[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
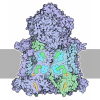
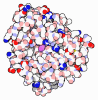
Yorodumi- PDB-8a5e: Cryo-EM structure of the electron bifurcating Fe-Fe hydrogenase H... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8a5e | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the electron bifurcating Fe-Fe hydrogenase HydABC complex from Acetobacterium woodii in the reduced state | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | (Iron hydrogenase ...) x 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ELECTRON TRANSPORT / flavin-based electron bifurcating hydrogenase / Fe-Fe hydrogenase / NAD / FMN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationferredoxin hydrogenase / ferredoxin hydrogenase activity / NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) activity / ATP synthesis coupled electron transport / 2 iron, 2 sulfur cluster binding / FMN binding / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / iron ion binding / metal ion binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Acetobacterium woodii DSM 1030 (bacteria) Acetobacterium woodii DSM 1030 (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kumar, A. / Saura, P. / Gamiz-Hernandez, A.P. / Kaila, V.R.I. / Mueller, V. / Schuller, J.M. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, European Union, Germany, European Union,  Sweden, 6items Sweden, 6items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Am Chem Soc / Year: 2023 Journal: J Am Chem Soc / Year: 2023Title: Molecular Basis of the Electron Bifurcation Mechanism in the [FeFe]-Hydrogenase Complex HydABC. Authors: Alexander Katsyv / Anuj Kumar / Patricia Saura / Maximilian C Pöverlein / Sven A Freibert / Sven T Stripp / Surbhi Jain / Ana P Gamiz-Hernandez / Ville R I Kaila / Volker Müller / Jan M Schuller /   Abstract: Electron bifurcation is a fundamental energy coupling mechanism widespread in microorganisms that thrive under anoxic conditions. These organisms employ hydrogen to reduce CO, but the molecular ...Electron bifurcation is a fundamental energy coupling mechanism widespread in microorganisms that thrive under anoxic conditions. These organisms employ hydrogen to reduce CO, but the molecular mechanisms have remained enigmatic. The key enzyme responsible for powering these thermodynamically challenging reactions is the electron-bifurcating [FeFe]-hydrogenase HydABC that reduces low-potential ferredoxins (Fd) by oxidizing hydrogen gas (H). By combining single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryoEM) under catalytic turnover conditions with site-directed mutagenesis experiments, functional studies, infrared spectroscopy, and molecular simulations, we show that HydABC from the acetogenic bacteria and employ a single flavin mononucleotide (FMN) cofactor to establish electron transfer pathways to the NAD(P) and Fd reduction sites by a mechanism that is fundamentally different from classical flavin-based electron bifurcation enzymes. By modulation of the NAD(P) binding affinity via reduction of a nearby iron-sulfur cluster, HydABC switches between the exergonic NAD(P) reduction and endergonic Fd reduction modes. Our combined findings suggest that the conformational dynamics establish a redox-driven kinetic gate that prevents the backflow of the electrons from the Fd reduction branch toward the FMN site, providing a basis for understanding general mechanistic principles of electron-bifurcating hydrogenases. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8a5e.cif.gz 8a5e.cif.gz | 319.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8a5e.ent.gz pdb8a5e.ent.gz | 252.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8a5e.json.gz 8a5e.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a5/8a5e https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a5/8a5e ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a5/8a5e ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a5/8a5e | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  15166MC  7q4vC  7q4wC  8a6tC  8bewC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Iron hydrogenase ... , 3 types, 4 molecules ADBC
| #1: Protein | Mass: 63692.887 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Acetobacterium woodii DSM 1030 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: H6LFG3, ferredoxin hydrogenase Acetobacterium woodii DSM 1030 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: H6LFG3, ferredoxin hydrogenase#2: Protein | | Mass: 64525.965 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Acetobacterium woodii DSM 1030 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: H6LFG4, ferredoxin hydrogenase Acetobacterium woodii DSM 1030 (bacteria) / References: UniProt: H6LFG4, ferredoxin hydrogenase#3: Protein | | Mass: 16999.689 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Acetobacterium woodii DSM 1030 (bacteria) / References: ferredoxin hydrogenase Acetobacterium woodii DSM 1030 (bacteria) / References: ferredoxin hydrogenase |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 6 types, 19 molecules 






| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-SF4 / #5: Chemical | #6: Chemical | #7: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / | #8: Chemical | ChemComp-FMN / | #9: Chemical | ChemComp-NAI / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Electron bifurcating Fe-Fe hydrogenase HydABC complex from Thermoanaerobacter kivui Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.348 MDa / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:   Thermoanaerobacter kivui (bacteria) Thermoanaerobacter kivui (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: JEOL CRYO ARM 200 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 172189 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj