+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7n9f | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
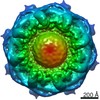
| Title | Structure of the in situ yeast NPC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSLOCASE / NPC / nucleocytoplasmic transport | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationresponse to spindle checkpoint signaling / nuclear pore linkers / regulation of protein desumoylation / peroxisomal importomer complex / mRNA export from nucleus in response to heat stress / positive regulation of ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / chromosome, subtelomeric region / Seh1-associated complex / protein localization to nuclear inner membrane / nuclear pore inner ring ...response to spindle checkpoint signaling / nuclear pore linkers / regulation of protein desumoylation / peroxisomal importomer complex / mRNA export from nucleus in response to heat stress / positive regulation of ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / chromosome, subtelomeric region / Seh1-associated complex / protein localization to nuclear inner membrane / nuclear pore inner ring / protein exit from endoplasmic reticulum / COPII-coated vesicle budding / nuclear pore localization / adenyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / nuclear pore central transport channel / transcription-dependent tethering of RNA polymerase II gene DNA at nuclear periphery / regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / nuclear pore complex assembly / regulation of TORC1 signaling / telomere tethering at nuclear periphery / nuclear pore outer ring / nuclear pore organization / nuclear migration along microtubule / nuclear pore cytoplasmic filaments / positive regulation of protein exit from endoplasmic reticulum / : / COPII vesicle coat / Regulation of HSF1-mediated heat shock response / establishment of mitotic spindle localization / post-transcriptional tethering of RNA polymerase II gene DNA at nuclear periphery / nuclear pore nuclear basket / tRNA export from nucleus / SUMOylation of SUMOylation proteins / protein localization to kinetochore / NLS-bearing protein import into nucleus / structural constituent of nuclear pore / nuclear localization sequence binding / SUMOylation of RNA binding proteins / RNA export from nucleus / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / vacuolar membrane / nucleocytoplasmic transport / cytoplasmic dynein complex / poly(A)+ mRNA export from nucleus / regulation of mitotic nuclear division / dynein intermediate chain binding / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / Hydrolases; Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases); Serine endopeptidases / ribosomal large subunit export from nucleus / positive regulation of TOR signaling / mRNA transport / nuclear pore / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / mRNA export from nucleus / cytoplasmic microtubule / ERAD pathway / ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus / Neutrophil degranulation / positive regulation of TORC1 signaling / nuclear periphery / protein export from nucleus / cellular response to amino acid starvation / cell periphery / chromosome segregation / promoter-specific chromatin binding / molecular condensate scaffold activity / phospholipid binding / protein import into nucleus / transcription corepressor activity / nuclear envelope / heterochromatin formation / double-strand break repair / single-stranded DNA binding / protein transport / cellular response to heat / nuclear membrane / amyloid fibril formation / chromosome, telomeric region / hydrolase activity / cell division / chromatin binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / protein-containing complex binding / structural molecule activity / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / endoplasmic reticulum / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / DNA binding / RNA binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / subtomogram averaging / cryo EM / Resolution: 37 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Villa, E. / Singh, D. / Ludtke, S.J. / Akey, C.W. / Rout, M.P. / Echeverria, I. / Suslov, S. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 7items United States, 7items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2022 Journal: Cell / Year: 2022Title: Comprehensive structure and functional adaptations of the yeast nuclear pore complex. Authors: Christopher W Akey / Digvijay Singh / Christna Ouch / Ignacia Echeverria / Ilona Nudelman / Joseph M Varberg / Zulin Yu / Fei Fang / Yi Shi / Junjie Wang / Daniel Salzberg / Kangkang Song / ...Authors: Christopher W Akey / Digvijay Singh / Christna Ouch / Ignacia Echeverria / Ilona Nudelman / Joseph M Varberg / Zulin Yu / Fei Fang / Yi Shi / Junjie Wang / Daniel Salzberg / Kangkang Song / Chen Xu / James C Gumbart / Sergey Suslov / Jay Unruh / Sue L Jaspersen / Brian T Chait / Andrej Sali / Javier Fernandez-Martinez / Steven J Ludtke / Elizabeth Villa / Michael P Rout /  Abstract: Nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) mediate the nucleocytoplasmic transport of macromolecules. Here we provide a structure of the isolated yeast NPC in which the inner ring is resolved by cryo-EM at sub- ...Nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) mediate the nucleocytoplasmic transport of macromolecules. Here we provide a structure of the isolated yeast NPC in which the inner ring is resolved by cryo-EM at sub-nanometer resolution to show how flexible connectors tie together different structural and functional layers. These connectors may be targets for phosphorylation and regulated disassembly in cells with an open mitosis. Moreover, some nucleoporin pairs and transport factors have similar interaction motifs, which suggests an evolutionary and mechanistic link between assembly and transport. We provide evidence for three major NPC variants that may foreshadow functional specializations at the nuclear periphery. Cryo-electron tomography extended these studies, providing a model of the in situ NPC with a radially expanded inner ring. Our comprehensive model reveals features of the nuclear basket and central transporter, suggests a role for the lumenal Pom152 ring in restricting dilation, and highlights structural plasticity that may be required for transport. