+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8f86 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
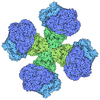
| Title | SIRT6 bound to an H3K9Ac nucleosome | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GENE REGULATION / nucleosome / SIRTUIN6 / histone deacylation / H3K9Ac | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhistone H3K56 deacetylase activity, NAD-dependent / histone H3K18 deacetylase activity, NAD-dependent / ketone biosynthetic process / histone H3K9 deacetylase activity, hydrolytic mechanism / histone H3K9 deacetylase activity, NAD-dependent / protein delipidation / NAD+-protein-lysine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / regulation of lipid catabolic process / chromosome, subtelomeric region / positive regulation of protein localization to chromatin ...histone H3K56 deacetylase activity, NAD-dependent / histone H3K18 deacetylase activity, NAD-dependent / ketone biosynthetic process / histone H3K9 deacetylase activity, hydrolytic mechanism / histone H3K9 deacetylase activity, NAD-dependent / protein delipidation / NAD+-protein-lysine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / regulation of lipid catabolic process / chromosome, subtelomeric region / positive regulation of protein localization to chromatin / NAD+-protein-arginine ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / DNA damage sensor activity / NAD-dependent protein demyristoylase activity / NAD-dependent protein depalmitoylase activity / positive regulation of stem cell differentiation / negative regulation of D-glucose import / positive regulation of chondrocyte proliferation / transposable element silencing / NAD-dependent protein lysine deacetylase activity / cardiac muscle cell differentiation / protein acetyllysine N-acetyltransferase / pericentric heterochromatin formation / protein deacetylation / histone deacetylase activity, NAD-dependent / protein localization to site of double-strand break / positive regulation of blood vessel branching / negative regulation of glycolytic process / TORC2 complex binding / negative regulation of protein localization to chromatin / positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation / histone deacetylase regulator activity / negative regulation of protein import into nucleus / regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / regulation of protein secretion / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / DNA repair-dependent chromatin remodeling / positive regulation of stem cell proliferation / lncRNA binding / negative regulation of gene expression, epigenetic / NAD+-protein mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / positive regulation of telomere maintenance / regulation of lipid metabolic process / site of DNA damage / negative regulation of cellular senescence / negative regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / Transferases; Glycosyltransferases; Pentosyltransferases / NAD+ poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase activity / NAD+ binding / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / positive regulation of fat cell differentiation / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / pericentric heterochromatin / response to UV / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / nucleosome binding / enzyme regulator activity / Transferases; Acyltransferases; Transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups / nucleotidyltransferase activity / positive regulation of protein export from nucleus / determination of adult lifespan / circadian regulation of gene expression / base-excision repair / regulation of circadian rhythm / positive regulation of insulin secretion / protein destabilization / chromatin DNA binding / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / positive regulation of fibroblast proliferation / protein import into nucleus / structural constituent of chromatin / transcription corepressor activity / positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / nucleosome / heterochromatin formation / glucose homeostasis / double-strand break repair / nucleosome assembly / site of double-strand break / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / damaged DNA binding / chromatin remodeling / protein heterodimerization activity / negative regulation of cell population proliferation / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / chromatin binding / chromatin / endoplasmic reticulum / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein homodimerization activity / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / nucleus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species | synthetic construct (others)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Markert, J. / Whedon, S. / Wang, Z. / Cole, P. / Farnung, L. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Am Chem Soc / Year: 2023 Journal: J Am Chem Soc / Year: 2023Title: Structural Basis of Sirtuin 6-Catalyzed Nucleosome Deacetylation. Authors: Zhipeng A Wang / Jonathan W Markert / Samuel D Whedon / Maheeshi Yapa Abeywardana / Kwangwoon Lee / Hanjie Jiang / Carolay Suarez / Hening Lin / Lucas Farnung / Philip A Cole /  Abstract: The reversible acetylation of histone lysine residues is controlled by the action of acetyltransferases and deacetylases (HDACs), which regulate chromatin structure and gene expression. The sirtuins ...The reversible acetylation of histone lysine residues is controlled by the action of acetyltransferases and deacetylases (HDACs), which regulate chromatin structure and gene expression. The sirtuins are a family of NAD-dependent HDAC enzymes, and one member, sirtuin 6 (Sirt6), influences DNA repair, transcription, and aging. Here, we demonstrate that Sirt6 is efficient at deacetylating several histone H3 acetylation sites, including its canonical site Lys9, in the context of nucleosomes but not free acetylated histone H3 protein substrates. By installing a chemical warhead at the Lys9 position of histone H3, we trap a catalytically poised Sirt6 in complex with a nucleosome and employ this in cryo-EM structural analysis. The structure of Sirt6 bound to a nucleosome reveals extensive interactions between distinct segments of Sirt6 and the H2A/H2B acidic patch and nucleosomal DNA, which accounts for the rapid deacetylation of nucleosomal H3 sites and the disfavoring of histone H2B acetylation sites. These findings provide a new framework for understanding how HDACs target and regulate chromatin. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8f86.cif.gz 8f86.cif.gz | 383.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8f86.ent.gz pdb8f86.ent.gz | 290.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8f86.json.gz 8f86.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8f86_validation.pdf.gz 8f86_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8f86_full_validation.pdf.gz 8f86_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8f86_validation.xml.gz 8f86_validation.xml.gz | 53.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8f86_validation.cif.gz 8f86_validation.cif.gz | 80.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f8/8f86 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f8/8f86 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f8/8f86 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f8/8f86 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  28915MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 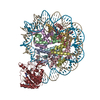
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 9 molecules AEBFCGDHK
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15271.863 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #2: Protein | Mass: 11263.231 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #3: Protein | Mass: 13978.241 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #4: Protein | Mass: 13524.752 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  #7: Protein | | Mass: 39152.863 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SIRT6, SIR2L6 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SIRT6, SIR2L6 / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q8N6T7, Transferases; Acyltransferases; Transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups, protein acetyllysine N-acetyltransferase, Transferases; Glycosyltransferases; Pentosyltransferases |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 57400.559 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 56831.191 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 2 molecules 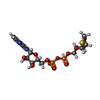


| #8: Chemical | ChemComp-ZSL / [( |
|---|---|
| #9: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: SIRT6 bound to H3K9Ac / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#7 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1700 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50.45 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20.1_4487: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 95205 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj