+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7y5a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the Mycolicibacterium smegmatis F1-ATPase | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / Complex / F-ATP synthase / cryo-EM / mycobacteria | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Wong, C.F. / Saw, W.-G. / Grueber, G. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Singapore, 1items Singapore, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Antimicrob Agents Chemother / Year: 2022 Journal: Antimicrob Agents Chemother / Year: 2022Title: Structural Elements Involved in ATP Hydrolysis Inhibition and ATP Synthesis of Tuberculosis and Nontuberculous Mycobacterial F-ATP Synthase Decipher New Targets for Inhibitors. Authors: Chui Fann Wong / Wuan-Geok Saw / Sandip Basak / Mio Sano / Hiroshi Ueno / Hwee Wen Kerk / Dennis Litty / Priya Ragunathan / Thomas Dick / Volker Müller / Hiroyuki Noji / Gerhard Grüber /     Abstract: The FF-ATP synthase is required for the viability of tuberculosis (TB) and nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) and has been validated as a drug target. Here, we present the cryo-EM structures of the ...The FF-ATP synthase is required for the viability of tuberculosis (TB) and nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) and has been validated as a drug target. Here, we present the cryo-EM structures of the Mycobacterium smegmatis F-ATPase and the FF-ATP synthase with different nucleotide occupation within the catalytic sites and visualize critical elements for latent ATP hydrolysis and efficient ATP synthesis. Mutational studies reveal that the extended C-terminal domain (αCTD) of subunit α is the main element for the self-inhibition mechanism of ATP hydrolysis for TB and NTM bacteria. Rotational studies indicate that the transition between the inhibition state by the αCTD and the active state is a rapid process. We demonstrate that the unique mycobacterial γ-loop and subunit δ are critical elements required for ATP formation. The data underline that these mycobacterium-specific elements of α, γ, and δ are attractive targets, providing a platform for the discovery of species-specific inhibitors. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7y5a.cif.gz 7y5a.cif.gz | 526.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7y5a.ent.gz pdb7y5a.ent.gz | 432.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7y5a.json.gz 7y5a.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y5/7y5a https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y5/7y5a ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y5/7y5a ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y5/7y5a | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  33614MC 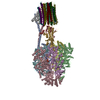 7y5bC 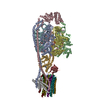 7y5cC 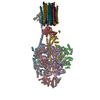 7y5dC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 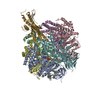
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ATP synthase subunit ... , 2 types, 6 molecules ABCDEF
| #1: Protein | Mass: 58951.461 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / Gene: atpA, MSMEG_4938, MSMEI_4811 / Plasmid: pYUB1049 / Production host: Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / Gene: atpA, MSMEG_4938, MSMEI_4811 / Plasmid: pYUB1049 / Production host:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain (production host): mc(2)4517 Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain (production host): mc(2)4517References: UniProt: A0R202, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #2: Protein | Mass: 52499.332 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / Gene: atpD, MSMEG_4936, MSMEI_4809 / Plasmid: pYUB1049 / Production host: Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / Gene: atpD, MSMEG_4936, MSMEI_4809 / Plasmid: pYUB1049 / Production host:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain (production host): mc(2)4517 Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain (production host): mc(2)4517References: UniProt: A0R200, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase |
|---|
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules G
| #3: Protein | Mass: 33439.836 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / Gene: atpG, MSMEG_4937, MSMEI_4810 / Plasmid: pYUB1049 / Production host: Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: ATCC 700084 / mc(2)155 / Gene: atpG, MSMEG_4937, MSMEI_4810 / Plasmid: pYUB1049 / Production host:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain (production host): mc(2)4517 / References: UniProt: A0R201 Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain (production host): mc(2)4517 / References: UniProt: A0R201 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 10 molecules 




| #4: Chemical | | #5: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #6: Chemical | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: F1-ATPase / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: RECOMBINANT | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.38 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: mc(2)155 Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: mc(2)155 | |||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: mc(2)4517 / Plasmid: pYUB1049 Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / Strain: mc(2)4517 / Plasmid: pYUB1049 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | |||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 6 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277.15 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / Alignment procedure: BASIC |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 2318 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 972956 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 119732 / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj





