[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7xqb: Structure of connexin43/Cx43/GJA1 gap junction intercellular chan... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7xqb | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of connexin43/Cx43/GJA1 gap junction intercellular channel in POPE/CHS nanodiscs at pH ~8.0 | ||||||
 Components Components | Gap junction alpha-1 protein | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Cx43 / Connexin / Gap junction channel / Gating mechanism | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationgap junction channel activity involved in cardiac conduction electrical coupling / negative regulation of gonadotropin secretion / microtubule-based transport / positive regulation of morphogenesis of an epithelium / positive regulation of mesodermal cell differentiation / cell communication by electrical coupling / negative regulation of trophoblast cell migration / SARS-CoV-2 targets PDZ proteins in cell-cell junction / gap junction channel activity involved in cell communication by electrical coupling / monoatomic ion transmembrane transporter activity ...gap junction channel activity involved in cardiac conduction electrical coupling / negative regulation of gonadotropin secretion / microtubule-based transport / positive regulation of morphogenesis of an epithelium / positive regulation of mesodermal cell differentiation / cell communication by electrical coupling / negative regulation of trophoblast cell migration / SARS-CoV-2 targets PDZ proteins in cell-cell junction / gap junction channel activity involved in cell communication by electrical coupling / monoatomic ion transmembrane transporter activity / gap junction hemi-channel activity / Oligomerization of connexins into connexons / Transport of connexins along the secretory pathway / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / gap junction assembly / Regulation of gap junction activity / atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / glutathione transmembrane transporter activity / cardiac conduction system development / cell-cell contact zone / cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Golgi-associated vesicle membrane / connexin complex / Formation of annular gap junctions / Gap junction degradation / gap junction / bone remodeling / Gap junction assembly / export across plasma membrane / gap junction channel activity / glutamate secretion / tight junction / Mechanical load activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in osteocytes / positive regulation of stem cell proliferation / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / RHOJ GTPase cycle / RHOQ GTPase cycle / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / intercalated disc / efflux transmembrane transporter activity / xenobiotic transport / alpha-tubulin binding / positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation / tubulin binding / negative regulation of cell growth / beta-catenin binding / bone development / cellular response to amyloid-beta / intracellular protein localization / cell junction / cell-cell signaling / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / heart development / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / spermatogenesis / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / apical plasma membrane / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / membrane raft / Golgi membrane / focal adhesion / positive regulation of gene expression / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / Golgi apparatus / signal transduction / mitochondrion / nucleoplasm / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Lee, H.J. / Cha, H.J. / Jeong, H. / Lee, S.N. / Lee, C.W. / Woo, J.S. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Korea, Republic Of, 1items Korea, Republic Of, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Conformational changes in the human Cx43/GJA1 gap junction channel visualized using cryo-EM. Authors: Hyuk-Joon Lee / Hyung Jin Cha / Hyeongseop Jeong / Seu-Na Lee / Chang-Won Lee / Minsoo Kim / Jejoong Yoo / Jae-Sung Woo /  Abstract: Connexin family proteins assemble into hexameric hemichannels in the cell membrane. The hemichannels dock together between two adjacent membranes to form gap junction intercellular channels (GJIChs). ...Connexin family proteins assemble into hexameric hemichannels in the cell membrane. The hemichannels dock together between two adjacent membranes to form gap junction intercellular channels (GJIChs). We report the cryo-electron microscopy structures of Cx43 GJICh, revealing the dynamic equilibrium state of various channel conformations in detergents and lipid nanodiscs. We identify three different N-terminal helix conformations of Cx43-gate-covering (GCN), pore-lining (PLN), and flexible intermediate (FIN)-that are randomly distributed in purified GJICh particles. The conformational equilibrium shifts to GCN by cholesteryl hemisuccinates and to PLN by C-terminal truncations and at varying pH. While GJIChs that mainly comprise GCN protomers are occluded by lipids, those containing conformationally heterogeneous protomers show markedly different pore sizes. We observe an α-to-π-helix transition in the first transmembrane helix, which creates a side opening to the membrane in the FIN and PLN conformations. This study provides basic structural information to understand the mechanisms of action and regulation of Cx43 GJICh. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7xqb.cif.gz 7xqb.cif.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7xqb.ent.gz pdb7xqb.ent.gz | 994 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7xqb.json.gz 7xqb.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xq/7xqb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xq/7xqb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xq/7xqb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xq/7xqb | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  33392MC  7f92C  7f93C  7f94C  7xq9C  7xqdC  7xqfC  7xqgC  7xqhC  7xqiC  7xqjC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 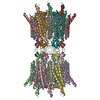
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 43061.336 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GJA1, GJAL / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GJA1, GJAL / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P17302 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P17302#2: Chemical | ChemComp-C14 / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-Y01 / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-PTY / Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Dodecameric complex of human Cx43/GJA1 in lipid nanodiscs (POPE/CHS) Type: COMPLEX Details: Human Cx43 gap junction channel with gate-covering NTH conformation Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2750 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1250 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 40 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 21621 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 PDBj
PDBj