+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Caenorhabditis elegans DPF-3 (apo) | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Full map processed with LocScale. | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Dipeptidylpeptidase / HYDROLASE | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology | : / Dipeptidylpeptidase IV, N-terminal domain / Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP IV) N-terminal region / Peptidase S9, prolyl oligopeptidase, catalytic domain / Prolyl oligopeptidase family / serine-type peptidase activity / Alpha/Beta hydrolase fold / proteolysis / Dipeptidyl Peptidase Four (IV) family Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||||||||
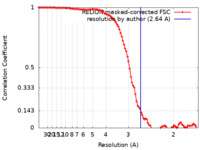
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.64 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gudipati RK / Cavadini S / Kempf G / Grosshans H | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, Switzerland,  Poland, 4 items Poland, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Syst Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Mol Syst Biol / Year: 2024Title: Deep quantification of substrate turnover defines protease subsite cooperativity. Authors: Rajani Kanth Gudipati / Dimos Gaidatzis / Jan Seebacher / Sandra Muehlhaeusser / Georg Kempf / Simone Cavadini / Daniel Hess / Charlotte Soneson / Helge Großhans /   Abstract: Substrate specificity determines protease functions in physiology and in clinical and biotechnological applications, yet quantitative cleavage information is often unavailable, biased, or limited to ...Substrate specificity determines protease functions in physiology and in clinical and biotechnological applications, yet quantitative cleavage information is often unavailable, biased, or limited to a small number of events. Here, we develop qPISA (quantitative Protease specificity Inference from Substrate Analysis) to study Dipeptidyl Peptidase Four (DPP4), a key regulator of blood glucose levels. We use mass spectrometry to quantify >40,000 peptides from a complex, commercially available peptide mixture. By analyzing changes in substrate levels quantitatively instead of focusing on qualitative product identification through a binary classifier, we can reveal cooperative interactions within DPP4's active pocket and derive a sequence motif that predicts activity quantitatively. qPISA distinguishes DPP4 from the related C. elegans DPF-3 (a DPP8/9-orthologue), and we relate the differences to the structural features of the two enzymes. We demonstrate that qPISA can direct protein engineering efforts like the stabilization of GLP-1, a key DPP4 substrate used in the treatment of diabetes and obesity. Thus, qPISA offers a versatile approach for profiling protease and especially exopeptidase specificity, facilitating insight into enzyme mechanisms and biotechnological and clinical applications. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_17582.map.gz emd_17582.map.gz | 41.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-17582-v30.xml emd-17582-v30.xml emd-17582.xml emd-17582.xml | 17.4 KB 17.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_17582_fsc.xml emd_17582_fsc.xml | 9.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_17582.png emd_17582.png | 119.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-17582.cif.gz emd-17582.cif.gz | 6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_17582_additional_1.map.gz emd_17582_additional_1.map.gz emd_17582_half_map_1.map.gz emd_17582_half_map_1.map.gz emd_17582_half_map_2.map.gz emd_17582_half_map_2.map.gz | 64 MB 64.1 MB 64.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17582 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17582 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17582 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17582 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_17582_validation.pdf.gz emd_17582_validation.pdf.gz | 751.3 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_17582_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_17582_full_validation.pdf.gz | 750.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_17582_validation.xml.gz emd_17582_validation.xml.gz | 17.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_17582_validation.cif.gz emd_17582_validation.cif.gz | 22.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-17582 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-17582 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-17582 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-17582 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8pbaMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_17582.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_17582.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Full map processed with LocScale. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.845 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
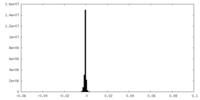
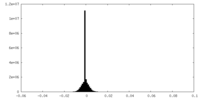
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Full map.
| File | emd_17582_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Full map. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
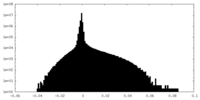
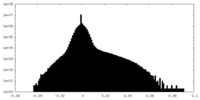
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map 2.
| File | emd_17582_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map 2. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map 1.
| File | emd_17582_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map 1. | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Homodimeric complex of DPF-3
| Entire | Name: Homodimeric complex of DPF-3 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Homodimeric complex of DPF-3
| Supramolecule | Name: Homodimeric complex of DPF-3 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Dipeptidyl Peptidase Four (IV) family
| Macromolecule | Name: Dipeptidyl Peptidase Four (IV) family / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 106.462812 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Sequence | String: MMFNFYQFLY NLQNVSPFID FSVLKQLTHT KMRENEPARF ETRSFSQLID HARSWKTEVR GMTTQGFTKI SLMRAEKDRL NMYAISSVP GTNTQSIFSV TIPLELVEKA QVADRKFELK LKSGYNVDSY IRKTPPSAEF TLQCERQRSQ VVTGISDYEI R NGKMILMA ...String: MMFNFYQFLY NLQNVSPFID FSVLKQLTHT KMRENEPARF ETRSFSQLID HARSWKTEVR GMTTQGFTKI SLMRAEKDRL NMYAISSVP GTNTQSIFSV TIPLELVEKA QVADRKFELK LKSGYNVDSY IRKTPPSAEF TLQCERQRSQ VVTGISDYEI R NGKMILMA GDQLFRYNPL NEALAAIPIA VPDDQSSTEP MDISEGSITS GTKGSGSEAP QSSTVPPVTR IPIKKPTTST EK PATAPPT NNFVSSAKVC PADSSLLAYV LNKQVYIEKN GKIIHRTSSN SKHITNGVPS YIVQEELERF EGIWWSESKT RLL YEHVNE EKVAESQFGV NGDPPVAPMK YPRAGTKNAY STLRMVILEN GKAYDVPLKD EVIYKHCPFY EYITRAGFFS DGTT VWVQV MSRDQAQCSL LLIPYTDFLL PEELGGSIKE DNLQLSTDLN MGVWDDKSHE ETMEKPPRGK LRGTVQIHKA RNDYW INTH NAIYPLKITD EEHPMYEFIY CLEKPNGSCL ALISAELDQN GYCRHTEEKL LMAENFSINK SMGIVVDEVR ELVYYV ANE SHPTEWNICV SHYRTGQHAQ LTESGICFKS ERANGKLALD LDHGFACYMT SVGSPAECRF YSFRWKENEV LPSTVYA AN ITVSGHPGQP DLHFDSPEMI EFQSKKTGLM HYAMILRPSN FDPYKKYPVF HYVYGGPGIQ IVHNDFSWIQ YIRFCRLG Y VVVFIDNRGS AHRGIEFERH IHKKMGTVEV EDQVEGLQML AERTGGFMDM SRVVVHGWSY GGYMALQMIA KHPNIYRAA IAGGAVSDWR LYDTAYTERY MGYPLEEHVY GASSITGLVE KLPDEPNRLM LVHGLMDENV HFAHLTHLVD ECIKKGKWHE LVIFPNERH GVRNNDASIY LDARMMYFAQ QAIQGFGPTT AAPRQGPLWS HPQFEK UniProtKB: Dipeptidyl Peptidase Four (IV) family |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-8pba: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)