[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8qbf: Compact state - Pil1 dimer with lipid headgroups fitted in native... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8qbf | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Compact state - Pil1 dimer with lipid headgroups fitted in native eisosome lattice bound to plasma membrane microdomain | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Sphingolipid long chain base-responsive protein PIL1 | |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIPID BINDING PROTEIN / BAR domain / lipid reconstitution / membrane microdomain | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationprotein localization to eisosome filament / eisosome filament / eisosome assembly / eisosome / lipid droplet / cell periphery / endocytosis / intracellular protein localization / mitochondrial outer membrane / lipid binding ...protein localization to eisosome filament / eisosome filament / eisosome assembly / eisosome / lipid droplet / cell periphery / endocytosis / intracellular protein localization / mitochondrial outer membrane / lipid binding / mitochondrion / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.67 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kefauver, J.M. / Zou, L. / Desfosses, A. / Loewith, R.J. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support | European Union,  Switzerland, 4items Switzerland, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Cryo-EM architecture of a near-native stretch-sensitive membrane microdomain. Authors: Jennifer M Kefauver / Markku Hakala / Luoming Zou / Josephine Alba / Javier Espadas / Maria G Tettamanti / Jelena Gajić / Caroline Gabus / Pablo Campomanes / Leandro F Estrozi / Nesli E Sen ...Authors: Jennifer M Kefauver / Markku Hakala / Luoming Zou / Josephine Alba / Javier Espadas / Maria G Tettamanti / Jelena Gajić / Caroline Gabus / Pablo Campomanes / Leandro F Estrozi / Nesli E Sen / Stefano Vanni / Aurélien Roux / Ambroise Desfosses / Robbie Loewith /    Abstract: Biological membranes are partitioned into functional zones termed membrane microdomains, which contain specific lipids and proteins. The composition and organization of membrane microdomains remain ...Biological membranes are partitioned into functional zones termed membrane microdomains, which contain specific lipids and proteins. The composition and organization of membrane microdomains remain controversial because few techniques are available that allow the visualization of lipids in situ without disrupting their native behaviour. The yeast eisosome, composed of the BAR-domain proteins Pil1 and Lsp1 (hereafter, Pil1/Lsp1), scaffolds a membrane compartment that senses and responds to mechanical stress by flattening and releasing sequestered factors. Here we isolated near-native eisosomes as helical tubules made up of a lattice of Pil1/Lsp1 bound to plasma membrane lipids, and solved their structures by helical reconstruction. Our structures reveal a striking organization of membrane lipids, and, using in vitro reconstitutions and molecular dynamics simulations, we confirmed the positioning of individual PI(4,5)P, phosphatidylserine and sterol molecules sequestered beneath the Pil1/Lsp1 coat. Three-dimensional variability analysis of the native-source eisosomes revealed a dynamic stretching of the Pil1/Lsp1 lattice that affects the sequestration of these lipids. Collectively, our results support a mechanism in which stretching of the Pil1/Lsp1 lattice liberates lipids that would otherwise be anchored by the Pil1/Lsp1 coat, and thus provide mechanistic insight into how eisosome BAR-domain proteins create a mechanosensitive membrane microdomain. #1: Journal: Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol / Year: 2018 Title: Real-space refinement in PHENIX for cryo-EM and crystallography. Authors: Pavel V Afonine / Billy K Poon / Randy J Read / Oleg V Sobolev / Thomas C Terwilliger / Alexandre Urzhumtsev / Paul D Adams /    Abstract: This article describes the implementation of real-space refinement in the phenix.real_space_refine program from the PHENIX suite. The use of a simplified refinement target function enables very fast ...This article describes the implementation of real-space refinement in the phenix.real_space_refine program from the PHENIX suite. The use of a simplified refinement target function enables very fast calculation, which in turn makes it possible to identify optimal data-restraint weights as part of routine refinements with little runtime cost. Refinement of atomic models against low-resolution data benefits from the inclusion of as much additional information as is available. In addition to standard restraints on covalent geometry, phenix.real_space_refine makes use of extra information such as secondary-structure and rotamer-specific restraints, as well as restraints or constraints on internal molecular symmetry. The re-refinement of 385 cryo-EM-derived models available in the Protein Data Bank at resolutions of 6 Å or better shows significant improvement of the models and of the fit of these models to the target maps. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8qbf.cif.gz 8qbf.cif.gz | 103.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8qbf.ent.gz pdb8qbf.ent.gz | 81.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8qbf.json.gz 8qbf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8qbf_validation.pdf.gz 8qbf_validation.pdf.gz | 1.6 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8qbf_full_validation.pdf.gz 8qbf_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.6 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8qbf_validation.xml.gz 8qbf_validation.xml.gz | 29.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8qbf_validation.cif.gz 8qbf_validation.cif.gz | 38.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qb/8qbf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qb/8qbf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qb/8qbf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qb/8qbf | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  18311MC  8qb7C  8qb8C  8qb9C  8qbbC  8qbdC  8qbeC  8qbgC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
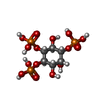
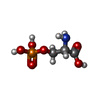
| #1: Protein | Mass: 30496.256 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Chemical | #3: Chemical | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: HELICAL ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Helical lattice of native Pil1/Lsp1 protein bound to plasma membrane microdomain Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7 / Details: 50mM PIPES pH 7, 300mM NaCl, 1mM CHAPS, 0.5mM DTT |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: EMS Lacey Carbon |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.67 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 63118 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Accession code: P53252 / Source name: AlphaFold / Type: in silico model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj