+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8a43 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human RNA polymerase I | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION / RNA polymerase I / human rDNA transcription | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationRNA polymerase I transcription regulator complex / negative regulation of protein localization to nucleolus / nucleologenesis / neural crest formation / RNA Polymerase III Chain Elongation / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Termination / DNA/RNA hybrid binding / RNA polymerase I general transcription initiation factor binding / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / RPAP3/R2TP/prefoldin-like complex ...RNA polymerase I transcription regulator complex / negative regulation of protein localization to nucleolus / nucleologenesis / neural crest formation / RNA Polymerase III Chain Elongation / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Termination / DNA/RNA hybrid binding / RNA polymerase I general transcription initiation factor binding / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I / RPAP3/R2TP/prefoldin-like complex / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 1 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 2 Promoter / RNA Polymerase III Transcription Initiation From Type 3 Promoter / Cytosolic sensors of pathogen-associated DNA / RNA polymerase I preinitiation complex assembly / RNA Polymerase III Abortive And Retractive Initiation / nucleobase-containing compound metabolic process / Abortive elongation of HIV-1 transcript in the absence of Tat / FGFR2 alternative splicing / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Termination / MicroRNA (miRNA) biogenesis / Viral Messenger RNA Synthesis / Signaling by FGFR2 IIIa TM / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE during HIV infection / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / Formation of the HIV-1 Early Elongation Complex / mRNA Capping / HIV Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II HIV Promoter Escape / Transcription of the HIV genome / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / termination of RNA polymerase I transcription / nucleolar large rRNA transcription by RNA polymerase I / mRNA Splicing - Minor Pathway / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase I promoter / PIWI-interacting RNA (piRNA) biogenesis / rRNA transcription / RNA Polymerase I Transcription Initiation / Pausing and recovery of Tat-mediated HIV elongation / Tat-mediated HIV elongation arrest and recovery / Processing of Capped Intron-Containing Pre-mRNA / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / HIV elongation arrest and recovery / Pausing and recovery of HIV elongation / Tat-mediated elongation of the HIV-1 transcript / Formation of HIV-1 elongation complex containing HIV-1 Tat / transcription by RNA polymerase III / transcription by RNA polymerase I / RNA polymerase I complex / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase I / Formation of HIV elongation complex in the absence of HIV Tat / RNA polymerase III complex / RNA polymerase II, core complex / tRNA transcription by RNA polymerase III / : / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Elongation / Formation of RNA Pol II elongation complex / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / embryo implantation / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / mRNA Splicing - Major Pathway / cell surface receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / protein-DNA complex / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / Transcription-Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair (TC-NER) / ribonucleoside binding / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / : / : / : / : / : / : / fibrillar center / DNA-directed RNA polymerase / Dual incision in TC-NER / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / single-stranded DNA binding / chromosome / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / transcription by RNA polymerase II / nucleic acid binding / protein dimerization activity / protein stabilization / chromatin binding / nucleolus / magnesium ion binding / mitochondrion / DNA binding / RNA binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.09 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Daiss, J.L. / Pilsl, M. / Straub, K. / Bleckmann, A. / Hoecherl, M. / Heiss, F.B. / Abascal-Palacios, G. / Ramsay, E. / Tluckova, K. / Mars, J.C. ...Daiss, J.L. / Pilsl, M. / Straub, K. / Bleckmann, A. / Hoecherl, M. / Heiss, F.B. / Abascal-Palacios, G. / Ramsay, E. / Tluckova, K. / Mars, J.C. / Fuertges, T. / Bruckmann, A. / Rudack, T. / Bernecky, C. / Lamour, V. / Panov, K. / Vannini, A. / Moss, T. / Engel, C. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 2items Germany, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Life Sci Alliance / Year: 2022 Journal: Life Sci Alliance / Year: 2022Title: The human RNA polymerase I structure reveals an HMG-like docking domain specific to metazoans. Authors: Julia L Daiß / Michael Pilsl / Kristina Straub / Andrea Bleckmann / Mona Höcherl / Florian B Heiss / Guillermo Abascal-Palacios / Ewan P Ramsay / Katarina Tlučková / Jean-Clement Mars / ...Authors: Julia L Daiß / Michael Pilsl / Kristina Straub / Andrea Bleckmann / Mona Höcherl / Florian B Heiss / Guillermo Abascal-Palacios / Ewan P Ramsay / Katarina Tlučková / Jean-Clement Mars / Torben Fürtges / Astrid Bruckmann / Till Rudack / Carrie Bernecky / Valérie Lamour / Konstantin Panov / Alessandro Vannini / Tom Moss / Christoph Engel /        Abstract: Transcription of the ribosomal RNA precursor by RNA polymerase (Pol) I is a major determinant of cellular growth, and dysregulation is observed in many cancer types. Here, we present the purification ...Transcription of the ribosomal RNA precursor by RNA polymerase (Pol) I is a major determinant of cellular growth, and dysregulation is observed in many cancer types. Here, we present the purification of human Pol I from cells carrying a genomic GFP fusion on the largest subunit allowing the structural and functional analysis of the enzyme across species. In contrast to yeast, human Pol I carries a single-subunit stalk, and in vitro transcription indicates a reduced proofreading activity. Determination of the human Pol I cryo-EM reconstruction in a close-to-native state rationalizes the effects of disease-associated mutations and uncovers an additional domain that is built into the sequence of Pol I subunit RPA1. This "dock II" domain resembles a truncated HMG box incapable of DNA binding which may serve as a downstream transcription factor-binding platform in metazoans. Biochemical analysis, in situ modelling, and ChIP data indicate that Topoisomerase 2a can be recruited to Pol I via the domain and cooperates with the HMG box domain-containing factor UBF. These adaptations of the metazoan Pol I transcription system may allow efficient release of positive DNA supercoils accumulating downstream of the transcription bubble. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8a43.cif.gz 8a43.cif.gz | 731.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8a43.ent.gz pdb8a43.ent.gz | 566.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8a43.json.gz 8a43.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a4/8a43 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a4/8a43 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a4/8a43 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/a4/8a43 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  15135MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 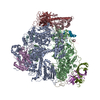
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA-directed RNA polymerase I subunit ... , 5 types, 5 molecules ABINM
| #1: Protein | Mass: 195069.047 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1A / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1A / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O95602, DNA-directed RNA polymerase Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O95602, DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 128379.219 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1B / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1B / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9H9Y6, DNA-directed RNA polymerase Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9H9Y6, DNA-directed RNA polymerase |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 13917.695 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1H, RPA12, ZNRD1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1H, RPA12, ZNRD1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9P1U0 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9P1U0 |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 47330.234 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1E, PAF53, PRAF1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1E, PAF53, PRAF1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9GZS1 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q9GZS1 |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 55065.523 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1G, ASE1, CAST, CD3EAP, PAF49 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1G, ASE1, CAST, CD3EAP, PAF49 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15446 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15446 |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerases I and III subunit ... , 2 types, 2 molecules CK
| #3: Protein | Mass: 39301.672 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1C, POLR1E / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1C, POLR1E / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15160 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: O15160 |
|---|---|
| #9: Protein | Mass: 15259.222 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1D / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR1D / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DPB6 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DPB6 |
-DNA-directed RNA polymerases I, II, and III subunit ... , 5 types, 5 molecules EFHJL
| #4: Protein | Mass: 24584.223 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2E / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2E / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P19388 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P19388 |
|---|---|
| #5: Protein | Mass: 14491.026 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2F, POLRF / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2F, POLRF / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P61218 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P61218 |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 17162.273 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2H / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2H / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P52434 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P52434 |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 7655.123 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2L / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2L / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62875 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62875 |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 7018.244 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2K / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: POLR2K / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P53803 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P53803 |
-Details
| Has protein modification | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: RNA polymerase I / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: JEOL CRYO ARM 200 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2700 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1200 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.09 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 108012 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 86.68 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj
















