[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7mo1: Crystal Structure of the ZnF1 of Nucleoporin NUP153 in complex wi... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7mo1 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal Structure of the ZnF1 of Nucleoporin NUP153 in complex with Ran-GDP | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / nuclear pore complex component / nucleocytoplasmic transport / complex (small GTPase-nuclear protein) | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnucleoplasmic side of nuclear pore / Transport of the SLBP independent Mature mRNA / Transport of the SLBP Dependant Mature mRNA / Transport of Mature mRNA Derived from an Intronless Transcript / Transport of Mature mRNA derived from an Intron-Containing Transcript / snRNP Assembly / SUMOylation of ubiquitinylation proteins / Nuclear Pore Complex (NPC) Disassembly / SUMOylation of SUMOylation proteins / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins ...nucleoplasmic side of nuclear pore / Transport of the SLBP independent Mature mRNA / Transport of the SLBP Dependant Mature mRNA / Transport of Mature mRNA Derived from an Intronless Transcript / Transport of Mature mRNA derived from an Intron-Containing Transcript / snRNP Assembly / SUMOylation of ubiquitinylation proteins / Nuclear Pore Complex (NPC) Disassembly / SUMOylation of SUMOylation proteins / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / SUMOylation of RNA binding proteins / SUMOylation of DNA replication proteins / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Regulation of Glucokinase by Glucokinase Regulatory Protein / SUMOylation of DNA damage response and repair proteins / negative regulation of RNA export from nucleus / Regulation of HSF1-mediated heat shock response / annulate lamellae / nuclear pore complex assembly / pre-miRNA export from nucleus / RNA nuclear export complex / snRNA import into nucleus / manchette / cellular response to mineralocorticoid stimulus / nuclear inclusion body / nuclear pore nuclear basket / Regulation of cholesterol biosynthesis by SREBP (SREBF) / importin-alpha family protein binding / structural constituent of nuclear pore / nuclear localization sequence binding / Rev-mediated nuclear export of HIV RNA / Nuclear import of Rev protein / protein localization to nucleolus / NEP/NS2 Interacts with the Cellular Export Machinery / RNA export from nucleus / tRNA processing in the nucleus / GTP metabolic process / Postmitotic nuclear pore complex (NPC) reformation / MicroRNA (miRNA) biogenesis / DNA metabolic process / dynein intermediate chain binding / mitotic sister chromatid segregation / viral process / spermatid development / ribosomal large subunit export from nucleus / mRNA transport / nuclear pore / positive regulation of protein binding / sperm flagellum / ribosomal subunit export from nucleus / protein-membrane adaptor activity / ribosomal small subunit export from nucleus / centriole / nuclear periphery / protein export from nucleus / mitotic spindle organization / male germ cell nucleus / hippocampus development / molecular condensate scaffold activity / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / recycling endosome / positive regulation of protein import into nucleus / small GTPase binding / protein import into nucleus / GDP binding / melanosome / nuclear envelope / mitotic cell cycle / G protein activity / actin cytoskeleton organization / double-stranded DNA binding / midbody / nuclear membrane / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / amyloid fibril formation / cadherin binding / protein heterodimerization activity / protein domain specific binding / cell division / GTPase activity / chromatin binding / chromatin / GTP binding / protein-containing complex binding / nucleolus / magnesium ion binding / protein-containing complex / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus / membrane / cytosol / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  SAD / Resolution: 1.6 Å SAD / Resolution: 1.6 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Bley, C.J. / Nie, S. / Mobbs, G.W. / Petrovic, S. / Gres, A.T. / Liu, X. / Mukherjee, S. / Harvey, S. / Huber, F.M. / Lin, D.H. ...Bley, C.J. / Nie, S. / Mobbs, G.W. / Petrovic, S. / Gres, A.T. / Liu, X. / Mukherjee, S. / Harvey, S. / Huber, F.M. / Lin, D.H. / Brown, B. / Tang, A.W. / Rundlet, E.J. / Correia, A.R. / Chen, S. / Regmi, S.G. / Stevens, T.A. / Jette, C.A. / Dasso, M. / Patke, A. / Palazzo, A.F. / Kossiakoff, A.A. / Hoelz, A. