[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8ch6: Structure of a late-stage activated spliceosome (BAqr) arrested w... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8ch6 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of a late-stage activated spliceosome (BAqr) arrested with a dominant-negative Aquarius mutant (state B complex). | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SPLICING / activated spliceosome / Aquarius / PRP2 | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpost-spliceosomal complex / RES complex / negative regulation of chemokine-mediated signaling pathway / snoRNA splicing / U11/U12 snRNP / regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / post-mRNA release spliceosomal complex / 3'-5' RNA helicase activity / U2 snRNP binding / U7 snRNA binding ...post-spliceosomal complex / RES complex / negative regulation of chemokine-mediated signaling pathway / snoRNA splicing / U11/U12 snRNP / regulation of retinoic acid receptor signaling pathway / post-mRNA release spliceosomal complex / 3'-5' RNA helicase activity / U2 snRNP binding / U7 snRNA binding / histone pre-mRNA DCP binding / generation of catalytic spliceosome for first transesterification step / U7 snRNP / cis assembly of pre-catalytic spliceosome / histone pre-mRNA 3'end processing complex / regulation of vitamin D receptor signaling pathway / SLBP independent Processing of Histone Pre-mRNAs / SLBP Dependent Processing of Replication-Dependent Histone Pre-mRNAs / spliceosome conformational change to release U4 (or U4atac) and U1 (or U11) / B-WICH complex / nuclear retinoic acid receptor binding / embryonic brain development / oocyte development / alternative mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / U12-type spliceosomal complex / protein methylation / poly(A) binding / 7-methylguanosine cap hypermethylation / U1 snRNP binding / RNA splicing, via transesterification reactions / U2-type catalytic step 1 spliceosome / methylosome / pre-mRNA binding / C2H2 zinc finger domain binding / pICln-Sm protein complex / positive regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / snRNP binding / mRNA 3'-end processing / regulation of mRNA splicing, via spliceosome / sno(s)RNA-containing ribonucleoprotein complex / small nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex / splicing factor binding / Notch binding / SMN-Sm protein complex / spliceosomal tri-snRNP complex / host-mediated activation of viral transcription / mRNA cis splicing, via spliceosome / U2-type precatalytic spliceosome / P granule / positive regulation of vitamin D receptor signaling pathway / commitment complex / telomerase holoenzyme complex / nuclear vitamin D receptor binding / U2-type prespliceosome assembly / U2-type spliceosomal complex / Regulation of gene expression in late stage (branching morphogenesis) pancreatic bud precursor cells / Transport of Mature mRNA derived from an Intron-Containing Transcript / telomerase RNA binding / RUNX3 regulates NOTCH signaling / U2-type catalytic step 2 spliceosome / NOTCH4 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / SAGA complex / U2 snRNP / U1 snRNP / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Termination / U4 snRNP / NOTCH3 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / positive regulation of neurogenesis / U2-type prespliceosome / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III / Basigin interactions / protein peptidyl-prolyl isomerization / K63-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / inner cell mass cell proliferation / ubiquitin-ubiquitin ligase activity / nuclear androgen receptor binding / cyclosporin A binding / precatalytic spliceosome / generation of catalytic spliceosome for second transesterification step / WD40-repeat domain binding / Notch-HLH transcription pathway / lipid biosynthetic process / Formation of paraxial mesoderm / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / pattern recognition receptor activity / SMAD binding / regulation of RNA splicing / spliceosomal complex assembly / mRNA 3'-splice site recognition / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / mRNA Splicing - Minor Pathway / spliceosomal tri-snRNP complex assembly / Prp19 complex / U5 snRNA binding / U5 snRNP / intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / blastocyst development / protein K63-linked ubiquitination / U2 snRNA binding / positive regulation of G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) unidentified adenovirus unidentified adenovirus | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.9 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Cretu, C. / Schmitzova, J. / Pena, V. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1items Germany, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis of catalytic activation in human splicing. Authors: Jana Schmitzová / Constantin Cretu / Christian Dienemann / Henning Urlaub / Vladimir Pena /   Abstract: Pre-mRNA splicing follows a pathway driven by ATP-dependent RNA helicases. A crucial event of the splicing pathway is the catalytic activation, which takes place at the transition between the ...Pre-mRNA splicing follows a pathway driven by ATP-dependent RNA helicases. A crucial event of the splicing pathway is the catalytic activation, which takes place at the transition between the activated B and the branching-competent B spliceosomes. Catalytic activation occurs through an ATP-dependent remodelling mediated by the helicase PRP2 (also known as DHX16). However, because PRP2 is observed only at the periphery of spliceosomes, its function has remained elusive. Here we show that catalytic activation occurs in two ATP-dependent stages driven by two helicases: PRP2 and Aquarius. The role of Aquarius in splicing has been enigmatic. Here the inactivation of Aquarius leads to the stalling of a spliceosome intermediate-the B complex-found halfway through the catalytic activation process. The cryogenic electron microscopy structure of B reveals how PRP2 and Aquarius remodel B and B, respectively. Notably, PRP2 translocates along the intron while it strips away the RES complex, opens the SF3B1 clamp and unfastens the branch helix. Translocation terminates six nucleotides downstream of the branch site through an assembly of PPIL4, SKIP and the amino-terminal domain of PRP2. Finally, Aquarius enables the dissociation of PRP2, plus the SF3A and SF3B complexes, which promotes the relocation of the branch duplex for catalysis. This work elucidates catalytic activation in human splicing, reveals how a DEAH helicase operates and provides a paradigm for how helicases can coordinate their activities. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8ch6.cif.gz 8ch6.cif.gz | 3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8ch6.ent.gz pdb8ch6.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8ch6.json.gz 8ch6.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ch/8ch6 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ch/8ch6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ch/8ch6 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ch/8ch6 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  16658MC 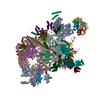 7qttC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
+Small nuclear ribonucleoprotein ... , 6 types, 12 molecules 1i2h3j4l5k9m
+Protein , 18 types, 19 molecules 8nDGLNOPQTXYZabquwy
+Splicing factor 3B subunit ... , 5 types, 5 molecules ABCEF
+Splicing factor 3A subunit ... , 3 types, 3 molecules HIJ
+Pre-mRNA-processing factor ... , 2 types, 5 molecules KMRvx
+Pre-mRNA-splicing factor ... , 5 types, 5 molecules SUWtz
+Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase-like ... , 2 types, 2 molecules Vp
+U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules co
+RNA chain , 4 types, 4 molecules defg
+U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules rs
+Non-polymers , 4 types, 21 molecules 





+Details
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Late human activated spliceosome arrested with a dominant-negative mutant of the splicing helicase Aquarius (Aquarius K829A) Type: COMPLEX Details: The spliceosome complex was assembled in vitro in the HeLa nuclear extract on a model pre-mRNA substrate (MINX) tagged with three MS2 aptamer sequences for affinity purification. Entity ID: #1-#49 / Source: NATURAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.9 Details: All solutions were sterile-filtered using a 0.22um vacuum filtration unit. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.6 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: The Baqr spliceosome was purified by affinity selection and gradient ultracentrifugation and crosslinked with 0.1% (v/v) glutaraldehyde in batch for cryo-EM grid preparation. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid type: UltrAuFoil R2/2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K Details: Volumes of 4 ul of the concentrated sample were applied to one side of glow-discharged UltrAuFoil 200 2/2 grids (Quantifoil) in a Vitrobot Mark IV (FEI), operated at 4 degrees Celsius and ...Details: Volumes of 4 ul of the concentrated sample were applied to one side of glow-discharged UltrAuFoil 200 2/2 grids (Quantifoil) in a Vitrobot Mark IV (FEI), operated at 4 degrees Celsius and 100% humidity. The grids were blotted for 2s with blotting force 5 and immediately frozen by plunging into liquid ethane. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 9 sec. / Electron dose: 45.47 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 10013 Details: Automated data acquisition for dataset 1 (untilted, 5229 micrographs) and dataset 2 (tilted, 25 degrees, 4784 micrographs) was performed with FEI EPU software package at a nominal ...Details: Automated data acquisition for dataset 1 (untilted, 5229 micrographs) and dataset 2 (tilted, 25 degrees, 4784 micrographs) was performed with FEI EPU software package at a nominal magnification of 130,000 (1.05 A per pixel). Micrographs for these two datasets, dose fractionated over 40 frames, were collected at a dose rate of 5.04 or 5.06 e/A2/s-1 over 9 s, resulting in a total dose of 45.38 and 45.55 e/A2, respectively. |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum LS / Energyfilter slit width: 30 eV |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 734691 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 5.9 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 12395 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj