[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8g0e: Cryo-EM structure of TBAJ-876-bound Mycobacterium smegmatis ATP s... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8g0e | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of TBAJ-876-bound Mycobacterium smegmatis ATP synthase rotational state 3 | ||||||
 Components Components | (ATP synthase ...) x 8 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSLOCASE/INHIBITOR / ATP synthase / mycobacterial / inhibitor / tuberculosis / antibiotic / HYDROLASE / TRANSLOCASE-INHIBITOR complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / hydrolase activity / lipid binding / ATP hydrolysis activity ...proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / hydrolase activity / lipid binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.6 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Courbon, G.M. / Rubinstein, J.L. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 1items Canada, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2023 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2023Title: Mechanism of mycobacterial ATP synthase inhibition by squaramides and second generation diarylquinolines. Authors: Gautier M Courbon / Paul R Palme / Lea Mann / Adrian Richter / Peter Imming / John L Rubinstein /   Abstract: Mycobacteria, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, depend on the activity of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase for growth. The diarylquinoline bedaquiline (BDQ), a mycobacterial ATP synthase ...Mycobacteria, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, depend on the activity of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase for growth. The diarylquinoline bedaquiline (BDQ), a mycobacterial ATP synthase inhibitor, is an important medication for treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis but suffers from off-target effects and is susceptible to resistance mutations. Consequently, both new and improved mycobacterial ATP synthase inhibitors are needed. We used electron cryomicroscopy and biochemical assays to study the interaction of Mycobacterium smegmatis ATP synthase with the second generation diarylquinoline TBAJ-876 and the squaramide inhibitor SQ31f. The aryl groups of TBAJ-876 improve binding compared with BDQ, while SQ31f, which blocks ATP synthesis ~10 times more potently than ATP hydrolysis, binds a previously unknown site in the enzyme's proton-conducting channel. Remarkably, BDQ, TBAJ-876, and SQ31f all induce similar conformational changes in ATP synthase, suggesting that the resulting conformation is particularly suited for drug binding. Further, high concentrations of the diarylquinolines uncouple the transmembrane proton motive force while for SQ31f they do not, which may explain why high concentrations of diarylquinolines, but not SQ31f, have been reported to kill mycobacteria. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8g0e.cif.gz 8g0e.cif.gz | 785.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8g0e.ent.gz pdb8g0e.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8g0e.json.gz 8g0e.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g0/8g0e https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g0/8g0e ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g0/8g0e ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g0/8g0e | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  29655MC  8g07C  8g08C  8g09C  8g0aC  8g0bC  8g0cC 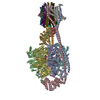 8g0dC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ATP synthase ... , 8 types, 20 molecules ABCDEFGHbd912345678a
| #1: Protein | Mass: 58951.461 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria)References: UniProt: A0R202, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #2: Protein | Mass: 51670.453 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria)References: UniProt: A0R200, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #3: Protein | | Mass: 33439.836 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria)References: UniProt: A0R201 #4: Protein | | Mass: 13277.741 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria)References: UniProt: A0R1Z9 #5: Protein | | Mass: 17636.701 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria)References: UniProt: A0R204 #6: Protein | | Mass: 47504.723 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria)References: UniProt: A0R203 #7: Protein | Mass: 8597.982 Da / Num. of mol.: 9 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria)References: UniProt: A0R205 #8: Protein | | Mass: 27568.482 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria)References: UniProt: A0R206 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 16 molecules 


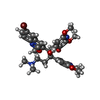



| #9: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / #10: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #11: Chemical | ChemComp-PO4 / | #12: Chemical | ChemComp-YGR / ( |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: TBAJ-876-bound Mycobacterium smegmatis ATP synthase rotational state 3 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#8 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis MC2 155 (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2100 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 44 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 166169 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj






