+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8jyl | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
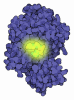
| Title | Acyl-ACP Synthetase structure bound to C10-AMS | ||||||
 Components Components | Acyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIGASE / Acyl-ACP synthetase / Tool enzyme / CYTOSOLIC PROTEIN | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.33 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Huang, H. / Chang, S. / Huang, M. / Zhang, H. / Zhou, C. / Zhang, X. / Feng, Y. | ||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2024 Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2024Title: An inhibitory mechanism of AasS, an exogenous fatty acid scavenger: Implications for re-sensitization of FAS II antimicrobials. Authors: Haomin Huang / Shenghai Chang / Tao Cui / Man Huang / Jiuxin Qu / Huimin Zhang / Ting Lu / Xing Zhang / Chun Zhou / Youjun Feng /   Abstract: Antimicrobial resistance is an ongoing "one health" challenge of global concern. The acyl-ACP synthetase (termed AasS) of the zoonotic pathogen Vibrio harveyi recycles exogenous fatty acid (eFA), ...Antimicrobial resistance is an ongoing "one health" challenge of global concern. The acyl-ACP synthetase (termed AasS) of the zoonotic pathogen Vibrio harveyi recycles exogenous fatty acid (eFA), bypassing the requirement of type II fatty acid synthesis (FAS II), a druggable pathway. A growing body of bacterial AasS-type isoenzymes compromises the clinical efficacy of FAS II-directed antimicrobials, like cerulenin. Very recently, an acyl adenylate mimic, C10-AMS, was proposed as a lead compound against AasS activity. However, the underlying mechanism remains poorly understood. Here we present two high-resolution cryo-EM structures of AasS liganded with C10-AMS inhibitor (2.33 Å) and C10-AMP intermediate (2.19 Å) in addition to its apo form (2.53 Å). Apart from our measurements for C10-AMS' Ki value of around 0.6 μM, structural and functional analyses explained how this inhibitor interacts with AasS enzyme. Unlike an open state of AasS, ready for C10-AMP formation, a closed conformation is trapped by the C10-AMS inhibitor. Tight binding of C10-AMS blocks fatty acyl substrate entry, and therefore inhibits AasS action. Additionally, this intermediate analog C10-AMS appears to be a mixed-type AasS inhibitor. In summary, our results provide the proof of principle that inhibiting salvage of eFA by AasS reverses the FAS II bypass. This facilitates the development of next-generation anti-bacterial therapeutics, esp. the dual therapy consisting of C10-AMS scaffold derivatives combined with certain FAS II inhibitors. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8jyl.cif.gz 8jyl.cif.gz | 604.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8jyl.ent.gz pdb8jyl.ent.gz | 504 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8jyl.json.gz 8jyl.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jy/8jyl https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jy/8jyl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jy/8jyl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jy/8jyl | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  36725MC  8hsyC  8jyuC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 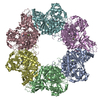
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 60383.102 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) / Gene: aasS / Production host: Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) / Gene: aasS / Production host:  #2: Chemical | ChemComp-VUL / [( Mass: 500.569 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Formula: C20H32N6O7S / Feature type: SUBJECT OF INVESTIGATION #3: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Acyl-ACP Synthetase bound to C10-AMS / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.33 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 212195 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj