+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8qud | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
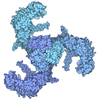
| Title | Cryo-EM Structure of Human Kv3.1 in Complex with Modulator AUT5 | |||||||||
 Components Components | Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily C member 1 | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Modulator / Homotetramer / Voltage-gated potassium channel / Kv3.1 / KCNC1 | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationresponse to nerve growth factor / globus pallidus development / response to fibroblast growth factor / response to potassium ion / corpus callosum development / response to auditory stimulus / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / Voltage gated Potassium channels / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport ...response to nerve growth factor / globus pallidus development / response to fibroblast growth factor / response to potassium ion / corpus callosum development / response to auditory stimulus / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / Voltage gated Potassium channels / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / response to light intensity / optic nerve development / neuronal cell body membrane / response to amine / action potential / kinesin binding / axolemma / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / axon terminus / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / dendrite membrane / calyx of Held / cerebellum development / protein tetramerization / protein homooligomerization / potassium ion transport / response to toxic substance / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / presynaptic membrane / transmembrane transporter binding / postsynaptic membrane / cell surface / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chi, G. / Mckinley, G. / Marsden, B. / Pike, A.C.W. / Ye, M. / Brooke, L.M. / Bakshi, S. / Lakshminarayana, B. / Pilati, N. / Marasco, A. ...Chi, G. / Mckinley, G. / Marsden, B. / Pike, A.C.W. / Ye, M. / Brooke, L.M. / Bakshi, S. / Lakshminarayana, B. / Pilati, N. / Marasco, A. / Gunthorpe, M. / Alvaro, G.S. / Large, C.H. / Williams, E. / Sauer, D.B. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  Switzerland, 2items Switzerland, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: The binding and mechanism of a positive allosteric modulator of Kv3 channels. Authors: Qiansheng Liang / Gamma Chi / Leonardo Cirqueira / Lianteng Zhi / Agostino Marasco / Nadia Pilati / Martin J Gunthorpe / Giuseppe Alvaro / Charles H Large / David B Sauer / Werner Treptow / ...Authors: Qiansheng Liang / Gamma Chi / Leonardo Cirqueira / Lianteng Zhi / Agostino Marasco / Nadia Pilati / Martin J Gunthorpe / Giuseppe Alvaro / Charles H Large / David B Sauer / Werner Treptow / Manuel Covarrubias /     Abstract: Small-molecule modulators of diverse voltage-gated K (Kv) channels may help treat a wide range of neurological disorders. However, developing effective modulators requires understanding of their ...Small-molecule modulators of diverse voltage-gated K (Kv) channels may help treat a wide range of neurological disorders. However, developing effective modulators requires understanding of their mechanism of action. We apply an orthogonal approach to elucidate the mechanism of action of an imidazolidinedione derivative (AUT5), a highly selective positive allosteric modulator of Kv3.1 and Kv3.2 channels. AUT5 modulation involves positive cooperativity and preferential stabilization of the open state. The cryo-EM structure of the Kv3.1/AUT5 complex at a resolution of 2.5 Å reveals four equivalent AUT5 binding sites at the extracellular inter-subunit interface between the voltage-sensing and pore domains of the channel's tetrameric assembly. Furthermore, we show that the unique extracellular turret regions of Kv3.1 and Kv3.2 essentially govern the selective positive modulation by AUT5. High-resolution apo and bound structures of Kv3.1 demonstrate how AUT5 binding promotes turret rearrangements and interactions with the voltage-sensing domain to favor the open conformation. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8qud.cif.gz 8qud.cif.gz | 328 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8qud.ent.gz pdb8qud.ent.gz | 260.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8qud.json.gz 8qud.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8qud_validation.pdf.gz 8qud_validation.pdf.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8qud_full_validation.pdf.gz 8qud_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.6 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8qud_validation.xml.gz 8qud_validation.xml.gz | 62.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8qud_validation.cif.gz 8qud_validation.cif.gz | 88.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qu/8qud https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qu/8qud ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qu/8qud ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qu/8qud | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  18660MC  8qucC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 4 molecules ABDC
| #1: Protein | Mass: 58850.078 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCNC1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCNC1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P48547 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P48547 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 6 types, 130 molecules 

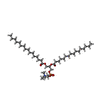






| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-WY0 / ( Mass: 365.383 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Formula: C20H19N3O4 / Feature type: SUBJECT OF INVESTIGATION #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-Y01 / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-PCF / #6: Chemical | ChemComp-K / #7: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Homotetramer of Human Kv3.1a with modulator AUT5 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.24 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 10 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2400 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 17329 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2975775 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 1484211 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 7PHI Accession code: 7PHI / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj