+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8gxu | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
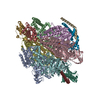
| Title | 1 ATP-bound V1EG of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / rotary ATPase / V/A-type ATPase / V-ATPase | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, catalytic domain / proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ATP binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.5 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Nakanishi, A. / Kishikawa, J. / Mitsuoka, K. / Yokoyama, K. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 5items Japan, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2023 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2023Title: Cryo-EM analysis of V/A-ATPase intermediates reveals the transition of the ground-state structure to steady-state structures by sequential ATP binding. Authors: Atsuko Nakanishi / Jun-Ichi Kishikawa / Kaoru Mitsuoka / Ken Yokoyama /  Abstract: Vacuolar/archaeal-type ATPase (V/A-ATPase) is a rotary ATPase that shares a common rotary catalytic mechanism with FF ATP synthase. Structural images of V/A-ATPase obtained by single-particle cryo- ...Vacuolar/archaeal-type ATPase (V/A-ATPase) is a rotary ATPase that shares a common rotary catalytic mechanism with FF ATP synthase. Structural images of V/A-ATPase obtained by single-particle cryo-electron microscopy during ATP hydrolysis identified several intermediates, revealing the rotary mechanism under steady-state conditions. However, further characterization is needed to understand the transition from the ground state to the steady state. Here, we identified the cryo-electron microscopy structures of V/A-ATPase corresponding to short-lived initial intermediates during the activation of the ground state structure by time-resolving snapshot analysis. These intermediate structures provide insights into how the ground-state structure changes to the active, steady state through the sequential binding of ATP to its three catalytic sites. All the intermediate structures of V/A-ATPase adopt the same asymmetric structure, whereas the three catalytic dimers adopt different conformations. This is significantly different from the initial activation process of FF, where the overall structure of the F domain changes during the transition from a pseudo-symmetric to a canonical asymmetric structure (PNAS NEXUS, pgac116, 2022). In conclusion, our findings provide dynamical information that will enhance the future prospects for studying the initial activation processes of the enzymes, which have unknown intermediate structures in their functional pathway. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8gxu.cif.gz 8gxu.cif.gz | 712.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8gxu.ent.gz pdb8gxu.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8gxu.json.gz 8gxu.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8gxu_validation.pdf.gz 8gxu_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8gxu_full_validation.pdf.gz 8gxu_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8gxu_validation.xml.gz 8gxu_validation.xml.gz | 104 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8gxu_validation.cif.gz 8gxu_validation.cif.gz | 163.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gx/8gxu https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gx/8gxu ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gx/8gxu ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/gx/8gxu | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  34362MC  8gxwC  8gxxC  8gxyC  8gxzC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 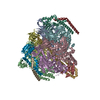
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-V-type ATP synthase ... , 5 types, 10 molecules ABCDEFGHJL
| #1: Protein | Mass: 63669.957 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: Authors state the bacterium they used has two mutations in its genome (S232A and T235S introduced by homologous recombination with engineered template DNA). Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8References: UniProt: Q56403, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #2: Protein | Mass: 53219.500 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: Q56404 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: Q56404#3: Protein | | Mass: 24715.566 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: O87880 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: O87880#4: Protein | | Mass: 11294.904 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: P74903 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: P74903#6: Protein | Mass: 20645.582 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: P74901 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: P74901 |
|---|
-Protein , 1 types, 2 molecules IK
| #5: Protein | Mass: 13166.218 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: Q5SIT5 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 / References: UniProt: Q5SIT5 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 3 molecules 


| #7: Chemical | | #8: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: 1 ATP-bound V1EG of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#6 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.6 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: MOLYBDENUM / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20rc4_4425: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 54047 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 7VAL Accession code: 7VAL / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj