactory Signaling Pathway / cognition / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / endocytic vesicle membrane / G beta:gamma signalling through PLC beta / Presynaptic function of Kainate receptors / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway / G-protein activation / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / Prostacyclin signalling through prostacyclin receptor / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Glucagon signaling in metabolic regulation / G beta:gamma signalling through BTK / Synthesis, secretion, and inactivation of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / photoreceptor disc membrane / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / G alpha (z) signalling events / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 1 / cellular response to catecholamine stimulus / ADORA2B mediated anti-inflammatory cytokines production / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma / sensory perception of smell / Cooperation of PDCL (PhLP1) and TRiC/CCT in G-protein beta folding / adenylate cyclase-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway / GPER1 signaling / Inactivation, recovery and regulation of the phototransduction cascade / cellular response to prostaglandin E stimulus / G-protein beta-subunit binding / heterotrimeric G-protein complex / G alpha (12/13) signalling events / sensory perception of taste / extracellular vesicle / signaling receptor complex adaptor activity / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / retina development in camera-type eye / G protein activity / GTPase binding / Ca2+ pathway / fibroblast proliferation / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / G alpha (i) signalling events / G alpha (s) signalling events / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / 加水分解酵素; 酸無水物に作用; GTPに作用・細胞または細胞小器官の運動に関与 / G alpha (q) signalling events / Ras protein signal transduction / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / cell population proliferation / cilium / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / lysosomal membrane / GTPase activity / synapse / GTP binding / protein-containing complex binding / signal transduction / extracellular exosome / metal ion binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm 類似検索 - 分子機能 | ||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | ||||||
| 手法 | 電子顕微鏡法 / 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 2.74 Å | ||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Hoppe, N. / Manglik, A. / Harrison, S. | ||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 1件 米国, 1件
| ||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年: 2024 ジャーナル: Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年: 2024タイトル: GPR161 structure uncovers the redundant role of sterol-regulated ciliary cAMP signaling in the Hedgehog pathway. 著者: Nicholas Hoppe / Simone Harrison / Sun-Hee Hwang / Ziwei Chen / Masha Karelina / Ishan Deshpande / Carl-Mikael Suomivuori / Vivek R Palicharla / Samuel P Berry / Philipp Tschaikner / Dominik ...著者: Nicholas Hoppe / Simone Harrison / Sun-Hee Hwang / Ziwei Chen / Masha Karelina / Ishan Deshpande / Carl-Mikael Suomivuori / Vivek R Palicharla / Samuel P Berry / Philipp Tschaikner / Dominik Regele / Douglas F Covey / Eduard Stefan / Debora S Marks / Jeremy F Reiter / Ron O Dror / Alex S Evers / Saikat Mukhopadhyay / Aashish Manglik /   要旨: The orphan G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) GPR161 plays a central role in development by suppressing Hedgehog signaling. The fundamental basis of how GPR161 is activated remains unclear. Here, we ...The orphan G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) GPR161 plays a central role in development by suppressing Hedgehog signaling. The fundamental basis of how GPR161 is activated remains unclear. Here, we determined a cryogenic-electron microscopy structure of active human GPR161 bound to heterotrimeric G. This structure revealed an extracellular loop 2 that occupies the canonical GPCR orthosteric ligand pocket. Furthermore, a sterol that binds adjacent to transmembrane helices 6 and 7 stabilizes a GPR161 conformation required for G coupling. Mutations that prevent sterol binding to GPR161 suppress G-mediated signaling. These mutants retain the ability to suppress GLI2 transcription factor accumulation in primary cilia, a key function of ciliary GPR161. By contrast, a protein kinase A-binding site in the GPR161 C terminus is critical in suppressing GLI2 ciliary accumulation. Our work highlights how structural features of GPR161 interface with the Hedgehog pathway and sets a foundation to understand the role of GPR161 function in other signaling pathways. #1: ジャーナル: bioRxiv / 年: 2023 タイトル: GPR161 structure uncovers the redundant role of sterol-regulated ciliary cAMP signaling in the Hedgehog pathway. 著者: Nicholas Hoppe / Simone Harrison / Sun-Hee Hwang / Ziwei Chen / Masha Karelina / Ishan Deshpande / Carl-Mikael Suomivuori / Vivek R Palicharla / Samuel P Berry / Philipp Tschaikner / Dominik ...著者: Nicholas Hoppe / Simone Harrison / Sun-Hee Hwang / Ziwei Chen / Masha Karelina / Ishan Deshpande / Carl-Mikael Suomivuori / Vivek R Palicharla / Samuel P Berry / Philipp Tschaikner / Dominik Regele / Douglas F Covey / Eduard Stefan / Debora S Marks / Jeremy Reiter / Ron O Dror / Alex S Evers / Saikat Mukhopadhyay / Aashish Manglik /   要旨: The orphan G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) GPR161 is enriched in primary cilia, where it plays a central role in suppressing Hedgehog signaling. GPR161 mutations lead to developmental defects and ...The orphan G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) GPR161 is enriched in primary cilia, where it plays a central role in suppressing Hedgehog signaling. GPR161 mutations lead to developmental defects and cancers. The fundamental basis of how GPR161 is activated, including potential endogenous activators and pathway-relevant signal transducers, remains unclear. To elucidate GPR161 function, we determined a cryogenic-electron microscopy structure of active GPR161 bound to the heterotrimeric G protein complex G. This structure revealed an extracellular loop 2 that occupies the canonical GPCR orthosteric ligand pocket. Furthermore, we identify a sterol that binds to a conserved extrahelical site adjacent to transmembrane helices 6 and 7 and stabilizes a GPR161 conformation required for G coupling. Mutations that prevent sterol binding to GPR161 suppress cAMP pathway activation. Surprisingly, these mutants retain the ability to suppress GLI2 transcription factor accumulation in cilia, a key function of ciliary GPR161 in Hedgehog pathway suppression. By contrast, a protein kinase A-binding site in the GPR161 C-terminus is critical in suppressing GLI2 ciliary accumulation. Our work highlights how unique structural features of GPR161 interface with the Hedgehog pathway and sets a foundation to understand the broader role of GPR161 function in other signaling pathways. #2:  ジャーナル: Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年: 2024 ジャーナル: Nat Struct Mol Biol / 年: 2024タイトル: GPR161 structure uncovers the redundant role of sterol-regulated ciliary cAMP signaling in the Hedgehog pathway. 著者: Nicholas Hoppe / Simone Harrison / Sun-Hee Hwang / Ziwei Chen / Masha Karelina / Ishan Deshpande / Carl-Mikael Suomivuori / Vivek R Palicharla / Samuel P Berry / Philipp Tschaikner / Dominik ...著者: Nicholas Hoppe / Simone Harrison / Sun-Hee Hwang / Ziwei Chen / Masha Karelina / Ishan Deshpande / Carl-Mikael Suomivuori / Vivek R Palicharla / Samuel P Berry / Philipp Tschaikner / Dominik Regele / Douglas F Covey / Eduard Stefan / Debora S Marks / Jeremy F Reiter / Ron O Dror / Alex S Evers / Saikat Mukhopadhyay / Aashish Manglik /   要旨: The orphan G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) GPR161 plays a central role in development by suppressing Hedgehog signaling. The fundamental basis of how GPR161 is activated remains unclear. Here, we ...The orphan G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) GPR161 plays a central role in development by suppressing Hedgehog signaling. The fundamental basis of how GPR161 is activated remains unclear. Here, we determined a cryogenic-electron microscopy structure of active human GPR161 bound to heterotrimeric G. This structure revealed an extracellular loop 2 that occupies the canonical GPCR orthosteric ligand pocket. Furthermore, a sterol that binds adjacent to transmembrane helices 6 and 7 stabilizes a GPR161 conformation required for G coupling. Mutations that prevent sterol binding to GPR161 suppress G-mediated signaling. These mutants retain the ability to suppress GLI2 transcription factor accumulation in primary cilia, a key function of ciliary GPR161. By contrast, a protein kinase A-binding site in the GPR161 C terminus is critical in suppressing GLI2 ciliary accumulation. Our work highlights how structural features of GPR161 interface with the Hedgehog pathway and sets a foundation to understand the role of GPR161 function in other signaling pathways. | ||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| 構造ビューア | 分子:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
- ダウンロード
ダウンロード
| PDBx/mmCIF形式 |  8smv.cif.gz 8smv.cif.gz | 223 KB | 表示 |  PDBx/mmCIF形式 PDBx/mmCIF形式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB形式 |  pdb8smv.ent.gz pdb8smv.ent.gz | 169 KB | 表示 |  PDB形式 PDB形式 |
| PDBx/mmJSON形式 |  8smv.json.gz 8smv.json.gz | ツリー表示 |  PDBx/mmJSON形式 PDBx/mmJSON形式 | |
| その他 |  その他のダウンロード その他のダウンロード |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  8smv_validation.pdf.gz 8smv_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | 表示 |  wwPDB検証レポート wwPDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  8smv_full_validation.pdf.gz 8smv_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  8smv_validation.xml.gz 8smv_validation.xml.gz | 42.4 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  8smv_validation.cif.gz 8smv_validation.cif.gz | 62.9 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sm/8smv https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sm/8smv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sm/8smv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sm/8smv | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  40603MC M: このデータのモデリングに利用したマップデータ C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ | 類似検索 - 機能・相同性  F&H 検索 F&H 検索 |
- リンク
リンク
- 集合体
集合体
| 登録構造単位 | 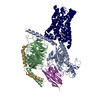
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- 要素
要素
-Guanine nucleotide-binding protein ... , 3種, 3分子 GAB
| #2: タンパク質 | 分子量: 7861.143 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: GNG2 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: GNG2 / 発現宿主:  Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ) / 参照: UniProt: P59768 Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ) / 参照: UniProt: P59768 |
|---|---|
| #4: タンパク質 | 分子量: 30137.025 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: GNAS, GNAS1, GSP / 細胞株 (発現宿主): Expi293 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: GNAS, GNAS1, GSP / 細胞株 (発現宿主): Expi293 / 発現宿主:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P63092 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P63092 |
| #5: タンパク質 | 分子量: 40857.641 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: GNB1 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: GNB1 / 発現宿主:  Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ) / 参照: UniProt: P62873 Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ) / 参照: UniProt: P62873 |
-タンパク質 / 抗体 / 非ポリマー , 3種, 3分子 RN

| #1: タンパク質 | 分子量: 59869.941 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: GPR161 / 細胞株 (発現宿主): Expi293 / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: GPR161 / 細胞株 (発現宿主): Expi293 / 発現宿主:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: Q8N6U8 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: Q8N6U8 |
|---|---|
| #3: 抗体 | 分子量: 15398.067 Da / 分子数: 1 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)   |
| #6: 化合物 | ChemComp-CLR / |
-詳細
| 研究の焦点であるリガンドがあるか | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-実験情報
-実験
| 実験 | 手法: 電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
| EM実験 | 試料の集合状態: PARTICLE / 3次元再構成法: 単粒子再構成法 |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 構成要素 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 由来(天然) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 由来(組換発現) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 試料 | 包埋: NO / シャドウイング: NO / 染色: NO / 凍結: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 急速凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE |
- 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| 顕微鏡 | モデル: TFS KRIOS |
| 電子銃 | 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: SPOT SCAN |
| 電子レンズ | モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2200 nm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 800 nm |
| 撮影 | 電子線照射量: 50.7 e/Å2 フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- 解析
解析
| EMソフトウェア | 名称: PHENIX / バージョン: 1.20.1_4487: / カテゴリ: モデル精密化 |
|---|---|
| CTF補正 | タイプ: NONE |
| 3次元再構成 | 解像度: 2.74 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 粒子像の数: 335928 / 対称性のタイプ: POINT |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー



 PDBj
PDBj



























