+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8f8q | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the CapZ-capped barbed end of F-actin | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | STRUCTURAL PROTEIN / Barbed end capping protein / F-actin / CapZ | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationF-actin capping protein complex / WASH complex / cell junction assembly / barbed-end actin filament capping / actin polymerization or depolymerization / RHOD GTPase cycle / regulation of cell morphogenesis / RHOF GTPase cycle / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / lamellipodium assembly ...F-actin capping protein complex / WASH complex / cell junction assembly / barbed-end actin filament capping / actin polymerization or depolymerization / RHOD GTPase cycle / regulation of cell morphogenesis / RHOF GTPase cycle / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / lamellipodium assembly / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / sperm head-tail coupling apparatus / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / cortical cytoskeleton / brush border / Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin filament bundle assembly / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / actin monomer binding / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / skeletal muscle fiber development / stress fiber / titin binding / actin filament polymerization / cytoskeleton organization / MHC class II antigen presentation / Gene and protein expression by JAK-STAT signaling after Interleukin-12 stimulation / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse / sarcomere / actin filament / filopodium / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / calcium-dependent protein binding / actin filament binding / lamellipodium / actin cytoskeleton / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / actin binding / actin cytoskeleton organization / cell body / protein-containing complex assembly / cytoskeleton / postsynaptic density / cadherin binding / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / magnesium ion binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / ATP binding / membrane / identical protein binding / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.79 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Carman, P.J. / Barrie, K.R. / Dominguez, R. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2023 Journal: Science / Year: 2023Title: Structures of the free and capped ends of the actin filament. Authors: Peter J Carman / Kyle R Barrie / Grzegorz Rebowski / Roberto Dominguez /  Abstract: The barbed and pointed ends of the actin filament (F-actin) are the sites of growth and shrinkage and the targets of capping proteins that block subunit exchange, including CapZ at the barbed end and ...The barbed and pointed ends of the actin filament (F-actin) are the sites of growth and shrinkage and the targets of capping proteins that block subunit exchange, including CapZ at the barbed end and tropomodulin at the pointed end. We describe cryo-electron microscopy structures of the free and capped ends of F-actin. Terminal subunits at the free barbed end adopt a "flat" F-actin conformation. CapZ binds with minor changes to the barbed end but with major changes to itself. By contrast, subunits at the free pointed end adopt a "twisted" monomeric actin (G-actin) conformation. Tropomodulin binding forces the second subunit into an F-actin conformation. The structures reveal how the ends differ from the middle in F-actin and how these differences control subunit addition, dissociation, capping, and interactions with end-binding proteins. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8f8q.cif.gz 8f8q.cif.gz | 533.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8f8q.ent.gz pdb8f8q.ent.gz | 440.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8f8q.json.gz 8f8q.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f8/8f8q https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f8/8f8q ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f8/8f8q ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f8/8f8q | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  28933MC 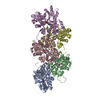 8f8pC 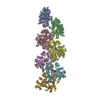 8f8rC  8f8sC 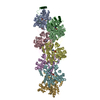 8f8tC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 42109.973 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | | Mass: 32964.727 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CAPZA1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CAPZA1 / Production host:  #3: Protein | | Mass: 31258.289 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CAPZB / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CAPZB / Production host:  #4: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / Has ligand of interest | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.05 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 278 K / Details: Blot force 0 Blot time 2.5 s |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 81000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 44.7 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1102793 / Details: Topaz particle picking with training | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.79 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 155516 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Cross-correlation coefficient | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj





























