[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7olz: Crystal structure of the SARS-CoV-2 RBD with neutralizing-VHHs Re... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7olz | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of the SARS-CoV-2 RBD with neutralizing-VHHs Re5D06 and Re9F06 | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | VIRAL PROTEIN / COVID19 / Neutralizing VHH | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationsymbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / membrane fusion ...symbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / membrane fusion / Attachment and Entry / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell surface receptor binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / receptor ligand activity / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / virion membrane / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.75 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.75 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Aksu, M. / Guttler, T. / Gorlich, D. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2021 Journal: EMBO J / Year: 2021Title: Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by highly potent, hyperthermostable, and mutation-tolerant nanobodies. Authors: Thomas Güttler / Metin Aksu / Antje Dickmanns / Kim M Stegmann / Kathrin Gregor / Renate Rees / Waltraud Taxer / Oleh Rymarenko / Jürgen Schünemann / Christian Dienemann / Philip Gunkel / ...Authors: Thomas Güttler / Metin Aksu / Antje Dickmanns / Kim M Stegmann / Kathrin Gregor / Renate Rees / Waltraud Taxer / Oleh Rymarenko / Jürgen Schünemann / Christian Dienemann / Philip Gunkel / Bianka Mussil / Jens Krull / Ulrike Teichmann / Uwe Groß / Volker C Cordes / Matthias Dobbelstein / Dirk Görlich /  Abstract: Monoclonal anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulins represent a treatment option for COVID-19. However, their production in mammalian cells is not scalable to meet the global demand. Single-domain (VHH) ...Monoclonal anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulins represent a treatment option for COVID-19. However, their production in mammalian cells is not scalable to meet the global demand. Single-domain (VHH) antibodies (also called nanobodies) provide an alternative suitable for microbial production. Using alpaca immune libraries against the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein, we isolated 45 infection-blocking VHH antibodies. These include nanobodies that can withstand 95°C. The most effective VHH antibody neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 at 17-50 pM concentration (0.2-0.7 µg per liter), binds the open and closed states of the Spike, and shows a tight RBD interaction in the X-ray and cryo-EM structures. The best VHH trimers neutralize even at 40 ng per liter. We constructed nanobody tandems and identified nanobody monomers that tolerate the K417N/T, E484K, N501Y, and L452R immune-escape mutations found in the Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Epsilon, Iota, and Delta/Kappa lineages. We also demonstrate neutralization of the Beta strain at low-picomolar VHH concentrations. We further discovered VHH antibodies that enforce native folding of the RBD in the E. coli cytosol, where its folding normally fails. Such "fold-promoting" nanobodies may allow for simplified production of vaccines and their adaptation to viral escape-mutations. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7olz.cif.gz 7olz.cif.gz | 187.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7olz.ent.gz pdb7olz.ent.gz | 145.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7olz.json.gz 7olz.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ol/7olz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ol/7olz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ol/7olz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ol/7olz | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7on5C  6yz5S S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 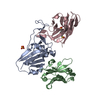
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 1 types, 1 molecules A
| #3: Protein | Mass: 21873.496 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: S, 2 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Antibody , 2 types, 2 molecules CB
| #1: Antibody | Mass: 14413.827 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #2: Antibody | Mass: 13808.122 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 277 molecules 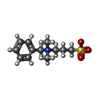




| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-DMX / |
|---|---|
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-SO4 / |
| #6: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.23 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 44.73 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop / pH: 7.5 Details: 0.1 M MOPS pH 7.5, 2.07 M ammonium sulfate, 0.1 M NDSB-256 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SLS SLS  / Beamline: X10SA / Wavelength: 1 Å / Beamline: X10SA / Wavelength: 1 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER2 X 16M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Oct 24, 2020 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.75→53.01 Å / Num. obs: 45701 / % possible obs: 85.05 % / Redundancy: 13.3 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 15.93 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.999 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.09045 / Rpim(I) all: 0.026 / Rrim(I) all: 0.094 / Net I/σ(I): 17.91 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 1.75→1.813 Å / Redundancy: 13 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 1.53 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 1.99 / Num. unique obs: 2363 / CC1/2: 0.873 / Rpim(I) all: 0.43 / Rrim(I) all: 1.59 / % possible all: 51.39 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 6YZ5 Resolution: 1.75→53.01 Å / SU ML: 0.16 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.34 / Phase error: 21.75 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 87.7 Å2 / Biso mean: 23.4695 Å2 / Biso min: 4.94 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 1.75→53.01 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Rfactor Rfree error: 0 / Total num. of bins used: 15
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj






