[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8oo9: CryoEM Structure INO80core Hexasome complex ATPase-DNA refinement... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8oo9 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
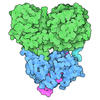
| Title | CryoEM Structure INO80core Hexasome complex ATPase-DNA refinement state1 | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN / ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology | P-loop containing nucleotide triphosphate hydrolases / Rossmann fold / 3-Layer(aba) Sandwich / Alpha Beta / ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / TETRAFLUOROALUMINATE ION / DNA / DNA (> 10) / DNA (> 100) Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Thermochaetoides thermophila (fungus) Thermochaetoides thermophila (fungus)synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang, M. / Jungblut, A. / Hoffmann, T. / Eustermann, S. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, European Union, 4items Germany, European Union, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2023 Journal: Science / Year: 2023Title: Hexasome-INO80 complex reveals structural basis of noncanonical nucleosome remodeling. Authors: Min Zhang / Anna Jungblut / Franziska Kunert / Luis Hauptmann / Thomas Hoffmann / Olga Kolesnikova / Felix Metzner / Manuela Moldt / Felix Weis / Frank DiMaio / Karl-Peter Hopfner / Sebastian Eustermann /   Abstract: Loss of H2A-H2B histone dimers is a hallmark of actively transcribed genes, but how the cellular machinery functions in the context of noncanonical nucleosomal particles remains largely elusive. In ...Loss of H2A-H2B histone dimers is a hallmark of actively transcribed genes, but how the cellular machinery functions in the context of noncanonical nucleosomal particles remains largely elusive. In this work, we report the structural mechanism for adenosine 5'-triphosphate-dependent chromatin remodeling of hexasomes by the INO80 complex. We show how INO80 recognizes noncanonical DNA and histone features of hexasomes that emerge from the loss of H2A-H2B. A large structural rearrangement switches the catalytic core of INO80 into a distinct, spin-rotated mode of remodeling while its nuclear actin module remains tethered to long stretches of unwrapped linker DNA. Direct sensing of an exposed H3-H4 histone interface activates INO80, independently of the H2A-H2B acidic patch. Our findings reveal how the loss of H2A-H2B grants remodelers access to a different, yet unexplored layer of energy-driven chromatin regulation. #1: Journal: Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol / Year: 2018 Title: Real-space refinement in PHENIX for cryo-EM and crystallography. Authors: Pavel V Afonine / Billy K Poon / Randy J Read / Oleg V Sobolev / Thomas C Terwilliger / Alexandre Urzhumtsev / Paul D Adams /    Abstract: This article describes the implementation of real-space refinement in the phenix.real_space_refine program from the PHENIX suite. The use of a simplified refinement target function enables very fast ...This article describes the implementation of real-space refinement in the phenix.real_space_refine program from the PHENIX suite. The use of a simplified refinement target function enables very fast calculation, which in turn makes it possible to identify optimal data-restraint weights as part of routine refinements with little runtime cost. Refinement of atomic models against low-resolution data benefits from the inclusion of as much additional information as is available. In addition to standard restraints on covalent geometry, phenix.real_space_refine makes use of extra information such as secondary-structure and rotamer-specific restraints, as well as restraints or constraints on internal molecular symmetry. The re-refinement of 385 cryo-EM-derived models available in the Protein Data Bank at resolutions of 6 Å or better shows significant improvement of the models and of the fit of these models to the target maps. #2: Journal: Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr / Year: 2010 Title: Features and development of Coot. Authors: P Emsley / B Lohkamp / W G Scott / K Cowtan /  Abstract: Coot is a molecular-graphics application for model building and validation of biological macromolecules. The program displays electron-density maps and atomic models and allows model manipulations ...Coot is a molecular-graphics application for model building and validation of biological macromolecules. The program displays electron-density maps and atomic models and allows model manipulations such as idealization, real-space refinement, manual rotation/translation, rigid-body fitting, ligand search, solvation, mutations, rotamers and Ramachandran idealization. Furthermore, tools are provided for model validation as well as interfaces to external programs for refinement, validation and graphics. The software is designed to be easy to learn for novice users, which is achieved by ensuring that tools for common tasks are 'discoverable' through familiar user-interface elements (menus and toolbars) or by intuitive behaviour (mouse controls). Recent developments have focused on providing tools for expert users, with customisable key bindings, extensions and an extensive scripting interface. The software is under rapid development, but has already achieved very widespread use within the crystallographic community. The current state of the software is presented, with a description of the facilities available and of some of the underlying methods employed. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8oo9.cif.gz 8oo9.cif.gz | 154.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8oo9.ent.gz pdb8oo9.ent.gz | 100.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8oo9.json.gz 8oo9.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/8oo9 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/8oo9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/8oo9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oo/8oo9 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  17007MC  8oo7C  8ooaC  8oocC  8oofC  8ookC  8oopC  8oorC  8oosC  8ootC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules G
| #1: Protein | Mass: 130887.656 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Ino80 N-terminal truncation C-terminal 2xFlagTag / Source: (gene. exp.)  Thermochaetoides thermophila (fungus) / Gene: TT172_LOCUS3790 / Production host: Thermochaetoides thermophila (fungus) / Gene: TT172_LOCUS3790 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules KL
| #2: DNA chain | Mass: 69527.195 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #3: DNA chain | Mass: 70043.562 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 3 molecules 

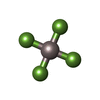

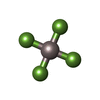
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / |
|---|---|
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-ALF / |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: INO80 core module in complex with hexasome / Type: COMPLEX Details: 11-subunit ct INO80 contains two modules (core and Arp8 module) Each module was picked and analyzed separately The core module + hexasome has an overall weight of 0.861MDa The 11-subunit ct ...Details: 11-subunit ct INO80 contains two modules (core and Arp8 module) Each module was picked and analyzed separately The core module + hexasome has an overall weight of 0.861MDa The 11-subunit ct INO80 + hexasome has an overall weight of 1.1MDa Ino80, Ies2, Ies6, Ies4,Arp6, Rvb1, Rvb2, Arp8, Arp4, Actin, Taf14 Hexasome DNA, 2xH3, 2xH4, H2A, H2B Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.861 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Thermochaetoides thermophila (fungus) Thermochaetoides thermophila (fungus) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 Details: 30mM HEPES, pH7.5 50mM NaCl 0.25mM CaCl2 0.25mM DTT 2mM ADP 3.3mM MgCl2 10mM NaF 2mM AlCl3 0.05% octyl-beta-glucoside |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.88 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: 11-subunit ctINO80 reconstituted with hexasome |
| Specimen support | Details: 10% Oxygene 90% Argone / Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K Details: wait time of 5s, blot force at 3, and a blot time of 2s with Whatman blotting paper (Cytiva, CAT No. 10311807) |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50.36 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 15384 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 2137460 Details: Particles were initially picked by WARP to generate an initial model, which was subsequently used for the 3D template picking | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 72400 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 PDBj
PDBj