+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7ock | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | MAT in complex with SAMH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / enzyme filamentation / metabolic regulation / phage-host interaction / Cryo-EM | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationS-adenosyl-L-methionine lyase / S-adenosyl-L-methionine lyase activity / methionine adenosyltransferase / methionine adenosyltransferase activity / S-adenosylmethionine biosynthetic process / one-carbon metabolic process / transferase activity / magnesium ion binding / ATP binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Escherichia virus T3 Escherichia virus T3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Simon, H. / Kleiner, D. / Shmulevich, F. / Zarivach, R. / Zalk, R. / Tang, H. / Ding, F. / Bershtein, S. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Israel, 1items Israel, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
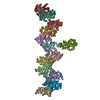
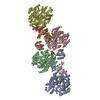
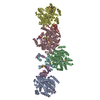
 Citation Citation |  Journal: mBio / Year: 2021 Journal: mBio / Year: 2021Title: SAMase of Bacteriophage T3 Inactivates Escherichia coli's Methionine -Adenosyltransferase by Forming Heteropolymers. Authors: Hadas Simon-Baram / Daniel Kleiner / Fannia Shmulevich / Raz Zarivach / Ran Zalk / Huayuan Tang / Feng Ding / Shimon Bershtein /   Abstract: -Adenosylmethionine lyase (SAMase) of bacteriophage T3 degrades the intracellular SAM pools of the host Escherichia coli cells, thereby inactivating a crucial metabolite involved in a plethora of ...-Adenosylmethionine lyase (SAMase) of bacteriophage T3 degrades the intracellular SAM pools of the host Escherichia coli cells, thereby inactivating a crucial metabolite involved in a plethora of cellular functions, including DNA methylation. SAMase is the first viral protein expressed upon infection, and its activity prevents methylation of the T3 genome. Maintenance of the phage genome in a fully unmethylated state has a profound effect on the infection strategy. It allows T3 to shift from a lytic infection under normal growth conditions to a transient lysogenic infection under glucose starvation. Using single-particle cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) and biochemical assays, we demonstrate that SAMase performs its function by not only degrading SAM but also by interacting with and efficiently inhibiting the host's methionine -adenosyltransferase (MAT), the enzyme that produces SAM. Specifically, SAMase triggers open-ended head-to-tail assembly of E. coli MAT into an unusual linear filamentous structure in which adjacent MAT tetramers are joined by two SAMase dimers. Molecular dynamics simulations together with normal mode analyses suggest that the entrapment of MAT tetramers within filaments leads to an allosteric inhibition of MAT activity due to a shift to low-frequency, high-amplitude active-site-deforming modes. The amplification of uncorrelated motions between active-site residues weakens MAT's substrate binding affinity, providing a possible explanation for the observed loss of function. We propose that the dual function of SAMase as an enzyme that degrades SAM and as an inhibitor of MAT activity has emerged to achieve an efficient depletion of the intracellular SAM pools. Self-assembly of enzymes into filamentous structures in response to specific metabolic cues has recently emerged as a widespread strategy of metabolic regulation. In many instances, filamentation of metabolic enzymes occurs in response to starvation and leads to functional inactivation. Here, we report that bacteriophage T3 modulates the metabolism of the host E. coli cells by recruiting a similar strategy: silencing a central metabolic enzyme by subjecting it to phage-mediated polymerization. This observation points to an intriguing possibility that virus-induced polymerization of the host metabolic enzymes is a common mechanism implemented by viruses to metabolically reprogram and subdue infected cells. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7ock.cif.gz 7ock.cif.gz | 604.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7ock.ent.gz pdb7ock.ent.gz | 509.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7ock.json.gz 7ock.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oc/7ock https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oc/7ock ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oc/7ock ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/oc/7ock | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  12809MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 42827.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: K12 / Gene: metK, FAZ83_06105 / Production host:  References: UniProt: A0A4S5B2W6, methionine adenosyltransferase #2: Protein | Mass: 17863.264 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Escherichia virus T3 / Production host: Escherichia virus T3 / Production host:  Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 / Details: 25mM Tris pH 8.0, 150 mM KCl,1 mM DTT. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI POLARA 300 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 80 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: dev_3689: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 65950 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj