[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8dxu: Fab arms of antibodies GAR03 and 10G4 bound to the receptor bindi... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8dxu | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Fab arms of antibodies GAR03 and 10G4 bound to the receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 in a 1:1:1 complex. | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ANTIVIRAL PROTEIN / anti-CoV-2 / antibodies / convalescent patients / receptor binding domain. | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsymbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / membrane fusion ...symbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / membrane fusion / Attachment and Entry / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell surface receptor binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / receptor ligand activity / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / virion membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT /  molecular replacement / Resolution: 2.728 Å molecular replacement / Resolution: 2.728 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Langley, D.B. / Christ, D. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 1items Australia, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Broadly neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 antibodies through epitope-based selection from convalescent patients. Authors: Romain Rouet / Jake Y Henry / Matt D Johansen / Meghna Sobti / Harikrishnan Balachandran / David B Langley / Gregory J Walker / Helen Lenthall / Jennifer Jackson / Stephanie Ubiparipovic / ...Authors: Romain Rouet / Jake Y Henry / Matt D Johansen / Meghna Sobti / Harikrishnan Balachandran / David B Langley / Gregory J Walker / Helen Lenthall / Jennifer Jackson / Stephanie Ubiparipovic / Ohan Mazigi / Peter Schofield / Deborah L Burnett / Simon H J Brown / Marianne Martinello / Bernard Hudson / Nicole Gilroy / Jeffrey J Post / Anthony Kelleher / Hans-Martin Jäck / Christopher C Goodnow / Stuart G Turville / William D Rawlinson / Rowena A Bull / Alastair G Stewart / Philip M Hansbro / Daniel Christ /   Abstract: Emerging variants of concern (VOCs) are threatening to limit the effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies and vaccines currently used in clinical practice; broadly neutralizing antibodies ...Emerging variants of concern (VOCs) are threatening to limit the effectiveness of SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies and vaccines currently used in clinical practice; broadly neutralizing antibodies and strategies for their identification are therefore urgently required. Here we demonstrate that broadly neutralizing antibodies can be isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells of convalescent patients using SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domains carrying epitope-specific mutations. This is exemplified by two human antibodies, GAR05, binding to epitope class 1, and GAR12, binding to a new epitope class 6 (located between class 3 and 5). Both antibodies broadly neutralize VOCs, exceeding the potency of the clinical monoclonal sotrovimab (S309) by orders of magnitude. They also provide prophylactic and therapeutic in vivo protection of female hACE2 mice against viral challenge. Our results indicate that exposure to SARS-CoV-2 induces antibodies that maintain broad neutralization against emerging VOCs using two unique strategies: either by targeting the divergent class 1 epitope in a manner resistant to VOCs (ACE2 mimicry, as illustrated by GAR05 and mAbs P2C-1F11/S2K14); or alternatively, by targeting rare and highly conserved epitopes, such as the new class 6 epitope identified here (as illustrated by GAR12). Our results provide guidance for next generation monoclonal antibody development and vaccine design. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8dxu.cif.gz 8dxu.cif.gz | 411.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8dxu.ent.gz pdb8dxu.ent.gz | 332.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8dxu.json.gz 8dxu.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dx/8dxu https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dx/8dxu ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dx/8dxu ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dx/8dxu | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7t5oC 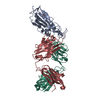 7t72C  8dxtC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
-Antibody , 4 types, 4 molecules HLAB
| #2: Antibody | Mass: 24475.314 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Heavy chain of Fab arm of antibody 10G4 / Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): ExpiCHO / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): ExpiCHO / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #3: Antibody | Mass: 23591.232 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Light chain of Fab arm of antibody 10G4 / Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): ExpiCHO / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): ExpiCHO / Production host:  |
| #4: Antibody | Mass: 24705.656 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Heavy chain of Fab arm of antibody GAR03 / Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): ExpiCHO / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): ExpiCHO / Production host:  |
| #5: Antibody | Mass: 22970.273 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Light chain of Fab arm of antibody GAR03 / Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): ExpiCHO / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): ExpiCHO / Production host:  |
-Protein / Sugars , 2 types, 2 molecules R

| #1: Protein | Mass: 22975.688 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: receptor binding domain Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain residues 333-528, with C-terminal 6His tag. Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: S, 2 / Cell line (production host): ExpiCHO / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #6: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 45 molecules 


| #7: Chemical | | #8: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.4 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 44 % / Description: thin plates |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 6 Details: Two uL of protein solution (~5 mg/mL of 1:1:1 complex in 25 mM Tris (pH 8.0), 200 mM NaCl) was combined with an equal volume of well solution (100 mM MMT buffer system (Molecular Dimensions) ...Details: Two uL of protein solution (~5 mg/mL of 1:1:1 complex in 25 mM Tris (pH 8.0), 200 mM NaCl) was combined with an equal volume of well solution (100 mM MMT buffer system (Molecular Dimensions) (pH 6.0), 19% (w/v) PEG6000. |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  Australian Synchrotron Australian Synchrotron  / Beamline: MX2 / Wavelength: 0.9537 Å / Beamline: MX2 / Wavelength: 0.9537 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER X 16M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Jun 11, 2022 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.9537 Å / Relative weight: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.728→49.48 Å / Num. obs: 31192 / % possible obs: 99.4 % / Redundancy: 11.9 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 59.81 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.998 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.156 / Rpim(I) all: 0.047 / Rrim(I) all: 0.163 / Net I/σ(I): 12.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1
|
-Phasing
| Phasing | Method:  molecular replacement molecular replacement | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phasing MR | Model details: Phaser MODE: MR_AUTO
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: generic fab and SARS-CoV-2 RBD Resolution: 2.728→45.547 Å / SU ML: 0.41 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 29.53 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 164.75 Å2 / Biso mean: 64.0261 Å2 / Biso min: 27.48 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 2.728→45.547 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Rfactor Rfree error: 0
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Origin x: -9.5853 Å / Origin y: 11.3813 Å / Origin z: -58.3439 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj






