[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
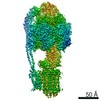
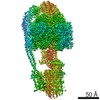
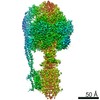
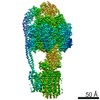
Yorodumi- PDB-7jga: Cryo-EM structure of bedaquiline-saturated Mycobacterium smegmati... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7jga | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
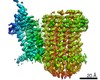
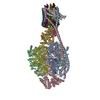
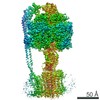
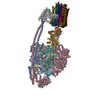
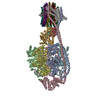
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of bedaquiline-saturated Mycobacterium smegmatis ATP synthase rotational state 3 | |||||||||
 Components Components | (ATP synthase ...) x 8 | |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / Bedaquiline / Sirturo / TMC207 / T207910 / ATP synthase / mycobacteria / tuberculosis | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / : / proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / membrane => GO:0016020 / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding ...: / : / proton motive force-driven plasma membrane ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / membrane => GO:0016020 / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / ADP binding / hydrolase activity / lipid binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Guo, H. / Courbon, G.M. / Rubinstein, J.L. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 2items Canada, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Structure of mycobacterial ATP synthase bound to the tuberculosis drug bedaquiline. Authors: Hui Guo / Gautier M Courbon / Stephanie A Bueler / Juntao Mai / Jun Liu / John L Rubinstein /  Abstract: Tuberculosis-the world's leading cause of death by infectious disease-is increasingly resistant to current first-line antibiotics. The bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (which causes tuberculosis) ...Tuberculosis-the world's leading cause of death by infectious disease-is increasingly resistant to current first-line antibiotics. The bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (which causes tuberculosis) can survive low-energy conditions, allowing infections to remain dormant and decreasing their susceptibility to many antibiotics. Bedaquiline was developed in 2005 from a lead compound identified in a phenotypic screen against Mycobacterium smegmatis. This drug can sterilize even latent M. tuberculosis infections and has become a cornerstone of treatment for multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Bedaquiline targets the mycobacterial ATP synthase, which is an essential enzyme in the obligate aerobic Mycobacterium genus, but how it binds the intact enzyme is unknown. Here we determined cryo-electron microscopy structures of M. smegmatis ATP synthase alone and in complex with bedaquiline. The drug-free structure suggests that hook-like extensions from the α-subunits prevent the enzyme from running in reverse, inhibiting ATP hydrolysis and preserving energy in hypoxic conditions. Bedaquiline binding induces large conformational changes in the ATP synthase, creating tight binding pockets at the interface of subunits a and c that explain the potency of this drug as an antibiotic for tuberculosis. #1:  Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2020 Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2020Title: Structure of mycobacterial ATP synthase with the TB drug bedaquiline Authors: Guo, H. / Courbon, G.M. / Bueler, S.A. / Mai, J. / Liu, J. / Rubinstein, J.L. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
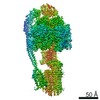
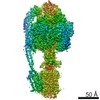
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7jga.cif.gz 7jga.cif.gz | 782.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7jga.ent.gz pdb7jga.ent.gz | 642.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7jga.json.gz 7jga.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jg/7jga https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jg/7jga ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jg/7jga ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jg/7jga | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 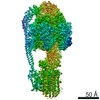 22316MC  7jg5C  7jg6C  7jg7C  7jg8C  7jg9C  7jgbC  7jgcC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ATP synthase ... , 8 types, 20 molecules ABCDEFGHabd123456789
| #1: Protein | Mass: 58951.461 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria)References: UniProt: A0A0D6IV93, UniProt: A0R202*PLUS, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #2: Protein | Mass: 51670.453 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria)References: UniProt: A0A0D6IU77, UniProt: A0R200*PLUS, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #3: Protein | | Mass: 33439.836 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A0D6IUE3, UniProt: A0R201*PLUS Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A0D6IUE3, UniProt: A0R201*PLUS#4: Protein | | Mass: 13277.741 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A0D6IU73, UniProt: A0R1Z9*PLUS Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A0D6IU73, UniProt: A0R1Z9*PLUS#5: Protein | | Mass: 27568.482 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0R206 Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0R206#6: Protein | | Mass: 17636.701 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A0D6IV98, UniProt: A0R204*PLUS Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0A0D6IV98, UniProt: A0R204*PLUS#7: Protein | | Mass: 47504.723 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0R203 Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / References: UniProt: A0R203#8: Protein | Mass: 8597.982 Da / Num. of mol.: 9 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q5TIX5, UniProt: A0R205*PLUS Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) / References: UniProt: Q5TIX5, UniProt: A0R205*PLUS |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 16 molecules 








| #9: Chemical | | #10: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #11: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / | #12: Chemical | ChemComp-PO4 / | #13: Chemical | ChemComp-BQ1 / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: ATP synthase from Mycobacterium smegmatis / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#8 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.55 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) Mycolicibacterium smegmatis (bacteria) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 6 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: COPPER/RHODIUM / Grid type: Homemade |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 75000 X / Calibrated defocus min: 600 nm / Calibrated defocus max: 3000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 50 µm / Alignment procedure: ZEMLIN TABLEAU |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 41 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 7589 |
| Image scans | Width: 4096 / Height: 4096 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 1825672 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 155488 / Algorithm: BACK PROJECTION / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: RECIPROCAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj







