+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7xhn | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of human inner kinetochore CCAN-DNA complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL CYCLE | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationFANCM-MHF complex / Mis6-Sim4 complex / positive regulation of protein localization to kinetochore / : / kinetochore organization / Fanconi anaemia nuclear complex / spindle attachment to meiosis I kinetochore / metaphase chromosome alignment / kinetochore binding / CENP-A containing chromatin assembly ...FANCM-MHF complex / Mis6-Sim4 complex / positive regulation of protein localization to kinetochore / : / kinetochore organization / Fanconi anaemia nuclear complex / spindle attachment to meiosis I kinetochore / metaphase chromosome alignment / kinetochore binding / CENP-A containing chromatin assembly / sex differentiation / centromeric DNA binding / resolution of meiotic recombination intermediates / chordate embryonic development / negative regulation of epithelial cell apoptotic process / kinetochore assembly / attachment of mitotic spindle microtubules to kinetochore / condensed chromosome, centromeric region / inner kinetochore / replication fork processing / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / chromosome, centromeric region / chromosome organization / interstrand cross-link repair / pericentric heterochromatin / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / positive regulation of protein ubiquitination / positive regulation of epithelial cell proliferation / mitotic spindle organization / chromosome segregation / Fanconi Anemia Pathway / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / PKR-mediated signaling / kinetochore / centriolar satellite / nuclear matrix / Separation of Sister Chromatids / mitotic cell cycle / actin cytoskeleton / chromosome / midbody / cell adhesion / nuclear body / protein heterodimerization activity / cell division / DNA repair / apoptotic process / DNA damage response / chromatin binding / regulation of DNA-templated transcription / chromatin / nucleolus / signal transduction / DNA binding / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus / membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.71 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Sun, L.F. / Tian, T. / Wang, C.L. / Yang, Z.S. / Zang, J.Y. | ||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Discov / Year: 2022 Journal: Cell Discov / Year: 2022Title: Structural insights into human CCAN complex assembled onto DNA. Authors: Tian Tian / Lili Chen / Zhen Dou / Zhisen Yang / Xinjiao Gao / Xiao Yuan / Chengliang Wang / Ran Liu / Zuojun Shen / Ping Gui / Maikun Teng / Xianlei Meng / Donald L Hill / Lin Li / Xuan ...Authors: Tian Tian / Lili Chen / Zhen Dou / Zhisen Yang / Xinjiao Gao / Xiao Yuan / Chengliang Wang / Ran Liu / Zuojun Shen / Ping Gui / Maikun Teng / Xianlei Meng / Donald L Hill / Lin Li / Xuan Zhang / Xing Liu / Linfeng Sun / Jianye Zang / Xuebiao Yao /   Abstract: In mitosis, accurate chromosome segregation depends on kinetochores that connect centromeric chromatin to spindle microtubules. The centromeres of budding yeast, which are relatively simple, are ...In mitosis, accurate chromosome segregation depends on kinetochores that connect centromeric chromatin to spindle microtubules. The centromeres of budding yeast, which are relatively simple, are connected to individual microtubules via a kinetochore constitutive centromere associated network (CCAN). However, the complex centromeres of human chromosomes comprise millions of DNA base pairs and attach to multiple microtubules. Here, by use of cryo-electron microscopy and functional analyses, we reveal the molecular basis of how human CCAN interacts with duplex DNA and facilitates accurate chromosome segregation. The overall structure relates to the cooperative interactions and interdependency of the constituent sub-complexes of the CCAN. The duplex DNA is topologically entrapped by human CCAN. Further, CENP-N does not bind to the RG-loop of CENP-A but to DNA in the CCAN complex. The DNA binding activity is essential for CENP-LN localization to centromere and chromosome segregation during mitosis. Thus, these analyses provide new insights into mechanisms of action underlying kinetochore assembly and function in mitosis. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7xhn.cif.gz 7xhn.cif.gz | 608.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7xhn.ent.gz pdb7xhn.ent.gz | 443.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7xhn.json.gz 7xhn.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xh/7xhn https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xh/7xhn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xh/7xhn ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xh/7xhn | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  33196MC 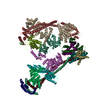 7xhoC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 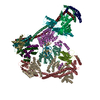
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Centromere protein ... , 15 types, 17 molecules oOHIKLMNPSTXCcQUR
| #1: Protein | Mass: 33830.637 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPO / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPO / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q9BU64 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q9BU64#2: Protein | | Mass: 29349.811 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPH / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPH / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q9H3R5 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q9H3R5#3: Protein | | Mass: 86820.188 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPI / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPI / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q92674 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q92674#4: Protein | | Mass: 31696.070 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPK / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPK / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q9BS16 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q9BS16#5: Protein | | Mass: 39039.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPL / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPL / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:  #6: Protein | | Mass: 19761.945 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPM / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPM / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9NSP4 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: Q9NSP4#7: Protein | | Mass: 40438.418 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPN / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPN / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:  #8: Protein | | Mass: 33210.949 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPP / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPP / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q6IPU0 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q6IPU0#9: Protein | | Mass: 15917.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPS / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPS / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:  #10: Protein | | Mass: 60502.613 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPT / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPT / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:  #12: Protein | | Mass: 8972.415 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPX / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPX / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:  #15: Protein | Mass: 107022.273 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPC / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPC / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:  #16: Protein | | Mass: 31477.244 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPQ / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPQ / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q7L2Z9 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q7L2Z9#17: Protein | | Mass: 47609.766 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPU / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPU / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q71F23 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q71F23#18: Protein | | Mass: 20228.297 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPR / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CENPR / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q13352 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / Strain (production host): Hi5 / References: UniProt: Q13352 |
|---|
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules W
| #11: Protein | Mass: 10087.236 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Cell line (production host): Sf9 / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules GJ
| #13: DNA chain | Mass: 7685.937 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|---|
| #14: DNA chain | Mass: 7676.923 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: CCAN-DNA / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: DIFFRACTION / Nominal defocus max: 2700 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1700 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20.1_4487: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.71 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 79777 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj












































