+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Acyl-ACP Synthetase structure bound to Decanoyl-AMP | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Acyl-ACP synthetase / Tool enzyme / CYTOSOLIC PROTEIN / LIGASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology | ligase activity, forming carbon-sulfur bonds / : / ANL, N-terminal domain / AMP-binding enzyme C-terminal domain / AMP-binding enzyme, C-terminal domain / AMP-dependent synthetase/ligase / AMP-binding enzyme / AMP-binding enzyme, C-terminal domain superfamily / Acyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.19 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Huang H / Chang S / Huang M / Zhang H / Zhou C / Zhang X / Feng Y | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2024 Journal: PLoS Pathog / Year: 2024Title: An inhibitory mechanism of AasS, an exogenous fatty acid scavenger: Implications for re-sensitization of FAS II antimicrobials. Authors: Haomin Huang / Shenghai Chang / Tao Cui / Man Huang / Jiuxin Qu / Huimin Zhang / Ting Lu / Xing Zhang / Chun Zhou / Youjun Feng /   Abstract: Antimicrobial resistance is an ongoing "one health" challenge of global concern. The acyl-ACP synthetase (termed AasS) of the zoonotic pathogen Vibrio harveyi recycles exogenous fatty acid (eFA), ...Antimicrobial resistance is an ongoing "one health" challenge of global concern. The acyl-ACP synthetase (termed AasS) of the zoonotic pathogen Vibrio harveyi recycles exogenous fatty acid (eFA), bypassing the requirement of type II fatty acid synthesis (FAS II), a druggable pathway. A growing body of bacterial AasS-type isoenzymes compromises the clinical efficacy of FAS II-directed antimicrobials, like cerulenin. Very recently, an acyl adenylate mimic, C10-AMS, was proposed as a lead compound against AasS activity. However, the underlying mechanism remains poorly understood. Here we present two high-resolution cryo-EM structures of AasS liganded with C10-AMS inhibitor (2.33 Å) and C10-AMP intermediate (2.19 Å) in addition to its apo form (2.53 Å). Apart from our measurements for C10-AMS' Ki value of around 0.6 μM, structural and functional analyses explained how this inhibitor interacts with AasS enzyme. Unlike an open state of AasS, ready for C10-AMP formation, a closed conformation is trapped by the C10-AMS inhibitor. Tight binding of C10-AMS blocks fatty acyl substrate entry, and therefore inhibits AasS action. Additionally, this intermediate analog C10-AMS appears to be a mixed-type AasS inhibitor. In summary, our results provide the proof of principle that inhibiting salvage of eFA by AasS reverses the FAS II bypass. This facilitates the development of next-generation anti-bacterial therapeutics, esp. the dual therapy consisting of C10-AMS scaffold derivatives combined with certain FAS II inhibitors. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_36731.map.gz emd_36731.map.gz | 97.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-36731-v30.xml emd-36731-v30.xml emd-36731.xml emd-36731.xml | 14.7 KB 14.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_36731.png emd_36731.png | 197.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-36731.cif.gz emd-36731.cif.gz | 5.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_36731_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36731_half_map_1.map.gz emd_36731_half_map_2.map.gz emd_36731_half_map_2.map.gz | 95.6 MB 95.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36731 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36731 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36731 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-36731 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_36731_validation.pdf.gz emd_36731_validation.pdf.gz | 848.7 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_36731_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_36731_full_validation.pdf.gz | 848.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_36731_validation.xml.gz emd_36731_validation.xml.gz | 13.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_36731_validation.cif.gz emd_36731_validation.cif.gz | 15.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36731 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36731 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36731 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-36731 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8jyuMC  8hsyC  8jylC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_36731.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_36731.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.93 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
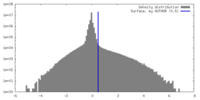
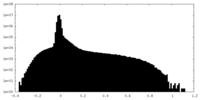
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_36731_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
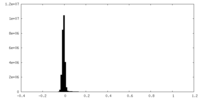
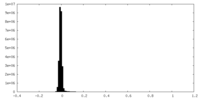
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_36731_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
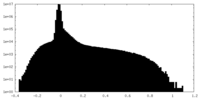
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Acyl-ACP Synthetase structure bound to Decanoyl-AMP
| Entire | Name: Acyl-ACP Synthetase structure bound to Decanoyl-AMP |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Acyl-ACP Synthetase structure bound to Decanoyl-AMP
| Supramolecule | Name: Acyl-ACP Synthetase structure bound to Decanoyl-AMP / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Acyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase
| Macromolecule | Name: Acyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 60.496258 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MNQYVNDPSN YQLLIKNLLF SPVAFNPEQE IVYANHRRHS YKTFHDRVRQ FANALTKMGV KKGDTVAVMD YDSHRYLECY FAIPMIGAK LHMINVRLSP EQILYTIDHA EDDIILIHEE FLPILDQIKG RIDTVTRYVV LRDDEECEYE RLLEQESTEY N FPDFDENT ...String: MNQYVNDPSN YQLLIKNLLF SPVAFNPEQE IVYANHRRHS YKTFHDRVRQ FANALTKMGV KKGDTVAVMD YDSHRYLECY FAIPMIGAK LHMINVRLSP EQILYTIDHA EDDIILIHEE FLPILDQIKG RIDTVTRYVV LRDDEECEYE RLLEQESTEY N FPDFDENT VATTFYTTGT TGFPKGVFFT HRQLVLHTMG ILSTIGTNAS QGRLHQGDIY MPITPMFHVH AWGLPYMATM LG VKQVYPG KYVPDVLLNL IEQEKVTFSH CVPTILHLLL SSPKSKAMDF SGWKVVIGGA ALPKALCKSA LERDIDVFAG YGM SETGPI LSIVQLTPEQ LELDVDQQAE YRSKTGKKVA LVEAYIVDED MNKLPHDGET AGEIVVRAPW LTPNYYKDNK NSKA LWRGG YLHTGDVAHI DDEGFIKITD RVKDMIKISG EWVSSLELED ILHQHQSVSE VAVIGMPHNK WGEVPLALVT LKEDA QVTE KELLGFAKDF INKGILAREA LLLKVKIVDE IAKTSVGKVD KKELRKLHL UniProtKB: Acyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase |
-Macromolecule #2: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE MONOPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE MONOPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: AMP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 347.221 Da |
| Chemical component information | 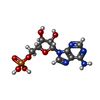 ChemComp-AMP: |
-Macromolecule #4: DECANOIC ACID
| Macromolecule | Name: DECANOIC ACID / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: DKA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 172.265 Da |
| Chemical component information | 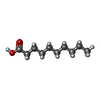 ChemComp-DKA: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.19 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 602383 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)