+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7st9 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
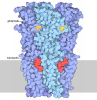
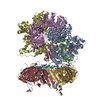
| Title | Open state of Rad24-RFC:9-1-1 bound to a 5' ss/dsDNA junction | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | REPLICATION/DNA / DNA damage / DNA replication / DNA sliding clamp / REPLICATION / REPLICATION-DNA complex | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmeiotic DNA integrity checkpoint signaling / checkpoint clamp complex / meiotic recombination checkpoint signaling / Rad17 RFC-like complex / : / Elg1 RFC-like complex / DNA replication factor C complex / Ctf18 RFC-like complex / Polymerase switching / DNA clamp loader activity ...meiotic DNA integrity checkpoint signaling / checkpoint clamp complex / meiotic recombination checkpoint signaling / Rad17 RFC-like complex / : / Elg1 RFC-like complex / DNA replication factor C complex / Ctf18 RFC-like complex / Polymerase switching / DNA clamp loader activity / nuclease activity / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / : / : / : / DNA replication checkpoint signaling / : / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / mitotic DNA replication checkpoint signaling / telomere maintenance via recombination / mitotic intra-S DNA damage checkpoint signaling / reciprocal meiotic recombination / recombinational repair / sister chromatid cohesion / mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / leading strand elongation / mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / Dual incision in TC-NER / protein kinase activator activity / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / mismatch repair / mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / telomere maintenance / DNA damage checkpoint signaling / condensed nuclear chromosome / cellular response to ionizing radiation / meiotic cell cycle / nucleotide-excision repair / double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / DNA-templated DNA replication / double-strand break repair / site of double-strand break / double-stranded DNA binding / damaged DNA binding / chromosome, telomeric region / DNA repair / chromatin binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / DNA binding / ATP binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.2 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Castaneda, J.C. / Schrecker, M. / Remus, D. / Hite, R.K. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support | 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2022Title: Mechanisms of loading and release of the 9-1-1 checkpoint clamp. Authors: Juan C Castaneda / Marina Schrecker / Dirk Remus / Richard K Hite /  Abstract: Single-stranded or double-stranded DNA junctions with recessed 5' ends serve as loading sites for the checkpoint clamp, 9-1-1, which mediates activation of the apical checkpoint kinase, ATR. However, ...Single-stranded or double-stranded DNA junctions with recessed 5' ends serve as loading sites for the checkpoint clamp, 9-1-1, which mediates activation of the apical checkpoint kinase, ATR. However, the basis for 9-1-1's recruitment to 5' junctions is unclear. Here, we present structures of the yeast checkpoint clamp loader, Rad24-replication factor C (RFC), in complex with 9-1-1 and a 5' junction and in a post-ATP-hydrolysis state. Unexpectedly, 9-1-1 adopts both closed and planar open states in the presence of Rad24-RFC and DNA. Moreover, Rad24-RFC associates with the DNA junction in the opposite orientation of processivity clamp loaders with Rad24 exclusively coordinating the double-stranded region. ATP hydrolysis stimulates conformational changes in Rad24-RFC, leading to disengagement of DNA-loaded 9-1-1. Together, these structures explain 9-1-1's recruitment to 5' junctions and reveal new principles of sliding clamp loading. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7st9.cif.gz 7st9.cif.gz | 991.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7st9.ent.gz pdb7st9.ent.gz | 807.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7st9.json.gz 7st9.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/st/7st9 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/st/7st9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/st/7st9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/st/7st9 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  25422MC  7stbC  7steC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 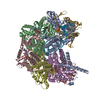
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules AG
| #1: Protein | Mass: 80096.828 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: RAD24, YER173W, SYGP-ORF60 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #7: Protein | Mass: 73850.672 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: DDC1, YPL194W / Production host:  |
-Replication factor C subunit ... , 4 types, 4 molecules BCDE
| #2: Protein | Mass: 36201.039 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: RFC4, YOL094C, O0923 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 38254.543 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: RFC3, YNL290W, N0533 / Production host:  |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 39794.473 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: RFC2, YJR068W, J1808 / Production host:  |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 39993.582 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: RFC5, YBR087W, YBR0810 / Production host:  |
-DNA damage checkpoint control protein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules FH
| #6: Protein | Mass: 45637.527 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: RAD17, YOR368W / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #8: Protein | Mass: 53207.797 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: MEC3, PIP3, PSO9, YLR288C, L8003.15 / Production host:  |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules JI
| #9: DNA chain | Mass: 15423.864 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
|---|---|
| #10: DNA chain | Mass: 6286.048 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
-Non-polymers , 6 types, 434 molecules 








| #11: Chemical | ChemComp-AGS / #12: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #13: Chemical | ChemComp-GLU / | #14: Chemical | ChemComp-THR / | #15: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / | #16: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Rad24-RFC:9-1-1:DNA / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#10 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO | ||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 | ||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 1 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GRAPHENE OXIDE / Grid mesh size: 400 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 | ||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 297 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 66 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.2_4158: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 4117022 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 938420 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj