[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8do4: Prefusion-stabilized Nipah virus fusion protein, dimer of trimers -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8do4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Prefusion-stabilized Nipah virus fusion protein, dimer of trimers | ||||||
 Components Components | Fusion glycoprotein F0 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / Nipah / Nipah virus / NiV / fusion / F / antibody / neutralizing / conserved epitope / neutralizing antibody / prefusion / prefusion-stabilized / vaccine / vaccine design / antigen / antigen design / dimer of trimers / oligomer | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationthymidylate synthase / thymidylate synthase activity / dTMP biosynthetic process / dTTP biosynthetic process / methylation / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Nipah henipavirus Nipah henipavirus | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Byrne, P.O. / Blade, E.G. / McLellan, J.S. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2024 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2024Title: Prefusion stabilization of the Hendra and Langya virus F proteins. Authors: Patrick O Byrne / Elizabeth G Blade / Brian E Fisher / David R Ambrozak / Ajit R Ramamohan / Barney S Graham / Rebecca J Loomis / Jason S McLellan /  Abstract: Nipah virus (NiV) and Hendra virus (HeV) are pathogenic paramyxoviruses that cause mild-to-severe disease in humans. As members of the genus, NiV and HeV use an attachment (G) glycoprotein and a ...Nipah virus (NiV) and Hendra virus (HeV) are pathogenic paramyxoviruses that cause mild-to-severe disease in humans. As members of the genus, NiV and HeV use an attachment (G) glycoprotein and a class I fusion (F) glycoprotein to invade host cells. The F protein rearranges from a metastable prefusion form to an extended postfusion form to facilitate host cell entry. Prefusion NiV F elicits higher neutralizing antibody titers than postfusion NiV F, indicating that stabilization of prefusion F may aid vaccine development. A combination of amino acid substitutions (L104C/I114C, L172F, and S191P) is known to stabilize NiV F in its prefusion conformation, although the extent to which substitutions transfer to other henipavirus F proteins is not known. Here, we perform biophysical and structural studies to investigate the mechanism of prefusion stabilization in F proteins from three henipaviruses: NiV, HeV, and Langya virus (LayV). Three known stabilizing substitutions from NiV F transfer to HeV F and exert similar structural and functional effects. One engineered disulfide bond, located near the fusion peptide, is sufficient to stabilize the prefusion conformations of both HeV F and LayV F. Although LayV F shares low overall sequence identity with NiV F and HeV F, the region around the fusion peptide exhibits high sequence conservation across all henipaviruses. Our findings indicate that substitutions targeting this site of conformational change might be applicable to prefusion stabilization of other henipavirus F proteins and support the use of NiV as a prototypical pathogen for henipavirus vaccine antigen design.IMPORTANCEPathogenic henipaviruses such as Nipah virus (NiV) and Hendra virus (HeV) cause respiratory symptoms, with severe cases resulting in encephalitis, seizures, and coma. The work described here shows that the NiV and HeV fusion (F) proteins share common structural features with the F protein from an emerging henipavirus Langya virus (LayV). Sequence alignment alone was sufficient to predict which known prefusion-stabilizing amino acid substitutions from NiV F would stabilize the prefusion conformations of HeV F and LayV F. This work also reveals an unexpected oligomeric interface shared by prefusion HeV F and NiV F. Together, these advances lay a foundation for future antigen design targeting henipavirus F proteins. In this way, Nipah virus can serve as a prototypical pathogen for the development of protective vaccines and monoclonal antibodies to prepare for potential henipavirus outbreaks. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8do4.cif.gz 8do4.cif.gz | 498.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8do4.ent.gz pdb8do4.ent.gz | 408.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8do4.json.gz 8do4.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/do/8do4 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/do/8do4 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/do/8do4 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/do/8do4 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  27590MC 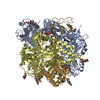 8dngC  8dnrC  8u1rC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 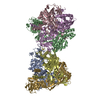
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 60039.879 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Nipah henipavirus / Production host: Nipah henipavirus / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9IH63 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9IH63Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Prefusion-stabilized Nipah virus fusion protein, dimer of trimers Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Nipah henipavirus Nipah henipavirus |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 49 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: SerialEM / Category: image acquisition |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 534823 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj