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2022 Journal: Science / Year: 2022Title: Architecture of the cytoplasmic face of the nuclear pore. Authors: Christopher J Bley / Si Nie / George W Mobbs / Stefan Petrovic / Anna T Gres / Xiaoyu Liu / Somnath Mukherjee / Sho Harvey / Ferdinand M Huber / Daniel H Lin / Bonnie Brown / Aaron W Tang / ...Authors: Christopher J Bley / Si Nie / George W Mobbs / Stefan Petrovic / Anna T Gres / Xiaoyu Liu / Somnath Mukherjee / Sho Harvey / Ferdinand M Huber / Daniel H Lin / Bonnie Brown / Aaron W Tang / Emily J Rundlet / Ana R Correia / Shane Chen / Saroj G Regmi / Taylor A Stevens / Claudia A Jette / Mary Dasso / Alina Patke / Alexander F Palazzo / Anthony A Kossiakoff / André Hoelz /   Abstract: INTRODUCTION The subcellular compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells requires selective transport of folded proteins and protein-nucleic acid complexes. Embedded in nuclear envelope pores, which are ...INTRODUCTION The subcellular compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells requires selective transport of folded proteins and protein-nucleic acid complexes. Embedded in nuclear envelope pores, which are generated by the circumscribed fusion of the inner and outer nuclear membranes, nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) are the sole bidirectional gateways for nucleocytoplasmic transport. The ~110-MDa human NPC is an ~1000-protein assembly that comprises multiple copies of ~34 different proteins, collectively termed nucleoporins. The symmetric core of the NPC is composed of an inner ring encircling the central transport channel and outer rings formed by Y‑shaped coat nucleoporin complexes (CNCs) anchored atop both sides of the nuclear envelope. The outer rings are decorated with compartment‑specific asymmetric nuclear basket and cytoplasmic filament nucleoporins, which establish transport directionality and provide docking sites for transport factors and the small guanosine triphosphatase Ran. The cytoplasmic filament nucleoporins also play an essential role in the irreversible remodeling of messenger ribonucleoprotein particles (mRNPs) as they exit the central transport channel. Unsurprisingly, the NPC's cytoplasmic face represents a hotspot for disease‑associated mutations and is commonly targeted by viral virulence factors. RATIONALE Previous studies established a near-atomic composite structure of the human NPC's symmetric core by combining (i) biochemical reconstitution to elucidate the interaction network between symmetric nucleoporins, (ii) crystal and single-particle cryo-electron microscopy structure determination of nucleoporins and nucleoporin complexes to reveal their three-dimensional shape and the molecular details of their interactions, (iii) quantitative docking in cryo-electron tomography (cryo-ET) maps of the intact human NPC to uncover nucleoporin stoichiometry and positioning, and (iv) cell‑based assays to validate the physiological relevance of the biochemical and structural findings. In this work, we extended our approach to the cytoplasmic filament nucleoporins to reveal the near-atomic architecture of the cytoplasmic face of the human NPC. RESULTS Using biochemical reconstitution, we elucidated the protein-protein and protein-RNA interaction networks of the human and cytoplasmic filament nucleoporins, establishing an evolutionarily conserved heterohexameric cytoplasmic filament nucleoporin complex (CFNC) held together by a central heterotrimeric coiled‑coil hub that tethers two separate mRNP‑remodeling complexes. Further biochemical analysis and determination of a series of crystal structures revealed that the metazoan‑specific cytoplasmic filament nucleoporin NUP358 is composed of 16 distinct domains, including an N‑terminal S‑shaped α‑helical solenoid followed by a coiled‑coil oligomerization element, numerous Ran‑interacting domains, an E3 ligase domain, and a C‑terminal prolyl‑isomerase domain. Physiologically validated quantitative docking into cryo-ET maps of the intact human NPC revealed that pentameric NUP358 bundles, conjoined by the oligomerization element, are anchored through their N‑terminal domains to the central stalk regions of the CNC, projecting flexibly attached domains as far as ~600 Å into the cytoplasm. Using cell‑based assays, we demonstrated that NUP358 is dispensable for the architectural integrity of the assembled interphase NPC and RNA export but is required for efficient translation. After NUP358 assignment, the remaining 4-shaped cryo‑ET density matched the dimensions of the CFNC coiled‑coil hub, in close proximity to an outer-ring NUP93. Whereas the N-terminal NUP93 assembly sensor motif anchors the properly assembled related coiled‑coil channel nucleoporin heterotrimer to the inner ring, biochemical reconstitution confirmed that the NUP93 assembly sensor is reused in anchoring the CFNC to the cytoplasmic face of the human NPC. By contrast, two CFNCs are anchored by a divergent mechanism that involves assembly sensors located in unstructured portions of two CNC nucleoporins. Whereas unassigned cryo‑ET density occupies the NUP358 and CFNC binding sites on the nuclear face, docking of the nuclear basket component ELYS established that the equivalent position on the cytoplasmic face is unoccupied, suggesting that mechanisms other than steric competition promote asymmetric distribution of nucleoporins. CONCLUSION We have substantially advanced the biochemical and structural characterization of the asymmetric nucleoporins' architecture and attachment at the cytoplasmic and nuclear faces of the NPC. Our near‑atomic composite structure of the human NPC's cytoplasmic face provides a biochemical and structural framework for elucidating the molecular basis of mRNP remodeling, viral virulence factor interference with NPC function, and the underlying mechanisms of nucleoporin diseases at the cytoplasmic face of the NPC. [Figure: see text]. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7mo1.cif.gz 7mo1.cif.gz | 166.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7mo1.ent.gz pdb7mo1.ent.gz | 132.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7mo1.json.gz 7mo1.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7mo1_validation.pdf.gz 7mo1_validation.pdf.gz | 782.7 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7mo1_full_validation.pdf.gz 7mo1_full_validation.pdf.gz | 787.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7mo1_validation.xml.gz 7mo1_validation.xml.gz | 14.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7mo1_validation.cif.gz 7mo1_validation.cif.gz | 20.4 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mo/7mo1 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mo/7mo1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mo/7mo1 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mo/7mo1 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7mniC  7mnjC  7mnkC  7mnlC  7mnmC  7mnnC  7mnoC  7mnpC  7mnqC  7mnrC  7mnsC  7mntC  7mnuC 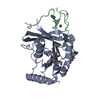 7mnvC  7mnwC  7mnxC  7mnyC  7mnzC  7mo0C  7mo2C  7mo3C  7mo4C  7mo5C  7tblC  7tbmC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| |||||||||
| Unit cell |
| |||||||||
| Components on special symmetry positions |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein / Protein/peptide , 2 types, 2 molecules AB
| #1: Protein | Mass: 24483.086 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: F35S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RAN, ARA24, OK/SW-cl.81 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: RAN, ARA24, OK/SW-cl.81 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 4573.210 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: ZINC FINGER 1 of NUP153 (UNP residues 648-687) Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
-Non-polymers , 4 types, 225 molecules 






| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-GDP / |
|---|---|
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
| #6: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.27 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 45.9 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 294 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 6 / Details: 22% w/v PEG3350, 0.1 M Bis-Tris |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SSRL SSRL  / Beamline: BL12-2 / Wavelength: 1.03317 Å / Beamline: BL12-2 / Wavelength: 1.03317 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Oct 19, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1.03317 Å / Relative weight: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.6→28.44 Å / Num. obs: 67816 / % possible obs: 100 % / Redundancy: 13 % / CC1/2: 1 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.078 / Rpim(I) all: 0.022 / Rrim(I) all: 0.081 / Net I/σ(I): 19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflection shell | Diffraction-ID: 1
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  SAD / Resolution: 1.6→28.44 Å / SU ML: 0.16 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.92 / Phase error: 18.52 / Stereochemistry target values: ML SAD / Resolution: 1.6→28.44 Å / SU ML: 0.16 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.92 / Phase error: 18.52 / Stereochemistry target values: ML
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å / Solvent model: FLAT BULK SOLVENT MODEL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 139.95 Å2 / Biso mean: 39.0357 Å2 / Biso min: 14.89 Å2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 1.6→28.44 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Rfactor Rfree error: 0 / Total num. of bins used: 24
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj











