+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7pux | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of p97 N-D1(L198W) in complex with Fragment TROLL2 | ||||||
 Components Components | Transitional endoplasmic reticulum ATPase | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / p97 / VCP / fragment screening | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcytoplasmic ubiquitin ligase complex / flavin adenine dinucleotide catabolic process / VCP-NSFL1C complex / endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced pre-emptive quality control / endosome to lysosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway / BAT3 complex binding / cellular response to arsenite ion / protein-DNA covalent cross-linking repair / Derlin-1 retrotranslocation complex / positive regulation of protein K63-linked deubiquitination ...cytoplasmic ubiquitin ligase complex / flavin adenine dinucleotide catabolic process / VCP-NSFL1C complex / endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced pre-emptive quality control / endosome to lysosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway / BAT3 complex binding / cellular response to arsenite ion / protein-DNA covalent cross-linking repair / Derlin-1 retrotranslocation complex / positive regulation of protein K63-linked deubiquitination / cytoplasm protein quality control / positive regulation of oxidative phosphorylation / aggresome assembly / deubiquitinase activator activity / ubiquitin-modified protein reader activity / regulation of protein localization to chromatin / mitotic spindle disassembly / cellular response to misfolded protein / VCP-NPL4-UFD1 AAA ATPase complex / ciliary transition zone / positive regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / vesicle-fusing ATPase / K48-linked polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / regulation of aerobic respiration / retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol / stress granule disassembly / NAD+ metabolic process / ATPase complex / regulation of synapse organization / ubiquitin-specific protease binding / ciliary tip / positive regulation of ATP biosynthetic process / MHC class I protein binding / ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding / RHOH GTPase cycle / polyubiquitin modification-dependent protein binding / autophagosome maturation / endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / negative regulation of hippo signaling / HSF1 activation / interstrand cross-link repair / ATP metabolic process / translesion synthesis / endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / proteasomal protein catabolic process / negative regulation of protein localization to chromatin / Attachment and Entry / Protein methylation / ERAD pathway / lipid droplet / proteasome complex / viral genome replication / Josephin domain DUBs / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / negative regulation of smoothened signaling pathway / macroautophagy / establishment of protein localization / Hh mutants are degraded by ERAD / positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly / Hedgehog ligand biogenesis / Defective CFTR causes cystic fibrosis / positive regulation of non-canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / Translesion Synthesis by POLH / ADP binding / autophagy / ABC-family proteins mediated transport / cytoplasmic stress granule / Aggrephagy / azurophil granule lumen / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / Ovarian tumor domain proteases / KEAP1-NFE2L2 pathway / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / double-strand break repair / positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / cellular response to heat / site of double-strand break / Neddylation / secretory granule lumen / protein phosphatase binding / regulation of apoptotic process / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / Attachment and Entry / ciliary basal body / protein ubiquitination / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / protein domain specific binding / DNA repair / DNA damage response / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / Neutrophil degranulation / lipid binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / glutamatergic synapse / endoplasmic reticulum / ATP hydrolysis activity Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.73 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.73 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Bothe, S. / Schindelin, H. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 1items Germany, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Commun Chem / Year: 2022 Journal: Commun Chem / Year: 2022Title: Fragment screening using biolayer interferometry reveals ligands targeting the SHP-motif binding site of the AAA+ ATPase p97 Authors: Bothe, S. / Hanzelmann, P. / Bohler, S. / Kehrein, J. / Zehe, M. / Wiedemann, C. / Hellmich, U.A. / Brenk, R. / Schindelin, H. / Sotriffer, C. #1: Journal: Acta Crystallogr.,Sect.D / Year: 2012 Title: Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.refine. Authors: Afonine, P.V. / Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W. / Echols, N. / Headd, J.J. / Moriarty, N.W. / Mustyakimov, M. / Terwilliger, T.C. / Urzhumtsev, A. / Zwart, P.H. / Adams, P.D. #2: Journal: Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol / Year: 2019 Title: Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: recent developments in Phenix. Authors: Dorothee Liebschner / Pavel V Afonine / Matthew L Baker / Gábor Bunkóczi / Vincent B Chen / Tristan I Croll / Bradley Hintze / Li Wei Hung / Swati Jain / Airlie J McCoy / Nigel W Moriarty ...Authors: Dorothee Liebschner / Pavel V Afonine / Matthew L Baker / Gábor Bunkóczi / Vincent B Chen / Tristan I Croll / Bradley Hintze / Li Wei Hung / Swati Jain / Airlie J McCoy / Nigel W Moriarty / Robert D Oeffner / Billy K Poon / Michael G Prisant / Randy J Read / Jane S Richardson / David C Richardson / Massimo D Sammito / Oleg V Sobolev / Duncan H Stockwell / Thomas C Terwilliger / Alexandre G Urzhumtsev / Lizbeth L Videau / Christopher J Williams / Paul D Adams /    Abstract: Diffraction (X-ray, neutron and electron) and electron cryo-microscopy are powerful methods to determine three-dimensional macromolecular structures, which are required to understand biological ...Diffraction (X-ray, neutron and electron) and electron cryo-microscopy are powerful methods to determine three-dimensional macromolecular structures, which are required to understand biological processes and to develop new therapeutics against diseases. The overall structure-solution workflow is similar for these techniques, but nuances exist because the properties of the reduced experimental data are different. Software tools for structure determination should therefore be tailored for each method. Phenix is a comprehensive software package for macromolecular structure determination that handles data from any of these techniques. Tasks performed with Phenix include data-quality assessment, map improvement, model building, the validation/rebuilding/refinement cycle and deposition. Each tool caters to the type of experimental data. The design of Phenix emphasizes the automation of procedures, where possible, to minimize repetitive and time-consuming manual tasks, while default parameters are chosen to encourage best practice. A graphical user interface provides access to many command-line features of Phenix and streamlines the transition between programs, project tracking and re-running of previous tasks. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7pux.cif.gz 7pux.cif.gz | 295.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7pux.ent.gz pdb7pux.ent.gz | 234.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7pux.json.gz 7pux.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pu/7pux https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pu/7pux ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pu/7pux ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/pu/7pux | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5dygS S: Starting model for refinement |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | x 6
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules A
| #1: Protein | Mass: 52388.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: L198W Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: VCP / Production host: Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) / References: UniProt: P55072, vesicle-fusing ATPase Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: VCP / Production host: Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) / References: UniProt: P55072, vesicle-fusing ATPase |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 6 types, 275 molecules 
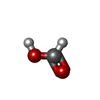
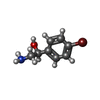
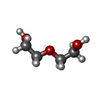


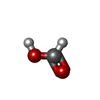




| #2: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-FMT / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-6LY / ( | #5: Chemical | ChemComp-PEG / | #6: Chemical | ChemComp-NA / | #7: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.49 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 50.53 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293.15 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 6 Details: Natriumformiat (pH 6.0) 4.0 M Glycerol (v/v) 10 % PEG 600 (v/v) 5 % |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  ESRF ESRF  / Beamline: ID30B / Wavelength: 0.9184 Å / Beamline: ID30B / Wavelength: 0.9184 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS3 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Oct 10, 2020 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.9184 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.73→47.87 Å / Num. obs: 42850 / % possible obs: 96.12 % / Redundancy: 26.47 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 26.19 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.9989 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.137 / Rpim(I) all: 0.027 / Rrim(I) all: 0.14 / Net I/σ(I): 16.684 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 1.73→1.83 Å / Rmerge(I) obs: 2.498 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 1.63 / Num. unique obs: 2143 / CC1/2: 0.6201 / Rpim(I) all: 0.492 / Rrim(I) all: 2.547 / % possible all: 25.31 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 5DYG Resolution: 1.73→47.87 Å / SU ML: 0.188 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 27.0693 Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 37.26 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 1.73→47.87 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj


















