+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8roz | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of CDK2-cyclin A in complex with CDC25A | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE / cell-cycle / CDK / phosphatase / cancer | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of G2/MI transition of meiotic cell cycle / cell cycle G1/S phase transition / Polo-like kinase mediated events / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by DREAM complex / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / Deregulated CDK5 triggers multiple neurodegenerative pathways in Alzheimer's disease models / cyclin A1-CDK2 complex / cyclin E2-CDK2 complex / cyclin E1-CDK2 complex ...positive regulation of G2/MI transition of meiotic cell cycle / cell cycle G1/S phase transition / Polo-like kinase mediated events / Transcription of E2F targets under negative control by DREAM complex / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / Deregulated CDK5 triggers multiple neurodegenerative pathways in Alzheimer's disease models / cyclin A1-CDK2 complex / cyclin E2-CDK2 complex / cyclin E1-CDK2 complex / cyclin A2-CDK2 complex / positive regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / cyclin-dependent protein kinase activity / G2 Phase / Y chromosome / Phosphorylation of proteins involved in G1/S transition by active Cyclin E:Cdk2 complexes / positive regulation of heterochromatin formation / p53-Dependent G1 DNA Damage Response / X chromosome / PTK6 Regulates Cell Cycle / regulation of anaphase-promoting complex-dependent catabolic process / Defective binding of RB1 mutants to E2F1,(E2F2, E2F3) / microtubule organizing center / centriole replication / Regulation of APC/C activators between G1/S and early anaphase / telomere maintenance in response to DNA damage / regulation of DNA replication / centrosome duplication / phosphoprotein phosphatase activity / Telomere Extension By Telomerase / G0 and Early G1 / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / cyclin-dependent kinase / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / TP53 Regulates Transcription of Genes Involved in G1 Cell Cycle Arrest / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in cell cycle and proliferation / Cajal body / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / Cyclin E associated events during G1/S transition / Cyclin A/B1/B2 associated events during G2/M transition / Cyclin A:Cdk2-associated events at S phase entry / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / condensed chromosome / regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / positive regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / protein tyrosine phosphatase activity / protein tyrosine phosphatase activity, metal-dependent / histone H2AXY142 phosphatase activity / protein-tyrosine-phosphatase / non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine phosphatase activity / cellular response to nitric oxide / post-translational protein modification / cyclin binding / regulation of mitotic cell cycle / male germ cell nucleus / positive regulation of DNA replication / meiotic cell cycle / Ubiquitin-Mediated Degradation of Phosphorylated Cdc25A / response to radiation / potassium ion transport / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Meiotic recombination / CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 / SCF(Skp2)-mediated degradation of p27/p21 / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / Orc1 removal from chromatin / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / Cyclin D associated events in G1 / cellular senescence / Regulation of TP53 Degradation / nuclear envelope / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / protein-folding chaperone binding / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / regulation of gene expression / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Phosphorylation / transcription regulator complex / Ras protein signal transduction / chromosome, telomeric region / cell population proliferation / DNA replication / endosome / Ub-specific processing proteases / protein phosphorylation / chromatin remodeling / protein domain specific binding / cell division / protein serine kinase activity / DNA repair / protein serine/threonine kinase activity / DNA-templated transcription / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / centrosome / protein kinase binding / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Rowland, R.J. / Noble, M.E.M. / Endicott, J.A. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2items United Kingdom, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: Cryo-EM structure of the CDK2-cyclin A-CDC25A complex. Authors: Rhianna J Rowland / Svitlana Korolchuk / Marco Salamina / Natalie J Tatum / James R Ault / Sam Hart / Johan P Turkenburg / James N Blaza / Martin E M Noble / Jane A Endicott /  Abstract: The cell division cycle 25 phosphatases CDC25A, B and C regulate cell cycle transitions by dephosphorylating residues in the conserved glycine-rich loop of CDKs to activate their activity. Here, we ...The cell division cycle 25 phosphatases CDC25A, B and C regulate cell cycle transitions by dephosphorylating residues in the conserved glycine-rich loop of CDKs to activate their activity. Here, we present the cryo-EM structure of CDK2-cyclin A in complex with CDC25A at 2.7 Å resolution, providing a detailed structural analysis of the overall complex architecture and key protein-protein interactions that underpin this 86 kDa complex. We further identify a CDC25A C-terminal helix that is critical for complex formation. Sequence conservation analysis suggests CDK1/2-cyclin A, CDK1-cyclin B and CDK2/3-cyclin E are suitable binding partners for CDC25A, whilst CDK4/6-cyclin D complexes appear unlikely substrates. A comparative structural analysis of CDK-containing complexes also confirms the functional importance of the conserved CDK1/2 GDSEID motif. This structure improves our understanding of the roles of CDC25 phosphatases in CDK regulation and may inform the development of CDC25-targeting anticancer strategies. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8roz.cif.gz 8roz.cif.gz | 162.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8roz.ent.gz pdb8roz.ent.gz | 125 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8roz.json.gz 8roz.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ro/8roz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ro/8roz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ro/8roz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ro/8roz | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  19408MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 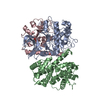
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 34136.449 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Human cyclin dependant protein kinase 2 (CDK2) phosphorylated at Tyr15 and Thr160 Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDK2, CDKN2 / Plasmid: PGEX6P1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDK2, CDKN2 / Plasmid: PGEX6P1 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 30119.799 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Bovine cyclin A2 / Source: (gene. exp.)   |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 22533.123 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: M-phase inducer phosphatase 1 (CDC25A) catalytic domain Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC25A / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CDC25A / Production host:  |
| Has ligand of interest | N |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Trimeric complex of CDK2-cyclin A-CDC25A / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.086 MDa / Experimental value: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 / Details: 50 mM HEPES, 200 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, pH 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.8 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: Grids were glow discharged for 1min at 20 mAmp/0.26 mBar Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 80 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 150000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 1.92 sec. / Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: Patch CTF / Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 4981705 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 670830 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 144 / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL Details: A model was generated using ModelAngelo. Initial local fitting was performed in ChimerX followed by real space refinement in Phenix and manual fitting in coot. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Details: ModelAngelo / Source name: Other / Type: in silico model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj














