[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8kd7: Rpd3S in complex with nucleosome with H3K36MLA modification and 1... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8kd7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Rpd3S in complex with nucleosome with H3K36MLA modification and 167bp DNA | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / Rpd3S / HDAC / Hho1 / cryptic transcription | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnucleosome disassembly/reassembly complex / negative regulation of antisense RNA transcription / Snt2C complex / negative regulation of silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / negative regulation of reciprocal meiotic recombination / Rpd3L complex / protein localization to nucleolar rDNA repeats / negative regulation of rDNA heterochromatin formation / Rpd3L-Expanded complex / Rpd3S complex ...nucleosome disassembly/reassembly complex / negative regulation of antisense RNA transcription / Snt2C complex / negative regulation of silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / negative regulation of reciprocal meiotic recombination / Rpd3L complex / protein localization to nucleolar rDNA repeats / negative regulation of rDNA heterochromatin formation / Rpd3L-Expanded complex / Rpd3S complex / rDNA chromatin condensation / regulation of RNA stability / nucleophagy / HDACs deacetylate histones / DNA replication-dependent chromatin assembly / histone H4K16 deacetylase activity, hydrolytic mechanism / histone H4K5 deacetylase activity, hydrolytic mechanism / histone H4K8 deacetylase activity, hydrolytic mechanism / histone H3K4 deacetylase activity, hydrolytic mechanism / histone H3K14 deacetylase activity, hydrolytic mechanism / histone H4K12 deacetylase activity, hydrolytic mechanism / histone deacetylase / histone H3K9 deacetylase activity, hydrolytic mechanism / nucleosome disassembly / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / cellular response to nitrogen starvation / regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / histone deacetylase activity / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / Sin3-type complex / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / positive regulation of macroautophagy / histone deacetylase complex / histone acetyltransferase complex / : / nuclear periphery / histone reader activity / meiotic cell cycle / positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle / transcription corepressor activity / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / structural constituent of chromatin / nucleosome / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome assembly / cellular response to heat / response to oxidative stress / transcription coactivator activity / protein heterodimerization activity / cell division / DNA repair / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / DNA-templated transcription / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / chromatin / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.09 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Dong, S. / Li, H. / Wang, M. / Rasheed, N. / Zou, B. / Gao, X. / Guan, J. / Li, W. / Zhang, J. / Wang, C. ...Dong, S. / Li, H. / Wang, M. / Rasheed, N. / Zou, B. / Gao, X. / Guan, J. / Li, W. / Zhang, J. / Wang, C. / Zhou, N. / Shi, X. / Li, M. / Zhou, M. / Huang, J. / Li, H. / Zhang, Y. / Wong, K.H. / Chang, X. / Chao, W.C.H. / He, J. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 8items China, 8items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2023 Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis of nucleosome deacetylation and DNA linker tightening by Rpd3S histone deacetylase complex. Authors: Shuqi Dong / Huadong Li / Meilin Wang / Nadia Rasheed / Binqian Zou / Xijie Gao / Jiali Guan / Weijie Li / Jiale Zhang / Chi Wang / Ningkun Zhou / Xue Shi / Mei Li / Min Zhou / Junfeng Huang ...Authors: Shuqi Dong / Huadong Li / Meilin Wang / Nadia Rasheed / Binqian Zou / Xijie Gao / Jiali Guan / Weijie Li / Jiale Zhang / Chi Wang / Ningkun Zhou / Xue Shi / Mei Li / Min Zhou / Junfeng Huang / He Li / Ying Zhang / Koon Ho Wong / Xiaofei Zhang / William Chong Hang Chao / Jun He /  Abstract: In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, cryptic transcription at the coding region is prevented by the activity of Sin3 histone deacetylase (HDAC) complex Rpd3S, which is carried by the transcribing RNA ...In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, cryptic transcription at the coding region is prevented by the activity of Sin3 histone deacetylase (HDAC) complex Rpd3S, which is carried by the transcribing RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) to deacetylate and stabilize chromatin. Despite its fundamental importance, the mechanisms by which Rpd3S deacetylates nucleosomes and regulates chromatin dynamics remain elusive. Here, we determined several cryo-EM structures of Rpd3S in complex with nucleosome core particles (NCPs), including the H3/H4 deacetylation states, the alternative deacetylation state, the linker tightening state, and a state in which Rpd3S co-exists with the Hho1 linker histone on NCP. These structures suggest that Rpd3S utilizes a conserved Sin3 basic surface to navigate through the nucleosomal DNA, guided by its interactions with H3K36 methylation and the extra-nucleosomal DNA linkers, to target acetylated H3K9 and sample other histone tails. Furthermore, our structures illustrate that Rpd3S reconfigures the DNA linkers and acts in concert with Hho1 to engage the NCP, potentially unraveling how Rpd3S and Hho1 work in tandem for gene silencing. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8kd7.cif.gz 8kd7.cif.gz | 686.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8kd7.ent.gz pdb8kd7.ent.gz | 508.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8kd7.json.gz 8kd7.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kd/8kd7 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kd/8kd7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kd/8kd7 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kd/8kd7 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  37127MC  8kc7C  8kd2C  8kd3C  8kd4C  8kd5C  8kd6C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 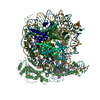
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 6 types, 11 molecules ADFOSPTQURV
| #1: Protein | Mass: 48961.957 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: RPD3 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P32561 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P32561 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 45266.406 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: EAF3 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q12432 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q12432#5: Protein | Mass: 15313.943 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: C110A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #6: Protein | Mass: 11263.231 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #7: Protein | Mass: 13978.241 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #8: Protein | Mass: 13524.752 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: S29T Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  |
-Transcriptional regulatory protein ... , 2 types, 3 molecules BEG
| #2: Protein | Mass: 157586.844 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: SIN3, CPE1, GAM2, RPD1, SDI1, SDS16, UME4, YOL004W / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P22579 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P22579 |
|---|---|
| #4: Protein | Mass: 84469.328 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: RCO1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q04779 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q04779 |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules XY
| #9: DNA chain | Mass: 51840.988 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #10: DNA chain | Mass: 51271.625 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: 3D ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.09 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 56949 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj






































