[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8ixb: GMPCPP-Alpha1A/Beta2A-microtubule decorated with kinesin seam region -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ixb | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | GMPCPP-Alpha1A/Beta2A-microtubule decorated with kinesin seam region | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / microtubule / tubulin isotype / cryo-EM structure | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMicrotubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Cilium Assembly / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Intraflagellar transport / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / regulation of modification of synapse structure, modulating synaptic transmission / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / plus-end-directed vesicle transport along microtubule / cytoplasm organization ...Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Cilium Assembly / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Intraflagellar transport / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / regulation of modification of synapse structure, modulating synaptic transmission / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / plus-end-directed vesicle transport along microtubule / cytoplasm organization / cytolytic granule membrane / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / anterograde dendritic transport of neurotransmitter receptor complex / Aggrephagy / Kinesins / anterograde neuronal dense core vesicle transport / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / mitocytosis / PKR-mediated signaling / retrograde neuronal dense core vesicle transport / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / Recycling pathway of L1 / anterograde axonal protein transport / axonemal microtubule / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Separation of Sister Chromatids / organelle transport along microtubule / Hedgehog 'off' state / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / forebrain morphogenesis / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / ciliary rootlet / cerebellar cortex morphogenesis / glial cell differentiation / dentate gyrus development / neuron projection arborization / lysosome localization / flagellated sperm motility / positive regulation of potassium ion transport / MHC class II antigen presentation / vesicle transport along microtubule / plus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / RHO GTPases activate KTN1 / Kinesins / response to L-glutamate / kinesin complex / pyramidal neuron differentiation / centrosome cycle / microtubule motor activity / centrosome localization / mitochondrion transport along microtubule / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / microtubule-based movement / smoothened signaling pathway / stress granule disassembly / natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / Insulin processing / synaptic vesicle transport / regulation of synapse organization / startle response / adult behavior / motor behavior / response to tumor necrosis factor / locomotory exploration behavior / microtubule polymerization / sperm flagellum / response to mechanical stimulus / postsynaptic cytosol / microtubule-based process / intercellular bridge / cytoplasmic microtubule / phagocytic vesicle / condensed chromosome / neurogenesis / axon cytoplasm / MHC class II antigen presentation / homeostasis of number of cells within a tissue / dendrite cytoplasm / axon guidance / cellular response to calcium ion / adult locomotory behavior / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic / regulation of membrane potential / positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / hippocampus development / locomotory behavior / neuromuscular junction / intracellular protein transport / synapse organization / recycling endosome / cerebral cortex development Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zheng, W. / Zhao, Q.Y. / Diao, L. / Bao, L. / Cong, Y. | ||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) / Year: 2023 Journal: Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) / Year: 2023Title: Cryo-EM of α-tubulin isotype-containing microtubules revealed a contracted structure of α4A/β2A microtubules. Authors: Lei Diao / Wei Zheng / Qiaoyu Zhao / Mingyi Liu / Zhenglin Fu / Xu Zhang / Lan Bao / Yao Cong /  Abstract: Microtubules are hollow α/β-tubulin heterodimeric polymers that play critical roles in cells. In vertebrates, both α- and β-tubulins have multiple isotypes encoded by different genes, which are ...Microtubules are hollow α/β-tubulin heterodimeric polymers that play critical roles in cells. In vertebrates, both α- and β-tubulins have multiple isotypes encoded by different genes, which are intrinsic factors in regulating microtubule functions. However, the structures of microtubules composed of different tubulin isotypes, especially α-tubulin isotypes, remain largely unknown. Here, we purify recombinant tubulin heterodimers composed of different mouse α-tubulin isotypes, including α1A, α1C and α4A, with the β-tubulin isotype β2A. We further assemble and determine the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of α1A/β2A, α1C/β2A, and α4A/β2A microtubules. Our structural analysis demonstrates that α4A/β2A microtubules exhibit longitudinal contraction between tubulin interdimers compared with α1A/β2A and α1C/β2A microtubules. Collectively, our findings reveal that α-tubulin isotype composition can tune microtubule structures, and also provide evidence for the "tubulin code" hypothesis. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ixb.cif.gz 8ixb.cif.gz | 823.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ixb.ent.gz pdb8ixb.ent.gz | 674.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ixb.json.gz 8ixb.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8ixb_validation.pdf.gz 8ixb_validation.pdf.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8ixb_full_validation.pdf.gz 8ixb_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8ixb_validation.xml.gz 8ixb_validation.xml.gz | 89.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8ixb_validation.cif.gz 8ixb_validation.cif.gz | 134.9 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ix/8ixb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ix/8ixb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ix/8ixb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ix/8ixb | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  35790MC  8ixaC  8ixdC  8ixeC  8ixfC  8ixgC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 12 molecules HAEFWQUVlgkm
| #1: Protein | Mass: 51017.320 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Insecta environmental sample (insect) Insecta environmental sample (insect)References: UniProt: P68369, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement #2: Protein | Mass: 51150.961 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Insecta environmental sample (insect) / References: UniProt: Q7TMM9 Insecta environmental sample (insect) / References: UniProt: Q7TMM9#3: Protein | Mass: 41721.066 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KIF5B, KNS, KNS1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KIF5B, KNS, KNS1 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 12 molecules 
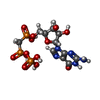



| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-GTP / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-G2P / #6: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: GMPCPP-Alpha1A/Beta2A-microtubule decorated with kinesin Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Insecta environmental sample (insect) Insecta environmental sample (insect) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 6.9 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 36 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.14_3260: / Classification: refinement |
|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement |
| CTF correction | Type: NONE |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 19287 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj
























