+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7tn1 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Multistate design to stabilize viral class I fusion proteins | |||||||||
 Components Components | Fusion glycoprotein F0 | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / Respiratory syncytial virus / Fusion protein | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsymbiont-mediated induction of syncytium formation / host cell Golgi membrane / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Respiratory syncytial virus Respiratory syncytial virus | |||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.1 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Huang, J. / Banerjee, A. / Gonzalez, K. / Mousa, J. / Strauch, E. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2024Title: A general computational design strategy for stabilizing viral class I fusion proteins. Authors: Karen J Gonzalez / Jiachen Huang / Miria F Criado / Avik Banerjee / Stephen M Tompkins / Jarrod J Mousa / Eva-Maria Strauch /  Abstract: Many pathogenic viruses rely on class I fusion proteins to fuse their viral membrane with the host cell membrane. To drive the fusion process, class I fusion proteins undergo an irreversible ...Many pathogenic viruses rely on class I fusion proteins to fuse their viral membrane with the host cell membrane. To drive the fusion process, class I fusion proteins undergo an irreversible conformational change from a metastable prefusion state to an energetically more stable postfusion state. Mounting evidence underscores that antibodies targeting the prefusion conformation are the most potent, making it a compelling vaccine candidate. Here, we establish a computational design protocol that stabilizes the prefusion state while destabilizing the postfusion conformation. With this protocol, we stabilize the fusion proteins of the RSV, hMPV, and SARS-CoV-2 viruses, testing fewer than a handful of designs. The solved structures of these designed proteins from all three viruses evidence the atomic accuracy of our approach. Furthermore, the humoral response of the redesigned RSV F protein compares to that of the recently approved vaccine in a mouse model. While the parallel design of two conformations allows the identification of energetically sub-optimal positions for one conformation, our protocol also reveals diverse molecular strategies for stabilization. Given the clinical significance of viruses using class I fusion proteins, our algorithm can substantially contribute to vaccine development by reducing the time and resources needed to optimize these immunogens. #1: Journal: Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr / Year: 2012 Title: Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.refine. Authors: Afonine, P.V. / Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W. / Echols, N. / Headd, J.J. / Moriarty, N.W. / Mustyakimov, M. / Terwilliger, T.C. / Urzhumtsev, A. / Zwart, P.H. / Adams, P.D. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7tn1.cif.gz 7tn1.cif.gz | 278.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7tn1.ent.gz pdb7tn1.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7tn1.json.gz 7tn1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tn/7tn1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tn/7tn1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tn/7tn1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tn/7tn1 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8e15C  8fezC  5c6bS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 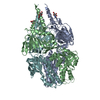
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 63198.398 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Respiratory syncytial virus / Cell line (production host): 293 / Production host: Respiratory syncytial virus / Cell line (production host): 293 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: W8RJF9 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: W8RJF9#2: Sugar | #3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has ligand of interest | N | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 3.28 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 62.49 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 298 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop / Details: 0.2 M Sodium formate, 20% w/v PEG 3,350 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS APS  / Beamline: 22-ID / Wavelength: 1 Å / Beamline: 22-ID / Wavelength: 1 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER X 16M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Apr 18, 2021 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 3.1→49.28 Å / Num. obs: 44788 / % possible obs: 96.04 % / Redundancy: 6.4 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 78.22 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.981 / CC star: 0.995 / Net I/σ(I): 6.32 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 3.1→3.211 Å / Redundancy: 7.2 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 1.336 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 1.72 / Num. unique obs: 4518 / CC1/2: 0.518 / CC star: 0.826 / % possible all: 99.47 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 5C6B Resolution: 3.1→49.28 Å / SU ML: 0.5077 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.33 / Phase error: 30.9922 Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 70.17 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 3.1→49.28 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj




