+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ffv | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
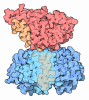
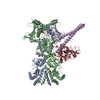
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the GR-Hsp90-FKBP52 complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CHAPERONE / steroid hormone receptor / ligand binding / ATP binding / protein folding | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsteroid hormone receptor complex assembly / negative regulation of microtubule polymerization or depolymerization / male sex differentiation / copper-dependent protein binding / Regulation of NPAS4 gene transcription / regulation of glucocorticoid biosynthetic process / nuclear glucocorticoid receptor activity / prostate gland development / steroid hormone binding / glucocorticoid metabolic process ...steroid hormone receptor complex assembly / negative regulation of microtubule polymerization or depolymerization / male sex differentiation / copper-dependent protein binding / Regulation of NPAS4 gene transcription / regulation of glucocorticoid biosynthetic process / nuclear glucocorticoid receptor activity / prostate gland development / steroid hormone binding / glucocorticoid metabolic process / response to cortisol / PTK6 Expression / copper ion transport / nuclear glucocorticoid receptor binding / neuroinflammatory response / mammary gland duct morphogenesis / microglia differentiation / astrocyte differentiation / maternal behavior / protein-containing complex localization / adrenal gland development / regulation of gluconeogenesis / cellular response to glucocorticoid stimulus / sperm mitochondrial sheath / sulfonylurea receptor binding / dATP binding / CTP binding / positive regulation of protein polymerization / Scavenging by Class F Receptors / vRNP Assembly / UTP binding / cellular response to steroid hormone stimulus / chaperone-mediated autophagy / sperm plasma membrane / androgen receptor signaling pathway / FK506 binding / Respiratory syncytial virus genome replication / Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor binding / telomerase holoenzyme complex assembly / mitochondrial transport / negative regulation of microtubule polymerization / Drug-mediated inhibition of ERBB2 signaling / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to trastuzumab / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to sapitinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to tesevatinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to neratinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to osimertinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to afatinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to AEE788 / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to lapatinib / Drug resistance in ERBB2 TMD/JMD mutants / Uptake and function of diphtheria toxin / : / protein import into mitochondrial matrix / TPR domain binding / dendritic growth cone / PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) biogenesis / motor behavior / Assembly and release of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) virions / non-chaperonin molecular chaperone ATPase / protein unfolding / Sema3A PAK dependent Axon repulsion / regulation of protein ubiquitination / estrogen response element binding / positive regulation of cell size / HSF1-dependent transactivation / protein folding chaperone complex / cellular response to dexamethasone stimulus / enzyme-substrate adaptor activity / response to unfolded protein / nuclear receptor-mediated steroid hormone signaling pathway / regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / HSF1 activation / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / Attenuation phase / cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus / chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly / neurofibrillary tangle assembly / RHOBTB2 GTPase cycle / core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding / regulation of postsynaptic membrane neurotransmitter receptor levels / axonal growth cone / telomere maintenance via telomerase / skeletal muscle contraction / positive regulation of lamellipodium assembly / : / nitric oxide metabolic process / steroid binding / heat shock protein binding / response to salt stress / positive regulation of defense response to virus by host / DNA polymerase binding / eNOS activation / positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase / Signaling by ERBB2 / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process / endocytic vesicle lumen / positive regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.01 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Noddings, C.M. / Agard, D.A. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2023Title: Cryo-EM reveals how Hsp90 and FKBP immunophilins co-regulate the glucocorticoid receptor. Authors: Chari M Noddings / Jill L Johnson / David A Agard /  Abstract: Hsp90 is an essential molecular chaperone responsible for the folding and activation of hundreds of 'client' proteins, including the glucocorticoid receptor (GR). Previously, we revealed that Hsp70 ...Hsp90 is an essential molecular chaperone responsible for the folding and activation of hundreds of 'client' proteins, including the glucocorticoid receptor (GR). Previously, we revealed that Hsp70 and Hsp90 remodel the conformation of GR to regulate ligand binding, aided by co-chaperones. In vivo, the co-chaperones FKBP51 and FKBP52 antagonistically regulate GR activity, but a molecular understanding is lacking. Here we present a 3.01 Å cryogenic electron microscopy structure of the human GR:Hsp90:FKBP52 complex, revealing how FKBP52 integrates into the GR chaperone cycle and directly binds to the active client, potentiating GR activity in vitro and in vivo. We also present a 3.23 Å cryogenic electron microscopy structure of the human GR:Hsp90:FKBP51 complex, revealing how FKBP51 competes with FKBP52 for GR:Hsp90 binding and demonstrating how FKBP51 can act as a potent antagonist to FKBP52. Altogether, we demonstrate how FKBP51 and FKBP52 integrate into the GR chaperone cycle to advance GR to the next stage of maturation. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ffv.cif.gz 8ffv.cif.gz | 739.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ffv.ent.gz pdb8ffv.ent.gz | 612.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ffv.json.gz 8ffv.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ff/8ffv https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ff/8ffv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ff/8ffv ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ff/8ffv | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  29068MC  8ffwC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 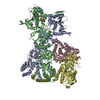
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 4 molecules ABCD
| #1: Protein | Mass: 84650.531 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HSP90AA1, HSP90A, HSPC1, HSPCA / Plasmid: pET151 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HSP90AA1, HSP90A, HSPC1, HSPCA / Plasmid: pET151 / Production host:  References: UniProt: P07900, non-chaperonin molecular chaperone ATPase #2: Protein | | Mass: 41198.973 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: F602S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NR3C1, GRL / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: NR3C1, GRL / Production host:  #3: Protein | | Mass: 51876.520 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FKBP4, FKBP52 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FKBP4, FKBP52 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 5 molecules 




| #4: Chemical | | #5: Chemical | #6: Chemical | ChemComp-DEX / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Complex of the Glucocorticoid Receptor ligand binding domain, Hsp90 alpha dimer, and the co-chaperone FKBP52 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.307 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 283 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 5.9 sec. / Electron dose: 67 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 11162 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.01 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 307109 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj