+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Prefusion-stabilized Hendra virus fusion protein | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Prefusion-stabilized Hendra virus fusion protein | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Hendra / nipah / henipavirus / Hendra virus / NiV / HeV / fusion / F / antibody / neutralizing / conserved epitope / neutralizing antibody / prefusion / prefusion-stabilized / vaccine / vaccine design / antigen / antigen design / VIRAL PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationhost cell surface / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Hendra henipavirus Hendra henipavirus | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Byrne PO / Blade EG / McLellan JS | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2024 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2024Title: Prefusion stabilization of the Hendra and Langya virus F proteins. Authors: Patrick O Byrne / Elizabeth G Blade / Brian E Fisher / David R Ambrozak / Ajit R Ramamohan / Barney S Graham / Rebecca J Loomis / Jason S McLellan /  Abstract: Nipah virus (NiV) and Hendra virus (HeV) are pathogenic paramyxoviruses that cause mild-to-severe disease in humans. As members of the genus, NiV and HeV use an attachment (G) glycoprotein and a ...Nipah virus (NiV) and Hendra virus (HeV) are pathogenic paramyxoviruses that cause mild-to-severe disease in humans. As members of the genus, NiV and HeV use an attachment (G) glycoprotein and a class I fusion (F) glycoprotein to invade host cells. The F protein rearranges from a metastable prefusion form to an extended postfusion form to facilitate host cell entry. Prefusion NiV F elicits higher neutralizing antibody titers than postfusion NiV F, indicating that stabilization of prefusion F may aid vaccine development. A combination of amino acid substitutions (L104C/I114C, L172F, and S191P) is known to stabilize NiV F in its prefusion conformation, although the extent to which substitutions transfer to other henipavirus F proteins is not known. Here, we perform biophysical and structural studies to investigate the mechanism of prefusion stabilization in F proteins from three henipaviruses: NiV, HeV, and Langya virus (LayV). Three known stabilizing substitutions from NiV F transfer to HeV F and exert similar structural and functional effects. One engineered disulfide bond, located near the fusion peptide, is sufficient to stabilize the prefusion conformations of both HeV F and LayV F. Although LayV F shares low overall sequence identity with NiV F and HeV F, the region around the fusion peptide exhibits high sequence conservation across all henipaviruses. Our findings indicate that substitutions targeting this site of conformational change might be applicable to prefusion stabilization of other henipavirus F proteins and support the use of NiV as a prototypical pathogen for henipavirus vaccine antigen design.IMPORTANCEPathogenic henipaviruses such as Nipah virus (NiV) and Hendra virus (HeV) cause respiratory symptoms, with severe cases resulting in encephalitis, seizures, and coma. The work described here shows that the NiV and HeV fusion (F) proteins share common structural features with the F protein from an emerging henipavirus Langya virus (LayV). Sequence alignment alone was sufficient to predict which known prefusion-stabilizing amino acid substitutions from NiV F would stabilize the prefusion conformations of HeV F and LayV F. This work also reveals an unexpected oligomeric interface shared by prefusion HeV F and NiV F. Together, these advances lay a foundation for future antigen design targeting henipavirus F proteins. In this way, Nipah virus can serve as a prototypical pathogen for the development of protective vaccines and monoclonal antibodies to prepare for potential henipavirus outbreaks. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_27577.map.gz emd_27577.map.gz | 97.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-27577-v30.xml emd-27577-v30.xml emd-27577.xml emd-27577.xml | 17.4 KB 17.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
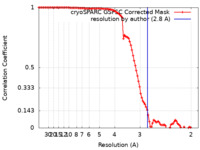
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_27577_fsc.xml emd_27577_fsc.xml | 9.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_27577.png emd_27577.png | 75.6 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_27577_msk_1.map emd_27577_msk_1.map | 103 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-27577.cif.gz emd-27577.cif.gz | 5.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_27577_additional_1.map.gz emd_27577_additional_1.map.gz emd_27577_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27577_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27577_half_map_2.map.gz emd_27577_half_map_2.map.gz | 51.6 MB 95.6 MB 95.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27577 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27577 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27577 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27577 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_27577_validation.pdf.gz emd_27577_validation.pdf.gz | 934 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_27577_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_27577_full_validation.pdf.gz | 933.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_27577_validation.xml.gz emd_27577_validation.xml.gz | 18.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_27577_validation.cif.gz emd_27577_validation.cif.gz | 23.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27577 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27577 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27577 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27577 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8dnrMC  8dngC  8do4C  8u1rC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_27577.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_27577.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Prefusion-stabilized Hendra virus fusion protein | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
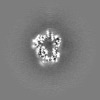
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.94 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
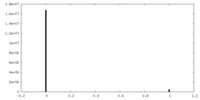
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_27577_msk_1.map emd_27577_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
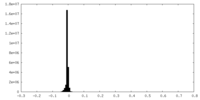
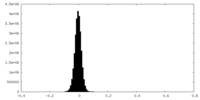
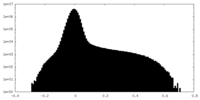
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Additional Map
| File | emd_27577_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Additional Map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
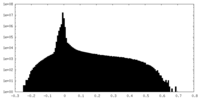
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half Map 1
| File | emd_27577_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half Map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half Map 2
| File | emd_27577_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half Map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Prefusion-stabilized Hendra virus fusion protein
| Entire | Name: Prefusion-stabilized Hendra virus fusion protein |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Prefusion-stabilized Hendra virus fusion protein
| Supramolecule | Name: Prefusion-stabilized Hendra virus fusion protein / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Hendra henipavirus Hendra henipavirus |
-Macromolecule #1: Fusion glycoprotein F0
| Macromolecule | Name: Fusion glycoprotein F0 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Hendra henipavirus / Strain: isolate Horse/Autralia/Hendra/1994 Hendra henipavirus / Strain: isolate Horse/Autralia/Hendra/1994 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 48.721742 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: GILHYEKLSK IGLVKGITRK YKIKSNPLTK DIVIKMIPNV SNVSKCTGTV MENYKSRLTG ILSPIKGAIE LYNNNTHDCV GDVKLAGVC MAGIAIGIAT AAQITAGVAL YEAMKNADNI NKLKSSIEST NEAVVKLQET AEKTVYVFTA LQDYINTNLV P TIDQIPCK ...String: GILHYEKLSK IGLVKGITRK YKIKSNPLTK DIVIKMIPNV SNVSKCTGTV MENYKSRLTG ILSPIKGAIE LYNNNTHDCV GDVKLAGVC MAGIAIGIAT AAQITAGVAL YEAMKNADNI NKLKSSIEST NEAVVKLQET AEKTVYVFTA LQDYINTNLV P TIDQIPCK QTELALDLAL SKYLSDLLFV FGPNLQDPVS NSMTIQAISQ AFGGNYETLL RTLGYATEDF DDLLESDSIA GQ IVYVDLS SYYIIVRVYF PILTEIQQAY VQELLPVSFN NDNSEWISIV PNFVLIRNTL ISNIEVKYCL ITKKSVICNQ DYA TPMTAS VRECLTGSTD KCPRELVVSS HVPRFALSGG VLFANCISVT CQCQTTGRAI SQSGEQTLLM IDNTTCTTVV LGNI IISLG KYLGSINYNS ESIAVGPPVY TDKVDISSQI SSMNQSLQQS K UniProtKB: Fusion glycoprotein F0 |
-Macromolecule #2: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 12 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 44.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller













 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)