[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7y1k: Structure of SUR2A in complex with Mg-ATP, Mg-ADP and repaglinide... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7y1k | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of SUR2A in complex with Mg-ATP, Mg-ADP and repaglinide in the inward-facing conformation | ||||||||||||
 Components Components | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 9 | ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / SUR2A / ABC transporter / repaglinide | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationvascular process in circulatory system / substrate-dependent cell migration, cell contraction / reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / oxygen metabolic process / ATP sensitive Potassium channels / response to decreased oxygen levels / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / response to peptide / potassium channel activator activity / inward rectifying potassium channel ...vascular process in circulatory system / substrate-dependent cell migration, cell contraction / reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / oxygen metabolic process / ATP sensitive Potassium channels / response to decreased oxygen levels / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / response to peptide / potassium channel activator activity / inward rectifying potassium channel / sulfonylurea receptor activity / response to potassium ion / cardiac conduction / response to oxygen levels / response to hydrogen sulfide / ATPase-coupled monoatomic cation transmembrane transporter activity / cellular respiration / coronary vasculature development / cellular response to chemical stress / cardiac muscle cell contraction / regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / cellular response to potassium ion / heterocyclic compound binding / circulatory system development / syntaxin binding / : / blood circulation / Ion homeostasis / blood vessel development / response to ATP / cellular response to ATP / fatty acid oxidation / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / response to stress / action potential / ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity / potassium channel regulator activity / potassium channel activity / ABC-type transporter activity / heart morphogenesis / skeletal muscle tissue development / ATP metabolic process / negative regulation of blood pressure / potassium ion transmembrane transport / T-tubule / acrosomal vesicle / cellular response to calcium ion / blood vessel diameter maintenance / sarcomere / response to activity / regulation of membrane potential / mitochondrion organization / response to hydrogen peroxide / sarcolemma / potassium ion transport / transmembrane transport / response to estrogen / regulation of blood pressure / vasodilation / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / MAPK cascade / heart development / fibroblast proliferation / gene expression / defense response to virus / transmembrane transporter binding / response to hypoxia / response to xenobiotic stimulus / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of apoptotic process / protein-containing complex binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / protein-containing complex / mitochondrion / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chen, L. / Ding, D. / Hou, T. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 3items China, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: The inhibition mechanism of the SUR2A-containing K channel by a regulatory helix. Authors: Dian Ding / Tianyi Hou / Miao Wei / Jing-Xiang Wu / Lei Chen /  Abstract: K channels are metabolic sensors for intracellular ATP/ADP ratios, play essential roles in many physiological processes, and are implicated in a spectrum of pathological conditions. SUR2A-containing ...K channels are metabolic sensors for intracellular ATP/ADP ratios, play essential roles in many physiological processes, and are implicated in a spectrum of pathological conditions. SUR2A-containing K channels differ from other subtypes in their sensitivity to Mg-ADP activation. However, the underlying structural mechanism remains poorly understood. Here we present a series of cryo-EM structures of SUR2A in the presence of different combinations of Mg-nucleotides and the allosteric inhibitor repaglinide. These structures uncover regulatory helix (R helix) on the NBD1-TMD2 linker, which wedges between NBD1 and NBD2. R helix stabilizes SUR2A in the NBD-separated conformation to inhibit channel activation. The competitive binding of Mg-ADP with Mg-ATP to NBD2 mobilizes the R helix to relieve such inhibition, allowing channel activation. The structures of SUR2B in similar conditions suggest that the C-terminal 42 residues of SUR2B enhance the structural dynamics of NBD2 and facilitate the dissociation of the R helix and the binding of Mg-ADP to NBD2, promoting NBD dimerization and subsequent channel activation. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7y1k.cif.gz 7y1k.cif.gz | 215.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7y1k.ent.gz pdb7y1k.ent.gz | 160.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7y1k.json.gz 7y1k.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y1/7y1k https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y1/7y1k ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y1/7y1k ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/y1/7y1k | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  33564MC  7y1jC  7y1lC  7y1mC  7y1nC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 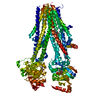
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 174300.422 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q63563 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q63563 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
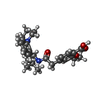
| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-ATP / | ||||||
| #3: Chemical | | #4: Chemical | ChemComp-BJX / | #5: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / | Has ligand of interest | Y | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 9, isoform A / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 174 kDa/nm / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1800 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 52 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: cryoSPARC / Version: 3.1.0 / Category: 3D reconstruction |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 61007 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj