[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8dhy: N-terminal fragment of MsbA fused to GFP in complex with copper(II) -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8dhy | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | N-terminal fragment of MsbA fused to GFP in complex with copper(II) | |||||||||
 Components Components | Fusion protein of MsbA N-terminal fragment and GFP,Green fluorescent protein | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | FLUORESCENT PROTEIN / copper binding / MsbA | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMsbA transporter complex / lipopolysaccharide floppase activity / lipid translocation / ABC-type lipid A-core oligosaccharide transporter / lipopolysaccharide transport / ATPase-coupled lipid transmembrane transporter activity / ABC-type xenobiotic transporter activity / lipid transport / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex / bioluminescence ...MsbA transporter complex / lipopolysaccharide floppase activity / lipid translocation / ABC-type lipid A-core oligosaccharide transporter / lipopolysaccharide transport / ATPase-coupled lipid transmembrane transporter activity / ABC-type xenobiotic transporter activity / lipid transport / ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter complex / bioluminescence / generation of precursor metabolites and energy / transmembrane transport / lipid binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.15 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.15 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Schrecke, S.R. / Zhang, T. / Lyu, J. / Laganowsky, A. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Structural basis for lipid and copper regulation of the ABC transporter MsbA. Authors: Jixing Lyu / Chang Liu / Tianqi Zhang / Samantha Schrecke / Nicklaus P Elam / Charles Packianathan / Georg K A Hochberg / David Russell / Minglei Zhao / Arthur Laganowsky /   Abstract: A critical step in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) biogenesis involves flipping lipooligosaccharide, an LPS precursor, from the cytoplasmic to the periplasmic leaflet of the inner membrane, an operation ...A critical step in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) biogenesis involves flipping lipooligosaccharide, an LPS precursor, from the cytoplasmic to the periplasmic leaflet of the inner membrane, an operation carried out by the ATP-binding cassette transporter MsbA. Although LPS binding to the inner cavity of MsbA is well established, the selectivity of MsbA-lipid interactions at other site(s) remains poorly understood. Here we use native mass spectrometry (MS) to characterize MsbA-lipid interactions and guide structural studies. We show the transporter co-purifies with copper(II) and metal binding modulates protein-lipid interactions. A 2.15 Å resolution structure of an N-terminal region of MsbA in complex with copper(II) is presented, revealing a structure reminiscent of the GHK peptide, a high-affinity copper(II) chelator. Our results demonstrate conformation-dependent lipid binding affinities, particularly for the LPS-precursor, 3-deoxy-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid (Kdo)-lipid A (KDL). We report a 3.6 Å-resolution structure of MsbA trapped in an open, outward-facing conformation with adenosine 5'-diphosphate and vanadate, revealing a distinct KDL binding site, wherein the lipid forms extensive interactions with the transporter. Additional studies provide evidence that the exterior KDL binding site is conserved and a positive allosteric modulator of ATPase activity, serving as a feedforward activation mechanism to couple transporter activity with LPS biosynthesis. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8dhy.cif.gz 8dhy.cif.gz | 75.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8dhy.ent.gz pdb8dhy.ent.gz | 44.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8dhy.json.gz 8dhy.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  8dhy_validation.pdf.gz 8dhy_validation.pdf.gz | 969.7 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  8dhy_full_validation.pdf.gz 8dhy_full_validation.pdf.gz | 971.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  8dhy_validation.xml.gz 8dhy_validation.xml.gz | 11.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  8dhy_validation.cif.gz 8dhy_validation.cif.gz | 14.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dh/8dhy https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dh/8dhy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dh/8dhy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/dh/8dhy | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8dmmC  8dmoC  2b3pS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 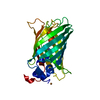
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 27179.508 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Gene: msbA, gfp / Production host:  References: UniProt: P60752, UniProt: A0A059PIQ0, ABC-type lipid A-core oligosaccharide transporter |
|---|---|
| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-CU / |
| #3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 4.95 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 75.15 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 7 / Details: 70% Tacsimate pH 7.0 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS APS  / Beamline: 24-ID-C / Wavelength: 1.3782 Å / Beamline: 24-ID-C / Wavelength: 1.3782 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER2 X 16M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Jun 7, 2022 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1.3782 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.15→70 Å / Num. obs: 56321 / % possible obs: 99.3 % / Redundancy: 6.7 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 52.32 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.997 / Rrim(I) all: 0.094 / Net I/σ(I): 12.35 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.15→2.21 Å / Redundancy: 6.8 % / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 1.61 / Num. unique obs: 4109 / CC1/2: 0.788 / Rrim(I) all: 1.45 / % possible all: 98 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 2B3P Resolution: 2.15→63.08 Å / SU ML: 0.2634 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 27.273 Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 59.36 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.15→63.08 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj