+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8pba | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Caenorhabditis elegans DPF-3 (apo) | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Dipeptidyl Peptidase Four (IV) family | |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / Dipeptidylpeptidase | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationdipeptidyl-peptidase activity / serine-type peptidase activity / proteolysis Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.64 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gudipati, R.K. / Cavadini, S. / Kempf, G. / Grosshans, H. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, Switzerland,  Poland, 4items Poland, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Syst Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Mol Syst Biol / Year: 2024Title: Deep quantification of substrate turnover defines protease subsite cooperativity. Authors: Rajani Kanth Gudipati / Dimos Gaidatzis / Jan Seebacher / Sandra Muehlhaeusser / Georg Kempf / Simone Cavadini / Daniel Hess / Charlotte Soneson / Helge Großhans /   Abstract: Substrate specificity determines protease functions in physiology and in clinical and biotechnological applications, yet quantitative cleavage information is often unavailable, biased, or limited to ...Substrate specificity determines protease functions in physiology and in clinical and biotechnological applications, yet quantitative cleavage information is often unavailable, biased, or limited to a small number of events. Here, we develop qPISA (quantitative Protease specificity Inference from Substrate Analysis) to study Dipeptidyl Peptidase Four (DPP4), a key regulator of blood glucose levels. We use mass spectrometry to quantify >40,000 peptides from a complex, commercially available peptide mixture. By analyzing changes in substrate levels quantitatively instead of focusing on qualitative product identification through a binary classifier, we can reveal cooperative interactions within DPP4's active pocket and derive a sequence motif that predicts activity quantitatively. qPISA distinguishes DPP4 from the related C. elegans DPF-3 (a DPP8/9-orthologue), and we relate the differences to the structural features of the two enzymes. We demonstrate that qPISA can direct protein engineering efforts like the stabilization of GLP-1, a key DPP4 substrate used in the treatment of diabetes and obesity. Thus, qPISA offers a versatile approach for profiling protease and especially exopeptidase specificity, facilitating insight into enzyme mechanisms and biotechnological and clinical applications. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8pba.cif.gz 8pba.cif.gz | 541.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8pba.ent.gz pdb8pba.ent.gz | 446.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8pba.json.gz 8pba.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8pba_validation.pdf.gz 8pba_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8pba_full_validation.pdf.gz 8pba_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8pba_validation.xml.gz 8pba_validation.xml.gz | 50.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8pba_validation.cif.gz 8pba_validation.cif.gz | 76.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pb/8pba https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pb/8pba ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pb/8pba ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pb/8pba | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  17582MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 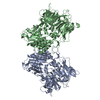
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 106462.812 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q965K3 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q965K3Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Homodimeric complex of DPF-3 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.64 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 223429 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj