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7n9f.cif.gz 7n9f.cif.gz | 4.8 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7n9f.ent.gz pdb7n9f.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7n9f.json.gz 7n9f.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n9/7n9f https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n9/7n9f ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n9/7n9f ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n9/7n9f | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  24258MC  7n84C  7n85C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | x 8
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 | 
|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: (Schoenflies symbol: C8 (8 fold cyclic)) |
- Components
Components
-Protein , 20 types, 54 molecules 0Y1ZADGJyzBEHKCFILMONPQRSTUWVX...
| #1: Protein | Mass: 169651.969 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | Mass: 156827.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #4: Protein | Mass: 86611.672 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #5: Protein | Mass: 57547.145 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #6: Protein | Mass: 49174.762 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #7: Protein | Mass: 191718.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #8: Protein | Mass: 188753.281 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #9: Protein | Mass: 96291.586 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #10: Protein | Mass: 52688.668 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #11: Protein | Mass: 58853.902 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #12: Protein | Mass: 82174.047 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #13: Protein | Mass: 159067.188 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #14: Protein | Mass: 120560.328 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #15: Protein | Mass: 84972.438 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #16: Protein | Mass: 81157.852 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #17: Protein | Mass: 33082.965 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #18: Protein | Mass: 39170.758 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #19: Protein | Mass: 83718.867 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #20: Protein | Mass: 133452.672 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #21: Protein | Mass: 10456.980 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 2 molecules 56
| #3: Protein/peptide | Mass: 3081.790 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Details
| Compound details | full C8 protomer |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: CELL / 3D reconstruction method: subtomogram averaging |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: yeast NPC / Type: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT / Details: Complete yeast NPC from vitrified cells / Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 52.0 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: W303 yeast cells were harvested during log-phase growth and diluted to an 0.8 x 107 cells/mL in YPD media. Five uL of this diluted sample was applied to glow-discharged 200-mesh, Quantafoil ...Details: W303 yeast cells were harvested during log-phase growth and diluted to an 0.8 x 107 cells/mL in YPD media. Five uL of this diluted sample was applied to glow-discharged 200-mesh, Quantafoil R2/1 grids (Electron Microscopy Sciences), excess media was manually blotted from the grid back side (opposite to the carbon substrate where the cells were deposited) and the grid was plunge frozen in a liquid ethane-propane mixture (50/50 volume, Airgas) then cryogenic, FIB milling was performed in an Aquilos DualBeam (Thermo Fisher Scientific) |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE Details: A custom-built vitrification device (Max Planck Institute for Biochemistry, Munich) |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS Details: Tilt series collection: dose-symmetric & bi-directional |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 42000 X / Nominal defocus max: 6000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 2500 nm / Calibrated defocus min: 2500 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 6000 nm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2 sec. / Electron dose: 4.5 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) Details: Images were collected in movie-mode at ~8 frames per second |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum LS / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Width: 3838 / Height: 3708 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image processing | Details: The tilt images were motion-corrected but not dose-weighted. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Details: e2spt_ctf.py was used to identify the precise z height of the particle in the tomogram. This precise height was then used for computing the CTF and performing the CTF correction. Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C8 (8 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 37 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 518 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EM volume selection | Method: Manual boxing Details: The full nuclear pores were manually identified in the tomograms for the manual boxing. Num. of tomograms: 293 / Num. of volumes extracted: 577 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: cross-correlation Details: Manual docking and limited molecular dynamics flexible fitting |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj










