+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8pki | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of NR5A2-nucleosome complex SHL+5.5 | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN / Nucleosome / nuclear receptor / NR5A2 | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDeposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / positive regulation of glucocorticoid biosynthetic process / zygotic genome activation / positive regulation of tendon cell differentiation / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / morula formation / Regulation of gene expression in early pancreatic precursor cells ...Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / positive regulation of glucocorticoid biosynthetic process / zygotic genome activation / positive regulation of tendon cell differentiation / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / morula formation / Regulation of gene expression in early pancreatic precursor cells / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / primary ovarian follicle growth / HDMs demethylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / HDACs deacetylate histones / pancreas morphogenesis / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / HATs acetylate histones / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / inner cell mass cell differentiation / tissue development / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / acinar cell differentiation / RMTs methylate histone arginines / negative regulation of chromosome condensation / Sertoli cell development / positive regulation of stem cell differentiation / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / Barr body / positive regulation of T cell anergy / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / : / embryonic cleavage / pericentric heterochromatin formation / inner kinetochore / embryo development ending in birth or egg hatching / bile acid metabolic process / exocrine pancreas development / muscle cell differentiation / cartilage development / negative regulation of chondrocyte differentiation / oocyte maturation / nucleosomal DNA binding / oogenesis / nucleus organization / homeostatic process / calcineurin-mediated signaling / somatic stem cell population maintenance / chromosome, centromeric region / spermatid development / single fertilization / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / positive regulation of viral genome replication / RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / CENP-A containing nucleosome / hormone-mediated signaling pathway / positive regulation of T cell proliferation / neurogenesis / embryo implantation / cholesterol homeostasis / cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor / transcription coregulator binding / SUMOylation of intracellular receptors / phospholipid binding / Nuclear Receptor transcription pathway / positive regulation of T cell activation / negative regulation of inflammatory response / RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex / male gonad development / multicellular organism growth / nuclear receptor activity / sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding / osteoblast differentiation / structural constituent of chromatin / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / chromosome / chromatin organization / positive regulation of cell growth / DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / spermatogenesis / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / sequence-specific DNA binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / chromosome, telomeric region / cell population proliferation / transcription cis-regulatory region binding / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / chromatin remodeling / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / protein heterodimerization activity / chromatin binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  synthetic construct (others)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.58 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kobayashi, W. / Sappler, A. / Bollschweiler, D. / Kummecke, M. / Basquin, J. / Arslantas, E. / Ruangroengkulrith, S. / Hornberger, R. / Duderstadt, K. / Tachibana, K. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, European Union, 2items Germany, European Union, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024Title: Nucleosome-bound NR5A2 structure reveals pioneer factor mechanism by DNA minor groove anchor competition. Authors: Wataru Kobayashi / Anna H Sappler / Daniel Bollschweiler / Maximilian Kümmecke / Jérôme Basquin / Eda Nur Arslantas / Siwat Ruangroengkulrith / Renate Hornberger / Karl Duderstadt / Kikuë Tachibana /  Abstract: Gene expression during natural and induced reprogramming is controlled by pioneer transcription factors that initiate transcription from closed chromatin. Nr5a2 is a key pioneer factor that regulates ...Gene expression during natural and induced reprogramming is controlled by pioneer transcription factors that initiate transcription from closed chromatin. Nr5a2 is a key pioneer factor that regulates zygotic genome activation in totipotent embryos, pluripotency in embryonic stem cells and metabolism in adult tissues, but the mechanism of its pioneer activity remains poorly understood. Here, we present a cryo-electron microscopy structure of human NR5A2 bound to a nucleosome. The structure shows that the conserved carboxy-terminal extension (CTE) loop of the NR5A2 DNA-binding domain competes with a DNA minor groove anchor of the nucleosome and releases entry-exit site DNA. Mutational analysis showed that NR5A2 D159 of the CTE is dispensable for DNA binding but required for stable nucleosome association and persistent DNA 'unwrapping'. These findings suggest that NR5A2 belongs to an emerging class of pioneer factors that can use DNA minor groove anchor competition to destabilize nucleosomes and facilitate gene expression during reprogramming. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8pki.cif.gz 8pki.cif.gz | 390.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8pki.ent.gz pdb8pki.ent.gz | 239.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8pki.json.gz 8pki.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8pki_validation.pdf.gz 8pki_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8pki_full_validation.pdf.gz 8pki_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8pki_validation.xml.gz 8pki_validation.xml.gz | 43 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8pki_validation.cif.gz 8pki_validation.cif.gz | 65.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pk/8pki https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pk/8pki ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pk/8pki ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pk/8pki | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  17740MC 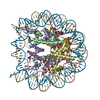 8pkjC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 9 molecules AEBFCGDHK
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15360.983 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Protein | Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: H4c1, Hist1h4a, H4c2, H4-53, Hist1h4b, H4c3, H4-12, Hist1h4c, H4c4, Hist1h4d, H4c6, Hist1h4f, H4c8, Hist1h4h, H4c9, Hist1h4i, H4c11, Hist1h4j, H4c12, Hist1h4k, Hist1h4m, H4c14, Hist2h4, ...Gene: H4c1, Hist1h4a, H4c2, H4-53, Hist1h4b, H4c3, H4-12, Hist1h4c, H4c4, Hist1h4d, H4c6, Hist1h4f, H4c8, Hist1h4h, H4c9, Hist1h4i, H4c11, Hist1h4j, H4c12, Hist1h4k, Hist1h4m, H4c14, Hist2h4, Hist2h4a, H4c16, H4f16, Hist4h4 Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 14165.551 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #4: Protein | Mass: 13937.213 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #7: Protein | | Mass: 10989.939 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NR5A2, B1F, CPF, FTF / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NR5A2, B1F, CPF, FTF / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 46968.922 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 47489.234 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 1 molecules 
| #8: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Cryo-EM structure of the nucleosome containing NR5A2 motif at SHL+5.5 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#7 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 65.4 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.58 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 653440 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 110.27 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj









































