[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8q7s: Crystal structure of the SARS-CoV-2 RBD (Wuhan) with neutralizing... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8q7s | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of the SARS-CoV-2 RBD (Wuhan) with neutralizing VHHs Ma6F06 and Re21H01 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ANTIVIRAL PROTEIN / SARS-CoV-2 / VHH Antibody / Nanobody | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsymbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / viral translation / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion ...symbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / viral translation / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / membrane fusion / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / Attachment and Entry / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell surface receptor binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / receptor ligand activity / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / virion attachment to host cell / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.7 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Guttler, T. / Aksu, M. / Gorlich, D. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1items Germany, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Antiviral Res / Year: 2024 Journal: Antiviral Res / Year: 2024Title: Nanobodies to multiple spike variants and inhalation of nanobody-containing aerosols neutralize SARS-CoV-2 in cell culture and hamsters. Authors: Metin Aksu / Priya Kumar / Thomas Güttler / Waltraud Taxer / Kathrin Gregor / Bianka Mußil / Oleh Rymarenko / Kim M Stegmann / Antje Dickmanns / Sabrina Gerber / Wencke Reineking / Claudia ...Authors: Metin Aksu / Priya Kumar / Thomas Güttler / Waltraud Taxer / Kathrin Gregor / Bianka Mußil / Oleh Rymarenko / Kim M Stegmann / Antje Dickmanns / Sabrina Gerber / Wencke Reineking / Claudia Schulz / Timo Henneck / Ahmed Mohamed / Gerhard Pohlmann / Mehmet Ramazanoglu / Kemal Mese / Uwe Groß / Tamar Ben-Yedidia / Oded Ovadia / Dalit Weinstein Fischer / Merav Kamensky / Amir Reichman / Wolfgang Baumgärtner / Maren von Köckritz-Blickwede / Matthias Dobbelstein / Dirk Görlich /   Abstract: The ongoing threat of COVID-19 has highlighted the need for effective prophylaxis and convenient therapies, especially for outpatient settings. We have previously developed highly potent single- ...The ongoing threat of COVID-19 has highlighted the need for effective prophylaxis and convenient therapies, especially for outpatient settings. We have previously developed highly potent single-domain (VHH) antibodies, also known as nanobodies, that target the Receptor Binding Domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein and neutralize the Wuhan strain of the virus. In this study, we present a new generation of anti-RBD nanobodies with superior properties. The primary representative of this group, Re32D03, neutralizes Alpha to Delta as well as Omicron BA.2.75; other members neutralize, in addition, Omicron BA.1, BA.2, BA.4/5, and XBB.1. Crystal structures of RBD-nanobody complexes reveal how ACE2-binding is blocked and also explain the nanobodies' tolerance to immune escape mutations. Through the cryo-EM structure of the Ma16B06-BA.1 Spike complex, we demonstrated how a single nanobody molecule can neutralize a trimeric spike. We also describe a method for large-scale production of these nanobodies in Pichia pastoris, and for formulating them into aerosols. Exposing hamsters to these aerosols, before or even 24 h after infection with SARS-CoV-2, significantly reduced virus load, weight loss and pathogenicity. These results show the potential of aerosolized nanobodies for prophylaxis and therapy of coronavirus infections. #1: Journal: Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol / Year: 2019 Title: Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: recent developments in Phenix. Authors: Dorothee Liebschner / Pavel V Afonine / Matthew L Baker / Gábor Bunkóczi / Vincent B Chen / Tristan I Croll / Bradley Hintze / Li Wei Hung / Swati Jain / Airlie J McCoy / Nigel W Moriarty ...Authors: Dorothee Liebschner / Pavel V Afonine / Matthew L Baker / Gábor Bunkóczi / Vincent B Chen / Tristan I Croll / Bradley Hintze / Li Wei Hung / Swati Jain / Airlie J McCoy / Nigel W Moriarty / Robert D Oeffner / Billy K Poon / Michael G Prisant / Randy J Read / Jane S Richardson / David C Richardson / Massimo D Sammito / Oleg V Sobolev / Duncan H Stockwell / Thomas C Terwilliger / Alexandre G Urzhumtsev / Lizbeth L Videau / Christopher J Williams / Paul D Adams /    Abstract: Diffraction (X-ray, neutron and electron) and electron cryo-microscopy are powerful methods to determine three-dimensional macromolecular structures, which are required to understand biological ...Diffraction (X-ray, neutron and electron) and electron cryo-microscopy are powerful methods to determine three-dimensional macromolecular structures, which are required to understand biological processes and to develop new therapeutics against diseases. The overall structure-solution workflow is similar for these techniques, but nuances exist because the properties of the reduced experimental data are different. Software tools for structure determination should therefore be tailored for each method. Phenix is a comprehensive software package for macromolecular structure determination that handles data from any of these techniques. Tasks performed with Phenix include data-quality assessment, map improvement, model building, the validation/rebuilding/refinement cycle and deposition. Each tool caters to the type of experimental data. The design of Phenix emphasizes the automation of procedures, where possible, to minimize repetitive and time-consuming manual tasks, while default parameters are chosen to encourage best practice. A graphical user interface provides access to many command-line features of Phenix and streamlines the transition between programs, project tracking and re-running of previous tasks. #2: Journal: Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr / Year: 2012 Title: Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.refine. Authors: Afonine, P.V. / Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W. / Echols, N. / Headd, J.J. / Moriarty, N.W. / Mustyakimov, M. / Terwilliger, T.C. / Urzhumtsev, A. / Zwart, P.H. / Adams, P.D. #4: Journal: Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr / Year: 2007 Title: Solving structures of protein complexes by molecular replacement with Phaser. Authors: McCoy, A.J. #5: Journal: Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr / Year: 2010 Title: Features and development of Coot. Authors: P Emsley / B Lohkamp / W G Scott / K Cowtan /  Abstract: Coot is a molecular-graphics application for model building and validation of biological macromolecules. The program displays electron-density maps and atomic models and allows model manipulations ...Coot is a molecular-graphics application for model building and validation of biological macromolecules. The program displays electron-density maps and atomic models and allows model manipulations such as idealization, real-space refinement, manual rotation/translation, rigid-body fitting, ligand search, solvation, mutations, rotamers and Ramachandran idealization. Furthermore, tools are provided for model validation as well as interfaces to external programs for refinement, validation and graphics. The software is designed to be easy to learn for novice users, which is achieved by ensuring that tools for common tasks are 'discoverable' through familiar user-interface elements (menus and toolbars) or by intuitive behaviour (mouse controls). Recent developments have focused on providing tools for expert users, with customisable key bindings, extensions and an extensive scripting interface. The software is under rapid development, but has already achieved very widespread use within the crystallographic community. The current state of the software is presented, with a description of the facilities available and of some of the underlying methods employed. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8q7s.cif.gz 8q7s.cif.gz | 513.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8q7s.ent.gz pdb8q7s.ent.gz | 338.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8q7s.json.gz 8q7s.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q7/8q7s https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q7/8q7s ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q7/8q7s ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/q7/8q7s | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8q93C  8q94C  8q95C C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 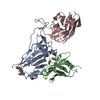
| ||||||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||||||
| 3 | 
| ||||||||||||
| 4 | 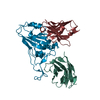
| ||||||||||||
| 5 | 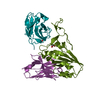
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 5 molecules ADGJM
| #1: Protein | Mass: 21949.504 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: S, 2 / Production host:  Komagataella pastoris (fungus) / References: UniProt: P0DTC2 Komagataella pastoris (fungus) / References: UniProt: P0DTC2 |
|---|
-Antibody , 2 types, 10 molecules BEHKNCFILO
| #2: Antibody | Mass: 12350.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Komagataella pastoris (fungus) Komagataella pastoris (fungus)#3: Antibody | Mass: 14052.618 Da / Num. of mol.: 5 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Komagataella pastoris (fungus) Komagataella pastoris (fungus) |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 228 molecules 






| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-P4G / | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-EDO / #6: Chemical | #7: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.64 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 53.44 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293.15 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop / pH: 4.5 / Details: 0.1 M Sodium Citrate pH 4.5 20% (w/v) PEG 4000 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SLS SLS  / Beamline: X10SA / Wavelength: 1 Å / Beamline: X10SA / Wavelength: 1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER X 16M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Apr 4, 2022 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1 Å / Relative weight: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.48→48.25 Å / Num. obs: 161468 / % possible obs: 91.6 % / Redundancy: 3 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 56.79 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.989 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.14 / Rrim(I) all: 0.169 / Net I/σ(I): 6.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell |
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.7→48.25 Å / SU ML: 0.5562 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 34.9673 MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.7→48.25 Å / SU ML: 0.5562 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 34.9673 Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 60.59 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.7→48.25 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj








