+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | 1 ATP-bound V1EG of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Masked map of 1 ATP-bound V1EG of V/A-ATPase | ||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | rotary ATPase / V/A-type ATPase / V-ATPase / HYDROLASE | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, catalytic domain / proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ATP binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.5 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Nakanishi A / Kishikawa J / Mitsuoka K / Yokoyama K | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 5 items Japan, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2023 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2023Title: Cryo-EM analysis of V/A-ATPase intermediates reveals the transition of the ground-state structure to steady-state structures by sequential ATP binding. Authors: Atsuko Nakanishi / Jun-Ichi Kishikawa / Kaoru Mitsuoka / Ken Yokoyama /  Abstract: Vacuolar/archaeal-type ATPase (V/A-ATPase) is a rotary ATPase that shares a common rotary catalytic mechanism with FF ATP synthase. Structural images of V/A-ATPase obtained by single-particle cryo- ...Vacuolar/archaeal-type ATPase (V/A-ATPase) is a rotary ATPase that shares a common rotary catalytic mechanism with FF ATP synthase. Structural images of V/A-ATPase obtained by single-particle cryo-electron microscopy during ATP hydrolysis identified several intermediates, revealing the rotary mechanism under steady-state conditions. However, further characterization is needed to understand the transition from the ground state to the steady state. Here, we identified the cryo-electron microscopy structures of V/A-ATPase corresponding to short-lived initial intermediates during the activation of the ground state structure by time-resolving snapshot analysis. These intermediate structures provide insights into how the ground-state structure changes to the active, steady state through the sequential binding of ATP to its three catalytic sites. All the intermediate structures of V/A-ATPase adopt the same asymmetric structure, whereas the three catalytic dimers adopt different conformations. This is significantly different from the initial activation process of FF, where the overall structure of the F domain changes during the transition from a pseudo-symmetric to a canonical asymmetric structure (PNAS NEXUS, pgac116, 2022). In conclusion, our findings provide dynamical information that will enhance the future prospects for studying the initial activation processes of the enzymes, which have unknown intermediate structures in their functional pathway. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_34362.map.gz emd_34362.map.gz | 20.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-34362-v30.xml emd-34362-v30.xml emd-34362.xml emd-34362.xml | 23.8 KB 23.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
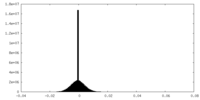
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_34362_fsc.xml emd_34362_fsc.xml | 14.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_34362.png emd_34362.png | 106.1 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_34362_msk_1.map emd_34362_msk_1.map | 244.1 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-34362.cif.gz emd-34362.cif.gz | 7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_34362_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34362_half_map_1.map.gz emd_34362_half_map_2.map.gz emd_34362_half_map_2.map.gz | 194.2 MB 194.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34362 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34362 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34362 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-34362 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_34362_validation.pdf.gz emd_34362_validation.pdf.gz | 934.9 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_34362_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_34362_full_validation.pdf.gz | 934.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_34362_validation.xml.gz emd_34362_validation.xml.gz | 21.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_34362_validation.cif.gz emd_34362_validation.cif.gz | 27.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34362 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34362 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34362 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-34362 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
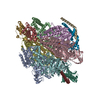
| Related structure data | 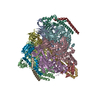 8gxuMC  8gxwC  8gxxC  8gxyC  8gxzC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_34362.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_34362.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
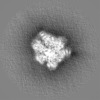
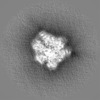
| Annotation | Masked map of 1 ATP-bound V1EG of V/A-ATPase | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
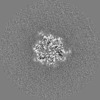
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.83 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
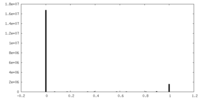
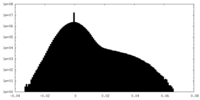
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_34362_msk_1.map emd_34362_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
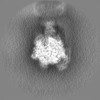
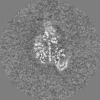
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
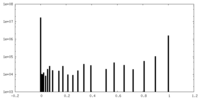
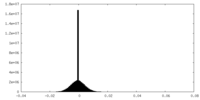
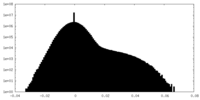
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Unfiltered half map of 1 ATP-bound V1EG of V/A-ATPase
| File | emd_34362_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
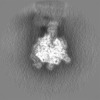
| Annotation | Unfiltered half map of 1 ATP-bound V1EG of V/A-ATPase | ||||||||||||
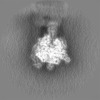
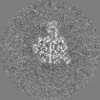
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Unfiltered half map of 1 ATP-bound V1EG of V/A-ATPase
| File | emd_34362_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unfiltered half map of 1 ATP-bound V1EG of V/A-ATPase | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : 1 ATP-bound V1EG of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus
| Entire | Name: 1 ATP-bound V1EG of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: 1 ATP-bound V1EG of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus
| Supramolecule | Name: 1 ATP-bound V1EG of V/A-ATPase from Thermus thermophilus type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#6 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 600 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: V-type ATP synthase alpha chain
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase alpha chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: Authors state the bacterium they used has two mutations in its genome (S232A and T235S introduced by homologous recombination with engineered template DNA). Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: H+-transporting two-sector ATPase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 63.669957 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MIQGVIQKIA GPAVIAKGML GARMYDICKV GEEGLVGEII RLDGDTAFVQ VYEDTSGLKV GEPVVSTGLP LAVELGPGML NGIYDGIQR PLERIREKTG IYITRGVVVH ALDREKKWAW TPMVKPGDEV RGGMVLGTVP EFGFTHKILV PPDVRGRVKE V KPAGEYTV ...String: MIQGVIQKIA GPAVIAKGML GARMYDICKV GEEGLVGEII RLDGDTAFVQ VYEDTSGLKV GEPVVSTGLP LAVELGPGML NGIYDGIQR PLERIREKTG IYITRGVVVH ALDREKKWAW TPMVKPGDEV RGGMVLGTVP EFGFTHKILV PPDVRGRVKE V KPAGEYTV EEPVVVLEDG TELKMYHTWP VRRARPVQRK LDPNTPFLTG MRILDVLFPV AMGGTAAIPG PFGAGKSVTQ QS LAKWSNA DVVVYVGCGE RGNEMTDVLV EFPELTDPKT GGPLMHRTVL IANTSNMPVA AREASIYVGV TIAEYFRDQG FSV ALMADS TSRWAEALRE ISSRLEEMPA EEGYPPYLAA RLAAFYERAG KVITLGGEEG AVTIVGAVSP PGGDMSEPVT QSTL RIVGA FWRLDASLAF RRHFPAINWN GSYSLFTSAL DPWYRENVAE DYPELRDAIS ELLQREAGLQ EIVQLVGPDA LQDAE RLVI EVGRIIREDF LQQNAYHEVD AYCSMKKAYG IMKMILAFYK EAEAAIKRGV SIDEILQLPV LERIGRARYV SEEEFP AYF EEAMKEIQGA FKALA UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase alpha chain |
-Macromolecule #2: V-type ATP synthase beta chain
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase beta chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 53.2195 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MDLLKKEYTG ITYISGPLLF VENAKDLAYG AIVDIKDGTG RVRGGQVIEV SEEYAVIQVF EETTGLDLAT TSVSLVEDVA RLGVSKEML GRRFNGIGKP IDGLPPITPE KRLPITGLPL NPVARRKPEQ FIQTGISTID VMNTLVRGQK LPIFSGSGLP A NEIAAQIA ...String: MDLLKKEYTG ITYISGPLLF VENAKDLAYG AIVDIKDGTG RVRGGQVIEV SEEYAVIQVF EETTGLDLAT TSVSLVEDVA RLGVSKEML GRRFNGIGKP IDGLPPITPE KRLPITGLPL NPVARRKPEQ FIQTGISTID VMNTLVRGQK LPIFSGSGLP A NEIAAQIA RQATVRPDLS GEGEKEEPFA VVFAAMGITQ RELSYFIQEF ERTGALSRSV LFLNKADDPT IERILTPRMA LT VAEYLAF EHDYHVLVIL TDMTNYCEAL REIGAAREEI PGRRGYPGYM YTDLATIYER AGVVEGKKGS VTQIPILSMP DDD RTHPIP DLTGYITEGQ IQLSRELHRK GIYPPIDPLP SLSRLMNNGV GKGKTREDHK QVSDQLYSAY ANGVDIRKLV AIIG EDALT ENDRRYLQFA DAFERFFINQ GQQNRSIEES LQIAWALLSM LPQGELKRIS KDHIGKYYGQ KLEEIWGAPQ ALD UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase beta chain |
-Macromolecule #3: V-type ATP synthase subunit D
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase subunit D / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.715566 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MSQVSPTRMN LLQRRGQLRL AQKGVDLLKK KRDALVAEFF GLVREAMEAR KALDQAAKEA YAALLLAQAF DGPEVVAGAA LGVPPLEGV EAEVENVWGS KVPRLKATFP DGALLSPVGT PAYTLEASRA FRRYAEALIR VANTETRLKK IGEEIKKTTR R VNALEQVV ...String: MSQVSPTRMN LLQRRGQLRL AQKGVDLLKK KRDALVAEFF GLVREAMEAR KALDQAAKEA YAALLLAQAF DGPEVVAGAA LGVPPLEGV EAEVENVWGS KVPRLKATFP DGALLSPVGT PAYTLEASRA FRRYAEALIR VANTETRLKK IGEEIKKTTR R VNALEQVV IPGIRAQIRF IQQVLEQRER EDTFRLKRIK GKIEAREAEE EGGRPNPQVE IGAGL UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase subunit D |
-Macromolecule #4: V-type ATP synthase subunit F
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase subunit F / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.294904 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MAVIADPETA QGFRLAGLEG YGASSAEEAQ SLLETLVERG GYALVAVDEA LLPDPERAVE RLMRGRDLPV LLPIAGLKEA FQGHDVEGY MRELVRKTIG FDIKL UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase subunit F |
-Macromolecule #5: V-type ATP synthase, subunit (VAPC-THERM)
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase, subunit (VAPC-THERM) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.166218 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MTGGLVLNAI SRAGGAMGGL GLIKSLAEKE KQLLERLEAA KKEAEERVKR AEAEAKALLE EAEAKAKALE AQYRERERAE TEALLARYR ERAEAEAKAV REKAMARLDE AVALVLKEVL P UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase, subunit (VAPC-THERM) |
-Macromolecule #6: V-type ATP synthase subunit E
| Macromolecule | Name: V-type ATP synthase subunit E / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 Thermus thermophilus HB8 (bacteria) / Strain: HB8 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 20.645582 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MSKLEAILSQ EVEAEIQALL QEAEAKAEAV KREAEEKAKA LLQARERALE AQYRAALRRA ESAGELLVAT ARTQARGEVL EEVRRRVRE ALEALPQKPE WPEVVRKLAL EALEALPGAK ALVANPEDLP HLEALARERG VELQAEPALR LGVRAVGAEG K TQVENSLL ARLDRAWDAL SSKVAQALWG UniProtKB: V-type ATP synthase subunit E |
-Macromolecule #7: SULFATE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: SULFATE ION / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: SO4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 96.063 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-SO4: |
-Macromolecule #8: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ATP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 4.0 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil / Material: MOLYBDENUM / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)