+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7mex | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
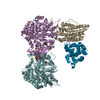
| Title | Structure of yeast Ubr1 in complex with Ubc2 and N-degron | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSFERASE / Ubiquitin E3 ligase / ubiquitination / Ubr1 / Ubc2 / Degron / N-end rule | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMUB1-RAD6-UBR2 ubiquitin ligase complex / RAD6-UBR2 ubiquitin ligase complex / Rad6-Rad18 complex / regulation of dipeptide transport / UBR1-RAD6 ubiquitin ligase complex / sno(s)RNA transcription / proteasome regulatory particle binding / HULC complex / error-free postreplication DNA repair / stress-induced homeostatically regulated protein degradation pathway ...MUB1-RAD6-UBR2 ubiquitin ligase complex / RAD6-UBR2 ubiquitin ligase complex / Rad6-Rad18 complex / regulation of dipeptide transport / UBR1-RAD6 ubiquitin ligase complex / sno(s)RNA transcription / proteasome regulatory particle binding / HULC complex / error-free postreplication DNA repair / stress-induced homeostatically regulated protein degradation pathway / : / meiotic DNA double-strand break formation / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the N-end rule pathway / mitochondria-associated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / cytoplasm protein quality control by the ubiquitin-proteasome system / : / telomere maintenance via recombination / proteasome regulatory particle, base subcomplex / ribosome-associated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme / error-free translesion synthesis / sporulation resulting in formation of a cellular spore / proteasome binding / ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity / Antigen processing: Ubiquitination & Proteasome degradation / cellular response to unfolded protein / protein monoubiquitination / error-prone translesion synthesis / ubiquitin ligase complex / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / ERAD pathway / mitotic G1 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / Maturation of protein E / Maturation of protein E / ER Quality Control Compartment (ERQC) / Myoclonic epilepsy of Lafora / FLT3 signaling by CBL mutants / Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex / Prevention of phagosomal-lysosomal fusion / Alpha-protein kinase 1 signaling pathway / Glycogen synthesis / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex / IRAK1 recruits IKK complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / Endosomal Sorting Complex Required For Transport (ESCRT) / Membrane binding and targetting of GAG proteins / Negative regulation of FLT3 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE)-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 / PTK6 Regulates RTKs and Their Effectors AKT1 and DOK1 / Regulation of TBK1, IKKε-mediated activation of IRF3, IRF7 upon TLR3 ligation / IRAK2 mediated activation of TAK1 complex upon TLR7/8 or 9 stimulation / NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus / TICAM1,TRAF6-dependent induction of TAK1 complex / TICAM1-dependent activation of IRF3/IRF7 / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Cyclin B / Downregulation of ERBB4 signaling / Regulation of FZD by ubiquitination / APC-Cdc20 mediated degradation of Nek2A / p75NTR recruits signalling complexes / InlA-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cells / TRAF6 mediated IRF7 activation in TLR7/8 or 9 signaling / TRAF6-mediated induction of TAK1 complex within TLR4 complex / Regulation of pyruvate metabolism / NF-kB is activated and signals survival / Regulation of innate immune responses to cytosolic DNA / Pexophagy / Downregulation of ERBB2:ERBB3 signaling / NRIF signals cell death from the nucleus / Regulation of PTEN localization / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / VLDLR internalisation and degradation / Regulation of BACH1 activity / Synthesis of active ubiquitin: roles of E1 and E2 enzymes / MAP3K8 (TPL2)-dependent MAPK1/3 activation / Translesion synthesis by REV1 / TICAM1, RIP1-mediated IKK complex recruitment / Translesion synthesis by POLK / InlB-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cell / Activation of IRF3, IRF7 mediated by TBK1, IKKε (IKBKE) / JNK (c-Jun kinases) phosphorylation and activation mediated by activated human TAK1 / Josephin domain DUBs / Downregulation of TGF-beta receptor signaling / Translesion synthesis by POLI / IKK complex recruitment mediated by RIP1 / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in GG-NER / Regulation of activated PAK-2p34 by proteasome mediated degradation / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / TGF-beta receptor signaling in EMT (epithelial to mesenchymal transition) / TNFR1-induced NF-kappa-B signaling pathway / Autodegradation of Cdh1 by Cdh1:APC/C / TCF dependent signaling in response to WNT / APC/C:Cdc20 mediated degradation of Securin / Regulation of NF-kappa B signaling / N-glycan trimming in the ER and Calnexin/Calreticulin cycle / activated TAK1 mediates p38 MAPK activation / Asymmetric localization of PCP proteins / SCF-beta-TrCP mediated degradation of Emi1 / NIK-->noncanonical NF-kB signaling / Ubiquitin-dependent degradation of Cyclin D / TNFR2 non-canonical NF-kB pathway Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.35 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Pan, M. / Zheng, Q. / Wang, T. / Liang, L. / Yu, Y. / Liu, L. / Zhao, M. | ||||||
| Funding support | 1items
| ||||||
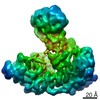
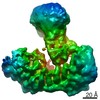
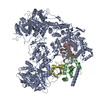
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Structural insights into Ubr1-mediated N-degron polyubiquitination. Authors: Man Pan / Qingyun Zheng / Tian Wang / Lujun Liang / Junxiong Mao / Chong Zuo / Ruichao Ding / Huasong Ai / Yuan Xie / Dong Si / Yuanyuan Yu / Lei Liu / Minglei Zhao /   Abstract: The N-degron pathway targets proteins that bear a destabilizing residue at the N terminus for proteasome-dependent degradation. In yeast, Ubr1-a single-subunit E3 ligase-is responsible for the Arg/N- ...The N-degron pathway targets proteins that bear a destabilizing residue at the N terminus for proteasome-dependent degradation. In yeast, Ubr1-a single-subunit E3 ligase-is responsible for the Arg/N-degron pathway. How Ubr1 mediates the initiation of ubiquitination and the elongation of the ubiquitin chain in a linkage-specific manner through a single E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (Ubc2) remains unknown. Here we developed chemical strategies to mimic the reaction intermediates of the first and second ubiquitin transfer steps, and determined the cryo-electron microscopy structures of Ubr1 in complex with Ubc2, ubiquitin and two N-degron peptides, representing the initiation and elongation steps of ubiquitination. Key structural elements, including a Ubc2-binding region and an acceptor ubiquitin-binding loop on Ubr1, were identified and characterized. These structures provide mechanistic insights into the initiation and elongation of ubiquitination catalysed by Ubr1. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7mex.cif.gz 7mex.cif.gz | 365.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7mex.ent.gz pdb7mex.ent.gz | 288.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7mex.json.gz 7mex.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7mex_validation.pdf.gz 7mex_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7mex_full_validation.pdf.gz 7mex_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.3 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7mex_validation.xml.gz 7mex_validation.xml.gz | 61.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7mex_validation.cif.gz 7mex_validation.cif.gz | 93.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/me/7mex https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/me/7mex ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/me/7mex ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/me/7mex | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  23806MC  7meyC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10886 (Title: Single-particle cryoEM data of yeast Ubr1-Ubc2-Ub-N-degron complex (initiation) EMPIAR-10886 (Title: Single-particle cryoEM data of yeast Ubr1-Ubc2-Ub-N-degron complex (initiation)Data size: 5.7 TB Data #1: Unaligned movie data of yeast Ubr1-Ubc2-Ub-N-degron complex (initiation complex) [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 8622.922 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: G76C / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0CG48 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0CG48 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 17203.389 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: RAD6, UBC2, YGL058W / Plasmid: p416CYC / Production host:  References: UniProt: P06104, E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme | ||
| #3: Protein/peptide | Mass: 4571.223 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  | ||
| #4: Protein | Mass: 225102.750 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / Gene: UBR1, PTR1, YGR184C, G7168 / Plasmid: p416CYC / Production host:  References: UniProt: P19812, RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase | ||
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / Has ligand of interest | N | |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: yeast Ubr1 in complex with Ubc2 and N-degron / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#4 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 48 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19.2_4158: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.35 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 232915 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj






















