+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8i6m | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
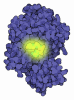
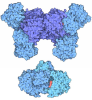
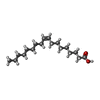
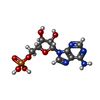
| Title | Acyl-ACP synthetase structure bound to AMP-C18:1 | ||||||
 Components Components | Acyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CYTOSOLIC PROTEIN / Acyl-ACP synthetase / Tool enzyme / TRANSFERASE | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||
| Biological species |  Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.59 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Huang, H. / Wang, C. / Chang, S. / Cui, T. / Xu, Y. / Zhang, H. / Zhou, C. / Zhang, X. / Feng, Y. | ||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025Title: Structure and catalytic mechanism of exogenous fatty acid recycling by AasS, a versatile acyl-ACP synthetase. Authors: Haomin Huang / Chen Wang / Shenghai Chang / Tao Cui / Yongchang Xu / Man Huang / Huimin Zhang / Chun Zhou / Xing Zhang / Youjun Feng /   Abstract: Fatty acids (FAs) are essential building blocks for all the domains of life, of which bacterial de novo synthesis, called type II FA synthesis (FAS II), is energetically expensive. The recycling of ...Fatty acids (FAs) are essential building blocks for all the domains of life, of which bacterial de novo synthesis, called type II FA synthesis (FAS II), is energetically expensive. The recycling of exogenous FAs (eFAs) partially relieves the FAS II demand and, therefore, compromises the efficacy of FAS II-directed antimicrobials. The versatile acyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP) synthetase, AasS, enables bacterial channeling of diverse eFA nutrients through holo-ACP, an activated form of ACP. However, the molecular mechanism for AasS catalysis is not fully understood. Here we report a series of cryo-electron microscopy structures of AasS from the bioluminescent bacterium Vibrio harveyi to provide insights into the catalytic cycle. AasS forms a ring-shaped hexamer, with each protomer folding into two distinct domains. Biochemical and structural analysis suggests that AasS accommodates distinct eFA substrates and the conserved W230 residue has a gating role. Adenosine triphosphate and Mg binding converts the AasS hexamer to a tetramer, which is likely needed for the acyl adenylate intermediate formation. Afterward, AasS reverts to the hexamer conformation in adaption to acyl-ACP production. The complete landscape for eFA scavenging lays a foundation for exploiting the versatility of AasS in biopharmaceuticals. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8i6m.cif.gz 8i6m.cif.gz | 611.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8i6m.ent.gz pdb8i6m.ent.gz | 505.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8i6m.json.gz 8i6m.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i6/8i6m https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i6/8i6m ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i6/8i6m ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i6/8i6m | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  35200MC 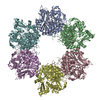 8i35C  8i3iC  8i49C  8i51C  8i8dC  8i8eC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 60496.258 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) / Gene: aasS, AL538_21690 / Production host: Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) / Gene: aasS, AL538_21690 / Production host:  #2: Chemical | ChemComp-OLA / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-AMP / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Acyl-ACP Synthetase bound to AMP-C18:1 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) Vibrio harveyi (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.59 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 337562 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj