+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8oou | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Double-ring nucleocapsid of the Respiratory Syncytial Virus | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / D10-symmetry / N-RNA / nucleoprotein / RSV | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRespiratory syncytial virus genome transcription / Translation of respiratory syncytial virus mRNAs / symbiont-mediated suppression of host PKR/eIFalpha signaling / helical viral capsid / Respiratory syncytial virus genome replication / RSV-host interactions / Assembly and release of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) virions / Maturation of hRSV A proteins / Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) attachment and entry / protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity ...Respiratory syncytial virus genome transcription / Translation of respiratory syncytial virus mRNAs / symbiont-mediated suppression of host PKR/eIFalpha signaling / helical viral capsid / Respiratory syncytial virus genome replication / RSV-host interactions / Assembly and release of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) virions / Maturation of hRSV A proteins / Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) attachment and entry / protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity / symbiont-mediated suppression of host cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway via inhibition of MDA-5 activity / symbiont-mediated suppression of host cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway via inhibition of MAVS activity / PKR-mediated signaling / Evasion by RSV of host interferon responses / viral capsid / viral nucleocapsid / symbiont-mediated suppression of host NF-kappaB cascade / host cell cytoplasm / symbiont-mediated suppression of host type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway / ribonucleoprotein complex / RNA binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Respiratory syncytial virus Respiratory syncytial virus Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Gonnin, L. / Desfosses, A. / Gutsche, I. | ||||||
| Funding support |  France, 1items France, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Structural landscape of the respiratory syncytial virus nucleocapsids. Authors: Lorène Gonnin / Ambroise Desfosses / Maria Bacia-Verloop / Didier Chevret / Marie Galloux / Jean-François Éléouët / Irina Gutsche /  Abstract: Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus (HRSV) is a prevalent cause of severe respiratory infections in children and the elderly. The helical HRSV nucleocapsid is a template for the viral RNA synthesis and ...Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus (HRSV) is a prevalent cause of severe respiratory infections in children and the elderly. The helical HRSV nucleocapsid is a template for the viral RNA synthesis and a scaffold for the virion assembly. This cryo-electron microscopy analysis reveals the non-canonical arrangement of the HRSV nucleocapsid helix, composed of 16 nucleoproteins per asymmetric unit, and the resulting systematic variations in the RNA accessibility. We demonstrate that this unique helical symmetry originates from longitudinal interactions by the C-terminal arm of the HRSV nucleoprotein. We explore the polymorphism of the nucleocapsid-like assemblies, report five structures of the full-length particles and two alternative arrangements formed by a C-terminally truncated nucleoprotein mutant, and demonstrate the functional importance of the identified longitudinal interfaces. We put all these findings in the context of the HRSV RNA synthesis machinery and delineate the structural basis for its further investigation. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8oou.cif.gz 8oou.cif.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8oou.ent.gz pdb8oou.ent.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8oou.json.gz 8oou.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/8oou https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/8oou ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/8oou ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/8oou | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  17031MC 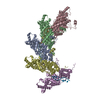 8op1C  8op2C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 43507.848 Da / Num. of mol.: 20 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Respiratory syncytial virus / Production host: Respiratory syncytial virus / Production host:  #2: RNA chain | Mass: 21317.777 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Double ring nucleocapsid of the human Respiratory Syncytial Virus Type: COMPLEX Details: Double ring nucleocapsid formed by the nucleoprotein N of the human RSV upon overexpression in insect cells and encapsidation of cellular RNA Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Human respiratory syncytial virus A strain Long Human respiratory syncytial virus A strain Long |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain: High Five / Plasmid: pFastBac Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain: High Five / Plasmid: pFastBac |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2400 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 42 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: D10 (2x10 fold dihedral) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 47212 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj





























