[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
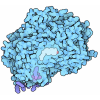
Yorodumi- PDB-8c60: Cryo-EM structure of the human SIN3B full-length complex at 3.4 A... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8c60 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human SIN3B full-length complex at 3.4 Angstrom resolution | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / Chromatin / Histone deacetylase / HDAC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationautosome / positive regulation of male mating behavior / protein de-2-hydroxyisobutyrylase activity / protein lysine delactylase activity / negative regulation of dendritic spine development / p75NTR negatively regulates cell cycle via SC1 / epidermal cell differentiation / histone decrotonylase activity / fungiform papilla formation / NuRD complex ...autosome / positive regulation of male mating behavior / protein de-2-hydroxyisobutyrylase activity / protein lysine delactylase activity / negative regulation of dendritic spine development / p75NTR negatively regulates cell cycle via SC1 / epidermal cell differentiation / histone decrotonylase activity / fungiform papilla formation / NuRD complex / regulation of cell fate specification / behavioral response to ethanol / positive regulation of interleukin-1 production / negative regulation of transcription by competitive promoter binding / EGR2 and SOX10-mediated initiation of Schwann cell myelination / negative regulation of stem cell population maintenance / histone deacetylase activity, hydrolytic mechanism / ESC/E(Z) complex / histone deacetylase / regulation of stem cell differentiation / cellular response to dopamine / cardiac muscle hypertrophy / STAT3 nuclear events downstream of ALK signaling / XY body / regulation of double-strand break repair / protein lysine deacetylase activity / Hydrolases; Acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds, other than peptide bonds; In linear amides / response to caffeine / histone deacetylase activity / embryonic digit morphogenesis / positive regulation of intracellular estrogen receptor signaling pathway / Notch-HLH transcription pathway / Y chromosome / X chromosome / histone deacetylase complex / eyelid development in camera-type eye / odontogenesis of dentin-containing tooth / Sin3-type complex / positive regulation of stem cell population maintenance / NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex / dendrite development / response to amyloid-beta / positive regulation of oligodendrocyte differentiation / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / positive regulation of proteolysis / progesterone receptor signaling pathway / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / response to hyperoxia / hair follicle placode formation / NF-kappaB binding / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition / cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus / Transcriptional regulation of brown and beige adipocyte differentiation by EBF2 / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / MECP2 regulates neuronal receptors and channels / Regulation of TP53 Activity through Acetylation / cellular response to retinoic acid / heat shock protein binding / Regulation of lipid metabolism by PPARalpha / transcription repressor complex / phosphatidylinositol binding / negative regulation of cell migration / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of PTEN gene transcription / transcription corepressor binding / response to amphetamine / transcription coregulator binding / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / response to nicotine / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / response to cocaine / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / circadian regulation of gene expression / HDACs deacetylate histones / promoter-specific chromatin binding / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / Cytoprotection by HMOX1 / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / NOTCH1 Intracellular Domain Regulates Transcription / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 PEST Domain Mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD+PEST Domain Mutants / histone deacetylase binding / cellular response to hydrogen peroxide / positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / transcription corepressor activity / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / negative regulation of neuron projection development / cellular response to heat / HATs acetylate histones / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / chromatin organization / fibroblast proliferation / regulation of apoptotic process / histone binding / response to lipopolysaccharide Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Alfieri, C. / Wan, S.M. / Muhammad, R. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Mechanism of assembly, activation and lysine selection by the SIN3B histone deacetylase complex. Authors: Mandy S M Wan / Reyhan Muhammad / Marios G Koliopoulos / Theodoros I Roumeliotis / Jyoti S Choudhary / Claudio Alfieri /  Abstract: Lysine acetylation in histone tails is a key post-translational modification that controls transcription activation. Histone deacetylase complexes remove histone acetylation, thereby repressing ...Lysine acetylation in histone tails is a key post-translational modification that controls transcription activation. Histone deacetylase complexes remove histone acetylation, thereby repressing transcription and regulating the transcriptional output of each gene. Although these complexes are drug targets and crucial regulators of organismal physiology, their structure and mechanisms of action are largely unclear. Here, we present the structure of a complete human SIN3B histone deacetylase holo-complex with and without a substrate mimic. Remarkably, SIN3B encircles the deacetylase and contacts its allosteric basic patch thereby stimulating catalysis. A SIN3B loop inserts into the catalytic tunnel, rearranges to accommodate the acetyl-lysine moiety, and stabilises the substrate for specific deacetylation, which is guided by a substrate receptor subunit. Our findings provide a model of specificity for a main transcriptional regulator conserved from yeast to human and a resource of protein-protein interactions for future drug designs. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8c60.cif.gz 8c60.cif.gz | 305.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8c60.ent.gz pdb8c60.ent.gz | 220.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8c60.json.gz 8c60.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c6/8c60 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c6/8c60 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c6/8c60 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c6/8c60 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  16449MC 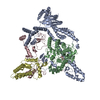 8bpaC  8bpbC  8bpcC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 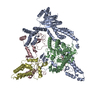
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 4 types, 4 molecules ABCD
| #1: Protein | Mass: 129547.133 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SIN3B, KIAA0700 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SIN3B, KIAA0700 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: O75182 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: O75182 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 55443.156 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HDAC2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HDAC2 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)References: UniProt: Q92769, histone deacetylase, Hydrolases; Acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds, other than peptide bonds; In linear amides |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 109841.586 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PHF12, KIAA1523 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: PHF12, KIAA1523 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96QT6 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q96QT6 |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 41540.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MORF4L1, MRG15, FWP006, HSPC008, HSPC061, PP368 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MORF4L1, MRG15, FWP006, HSPC008, HSPC061, PP368 / Production host:  Trichoplusia (butterflies/moths) / References: UniProt: Q9UBU8 Trichoplusia (butterflies/moths) / References: UniProt: Q9UBU8 |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 7 molecules 


| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #6: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Human SIN3B complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.385 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: TFS GLACIOS |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1600 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20.1_4487: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 38352 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj