[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8cr1: Homo sapiens Get1/Get2 heterotetramer in complex with a Get3 dimer -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8cr1 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Homo sapiens Get1/Get2 heterotetramer in complex with a Get3 dimer | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / membrane protein insertion / GET pathway / tail anchored membrane protein | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationarsenite transmembrane transporter activity / otic vesicle development / membrane insertase activity / GET complex / tail-anchored membrane protein insertion into ER membrane / receptor recycling / protein insertion into ER membrane / post-translational protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum membrane / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / B cell homeostasis ...arsenite transmembrane transporter activity / otic vesicle development / membrane insertase activity / GET complex / tail-anchored membrane protein insertion into ER membrane / receptor recycling / protein insertion into ER membrane / post-translational protein targeting to endoplasmic reticulum membrane / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / B cell homeostasis / vesicle-mediated transport / protein-membrane adaptor activity / negative regulation of protein ubiquitination / negative regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / establishment of localization in cell / sensory perception of sound / defense response / synapse organization / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway / protein stabilization / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / nucleolus / endoplasmic reticulum / signal transduction / ATP hydrolysis activity / extracellular exosome / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / metal ion binding / nucleus / membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | McDowell, M.A. / Heimes, M. / Wild, K. / Sinning, I. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 2items Germany, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: The GET insertase exhibits conformational plasticity and induces membrane thinning. Authors: Melanie A McDowell / Michael Heimes / Giray Enkavi / Ákos Farkas / Daniel Saar / Klemens Wild / Blanche Schwappach / Ilpo Vattulainen / Irmgard Sinning /   Abstract: The eukaryotic guided entry of tail-anchored proteins (GET) pathway mediates the biogenesis of tail-anchored (TA) membrane proteins at the endoplasmic reticulum. In the cytosol, the Get3 chaperone ...The eukaryotic guided entry of tail-anchored proteins (GET) pathway mediates the biogenesis of tail-anchored (TA) membrane proteins at the endoplasmic reticulum. In the cytosol, the Get3 chaperone captures the TA protein substrate and delivers it to the Get1/Get2 membrane protein complex (GET insertase), which then inserts the substrate via a membrane-embedded hydrophilic groove. Here, we present structures, atomistic simulations and functional data of human and Chaetomium thermophilum Get1/Get2/Get3. The core fold of the GET insertase is conserved throughout eukaryotes, whilst thinning of the lipid bilayer occurs in the vicinity of the hydrophilic groove to presumably lower the energetic barrier of membrane insertion. We show that the gating interaction between Get2 helix α3' and Get3 drives conformational changes in both Get3 and the Get1/Get2 membrane heterotetramer. Thus, we provide a framework to understand the conformational plasticity of the GET insertase and how it remodels its membrane environment to promote substrate insertion. #1:  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2020 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2020Title: Structural Basis of Tail-Anchored Membrane Protein Biogenesis by the GET Insertase Complex. Authors: Melanie A McDowell / Michael Heimes / Francesco Fiorentino / Shahid Mehmood / Ákos Farkas / Javier Coy-Vergara / Di Wu / Jani Reddy Bolla / Volker Schmid / Roger Heinze / Klemens Wild / ...Authors: Melanie A McDowell / Michael Heimes / Francesco Fiorentino / Shahid Mehmood / Ákos Farkas / Javier Coy-Vergara / Di Wu / Jani Reddy Bolla / Volker Schmid / Roger Heinze / Klemens Wild / Dirk Flemming / Stefan Pfeffer / Blanche Schwappach / Carol V Robinson / Irmgard Sinning /   Abstract: Membrane protein biogenesis faces the challenge of chaperoning hydrophobic transmembrane helices for faithful membrane insertion. The guided entry of tail-anchored proteins (GET) pathway targets and ...Membrane protein biogenesis faces the challenge of chaperoning hydrophobic transmembrane helices for faithful membrane insertion. The guided entry of tail-anchored proteins (GET) pathway targets and inserts tail-anchored (TA) proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane with an insertase (yeast Get1/Get2 or mammalian WRB/CAML) that captures the TA from a cytoplasmic chaperone (Get3 or TRC40, respectively). Here, we present cryo-electron microscopy reconstructions, native mass spectrometry, and structure-based mutagenesis of human WRB/CAML/TRC40 and yeast Get1/Get2/Get3 complexes. Get3 binding to the membrane insertase supports heterotetramer formation, and phosphatidylinositol binding at the heterotetramer interface stabilizes the insertase for efficient TA insertion in vivo. We identify a Get2/CAML cytoplasmic helix that forms a "gating" interaction with Get3/TRC40 important for TA insertion. Structural homology with YidC and the ER membrane protein complex (EMC) implicates an evolutionarily conserved insertion mechanism for divergent substrates utilizing a hydrophilic groove. Thus, we provide a detailed structural and mechanistic framework to understand TA membrane insertion. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8cr1.cif.gz 8cr1.cif.gz | 214.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8cr1.ent.gz pdb8cr1.ent.gz | 168.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8cr1.json.gz 8cr1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cr/8cr1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cr/8cr1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cr/8cr1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/cr/8cr1 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  16801MC  8cqzC  8cr2C  8oduC  8odvC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 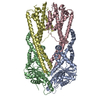
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 40146.070 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ASNA1, ARSA, TRC40 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ASNA1, ARSA, TRC40 / Production host:  References: UniProt: O43681, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides #2: Protein | Mass: 35083.309 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: Truncation of 185 N-terminal residues. Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CAMLG, CAML, GET2, GET1, CHD5, WRB / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CAMLG, CAML, GET2, GET1, CHD5, WRB / Production host:  #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / | Has ligand of interest | N | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.150 MDa / Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1.8 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: Complex stabilised in PMAL-C8 amphipol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER/RHODIUM / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 279 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 12 sec. / Electron dose: 45.6 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 9470 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19_4092: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1561837 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 189844 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj




