[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8hgx: NMR solution structure of subunit epsilon of the Acinetobacter ba... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8hgx | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | NMR solution structure of subunit epsilon of the Acinetobacter baumannii F-ATP synthase | ||||||
 Components Components | ATP synthase epsilon chain | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ELECTRON TRANSPORT / F-ATP synthase / subunit eosilon / bioenergetics / Acinetobacter / baumannii | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / hydrolase activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Acinetobacter baumannii (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | SOLUTION NMR / simulated annealing | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Shin, J. / Grueber, G. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Singapore, 1items Singapore, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: FASEB J / Year: 2023 Journal: FASEB J / Year: 2023Title: Atomic insights of an up and down conformation of the Acinetobacter baumannii F -ATPase subunit ε and deciphering the residues critical for ATP hydrolysis inhibition and ATP synthesis. Authors: Wuan-Geok Saw / Khoa Cong Minh Le / Joon Shin / Jes Hui Min Kwek / Chui Fann Wong / Priya Ragunathan / Tuck Choy Fong / Volker Müller / Gerhard Grüber /   Abstract: The Acinetobacter baumannii F F -ATP synthase (α :β :γ:δ:ε:a:b :c ), which is essential for this strictly respiratory opportunistic human pathogen, is incapable of ATP-driven proton ...The Acinetobacter baumannii F F -ATP synthase (α :β :γ:δ:ε:a:b :c ), which is essential for this strictly respiratory opportunistic human pathogen, is incapable of ATP-driven proton translocation due to its latent ATPase activity. Here, we generated and purified the first recombinant A. baumannii F -ATPase (AbF -ATPase) composed of subunits α :β :γ:ε, showing latent ATP hydrolysis. A 3.0 Å cryo-electron microscopy structure visualizes the architecture and regulatory element of this enzyme, in which the C-terminal domain of subunit ε (Abε) is present in an extended position. An ε-free AbF -ɑβγ complex generated showed a 21.5-fold ATP hydrolysis increase, demonstrating that Abε is the major regulator of AbF -ATPase's latent ATP hydrolysis. The recombinant system enabled mutational studies of single amino acid substitutions within Abε or its interacting subunits β and γ, respectively, as well as C-terminal truncated mutants of Abε, providing a detailed picture of Abε's main element for the self-inhibition mechanism of ATP hydrolysis. Using a heterologous expression system, the importance of Abε's C-terminus in ATP synthesis of inverted membrane vesicles, including AbF F -ATP synthases, has been explored. In addition, we are presenting the first NMR solution structure of the compact form of Abε, revealing interaction of its N-terminal β-barrel and C-terminal ɑ-hairpin domain. A double mutant of Abε highlights critical residues for Abε's domain-domain formation which is important also for AbF -ATPase's stability. Abε does not bind MgATP, which is described to regulate the up and down movements in other bacterial counterparts. The data are compared to regulatory elements of F -ATPases in bacteria, chloroplasts, and mitochondria to prevent wasting of ATP. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8hgx.cif.gz 8hgx.cif.gz | 974.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8hgx.ent.gz pdb8hgx.ent.gz | 835.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8hgx.json.gz 8hgx.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hg/8hgx https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hg/8hgx ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hg/8hgx ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hg/8hgx | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7yryC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
| Other databases |
|
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 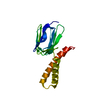
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| |||||||||
| NMR ensembles |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15511.765 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Acinetobacter baumannii (bacteria) Acinetobacter baumannii (bacteria)Gene: atpC, A7M90_08520, AB945B12_00682, Aba9201_12755, ABCAM1_0172, ABKPCSM17A_01727, ABR2091_0173, ABUW_3731, ACX61_17950, APC21_14385, APD31_00885, AUO97_06420, AYR68_18050, B7L45_18620, B9X95_ ...Gene: atpC, A7M90_08520, AB945B12_00682, Aba9201_12755, ABCAM1_0172, ABKPCSM17A_01727, ABR2091_0173, ABUW_3731, ACX61_17950, APC21_14385, APD31_00885, AUO97_06420, AYR68_18050, B7L45_18620, B9X95_01230, BAA1790NC_3496, BS065_18355, C2U32_15275, C6N18_19570, CBE85_14435, CBL15_17785, CSB70_3895, CTZ19_18500, D8O08_000335, DLI71_10775, DLI72_06180, DOL94_02920, DVA69_09710, E1A86_02075, E1A87_05110, E2532_15790, E2533_14640, E2534_11110, E2535_10530, E2536_13180, E2538_11270, E2539_11975, E2540_15325, E2541_09260, EA686_08570, EA706_05510, EA720_009765, EA722_10625, EGM95_19705, EKS29_01635, EWO96_15825, F2P40_12650, F4T85_15175, FDN00_02385, FE003_18665, FJU36_14065, FJU42_13255, FJU76_16610, FR761_02125, G3N53_14500, GNY86_14290, GSE42_00725, H0529_15450, H1058_00785, HB367_12610, HBK86_18985, HIN86_18905, IMO23_00750, NCTC13305_02274, NCTC13421_03737, SAMEA104305318_03328, SAMEA104305340_02247, SAMEA104305385_03000, SI89_14475 Production host:  References: UniProt: V5VHG0 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: SOLUTION NMR | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMR experiment |
|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Details |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sample conditions |
|
-NMR measurement
| NMR spectrometer | Type: Bruker AVANCE / Manufacturer: Bruker / Model: AVANCE / Field strength: 700 MHz |
|---|
- Processing
Processing
| NMR software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method: simulated annealing / Software ordinal: 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR representative | Selection criteria: minimized average structure | |||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR ensemble | Conformer selection criteria: structures with the lowest energy Conformers calculated total number: 200 / Conformers submitted total number: 21 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj

 HSQC
HSQC