[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7f1o: Cryo-EM structure of the GDP-bound dopamine receptor 1 and mini-G... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7f1o | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the GDP-bound dopamine receptor 1 and mini-Gs complex with Nb35 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / GPCR / dopamine receptor / mini-Gs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationdopamine neurotransmitter receptor activity, coupled via Gs / dopamine neurotransmitter receptor activity / operant conditioning / cerebral cortex GABAergic interneuron migration / Dopamine receptors / dopamine binding / regulation of dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / phospholipase C-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway / peristalsis / heterotrimeric G-protein binding ...dopamine neurotransmitter receptor activity, coupled via Gs / dopamine neurotransmitter receptor activity / operant conditioning / cerebral cortex GABAergic interneuron migration / Dopamine receptors / dopamine binding / regulation of dopamine uptake involved in synaptic transmission / phospholipase C-activating dopamine receptor signaling pathway / peristalsis / heterotrimeric G-protein binding / modification of postsynaptic structure / G protein-coupled receptor complex / regulation of dopamine metabolic process / positive regulation of neuron migration / grooming behavior / habituation / sensitization / dopamine transport / astrocyte development / dentate gyrus development / striatum development / conditioned taste aversion / positive regulation of potassium ion transport / maternal behavior / arrestin family protein binding / non-motile cilium / long-term synaptic depression / mating behavior / adult walking behavior / G protein-coupled dopamine receptor signaling pathway / ciliary membrane / temperature homeostasis / D-glucose import / dopamine metabolic process / transmission of nerve impulse / PKA activation in glucagon signalling / G-protein alpha-subunit binding / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger / developmental growth / hair follicle placode formation / D1 dopamine receptor binding / behavioral fear response / prepulse inhibition / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / intracellular transport / vascular endothelial cell response to laminar fluid shear stress / renal water homeostasis / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / neuronal action potential / Hedgehog 'off' state / behavioral response to cocaine / synapse assembly / adenylate cyclase-activating adrenergic receptor signaling pathway / cellular response to glucagon stimulus / presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / regulation of insulin secretion / response to amphetamine / positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / adenylate cyclase activator activity / trans-Golgi network membrane / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / negative regulation of inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus / G protein-coupled receptor activity / bone development / GABA-ergic synapse / visual learning / platelet aggregation / G-protein beta/gamma-subunit complex binding / vasodilation / cognition / memory / Olfactory Signaling Pathway / Activation of the phototransduction cascade / G beta:gamma signalling through PLC beta / Presynaptic function of Kainate receptors / long-term synaptic potentiation / Thromboxane signalling through TP receptor / G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway / adenylate cyclase-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / Activation of G protein gated Potassium channels / Inhibition of voltage gated Ca2+ channels via Gbeta/gamma subunits / G-protein activation / Prostacyclin signalling through prostacyclin receptor / G beta:gamma signalling through CDC42 / Glucagon signaling in metabolic regulation / protein import into nucleus / G beta:gamma signalling through BTK / Synthesis, secretion, and inactivation of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 12 / photoreceptor disc membrane / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / Glucagon-type ligand receptors / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / G alpha (z) signalling events / cellular response to catecholamine stimulus / ADP signalling through P2Y purinoceptor 1 / ADORA2B mediated anti-inflammatory cytokines production / G beta:gamma signalling through PI3Kgamma Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.13 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Xiao, T. / Zheng, S. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1items China, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2022 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2022Title: Structural insights into G protein activation by D1 dopamine receptor. Authors: Xiao Teng / Sijia Chen / Qing Wang / Zhao Chen / Xiaoying Wang / Niu Huang / Sanduo Zheng /  Abstract: G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) comprise the largest family of membrane receptors and are the most important drug targets. An agonist-bound GPCR engages heterotrimeric G proteins and triggers the ...G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) comprise the largest family of membrane receptors and are the most important drug targets. An agonist-bound GPCR engages heterotrimeric G proteins and triggers the exchange of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) with guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to promote G protein activation. A complete understanding of molecular mechanisms of G protein activation has been hindered by a lack of structural information of GPCR-G protein complex in nucleotide-bound states. Here, we report the cryo-EM structures of the D1 dopamine receptor and mini-G complex in the nucleotide-free and nucleotide-bound states. These structures reveal major conformational changes in Gα such as structural rearrangements of the carboxyl- and amino-terminal α helices that account for the release of GDP and the GTP-dependent dissociation of Gα from Gβγ subunits. As validated by biochemical and cellular signaling studies, our structures shed light into the molecular basis of the entire signaling events of GPCR-mediated G protein activation. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7f1o.cif.gz 7f1o.cif.gz | 230.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7f1o.ent.gz pdb7f1o.ent.gz | 171.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7f1o.json.gz 7f1o.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7f1o_validation.pdf.gz 7f1o_validation.pdf.gz | 985.1 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7f1o_full_validation.pdf.gz 7f1o_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1005.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7f1o_validation.xml.gz 7f1o_validation.xml.gz | 34.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7f1o_validation.cif.gz 7f1o_validation.cif.gz | 53.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f1/7f1o https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f1/7f1o ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f1/7f1o ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/f1/7f1o | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  31421MC 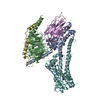 7f0tC  7f1zC  7f23C  7f24C C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Guanine nucleotide-binding protein ... , 3 types, 3 molecules ABD
| #2: Protein | Mass: 28907.684 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: G49D, E50N, A235D, S238D, I358A, V361I Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNAS, GNAS1, GSP / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNAS, GNAS1, GSP / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P63092 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P63092 |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 39286.891 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNB1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNB1 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P62873 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P62873 |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 7845.078 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Mutation: C68S Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNG2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: GNG2 / Production host:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P59768 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) / References: UniProt: P59768 |
-Protein / Antibody , 2 types, 2 molecules FE
| #1: Protein | Mass: 52409.656 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DRD1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DRD1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P21728 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P21728 |
|---|---|
| #5: Antibody | Mass: 17352.498 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.) synthetic construct (others) / Production host:  |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 3 molecules 




| #6: Chemical | ChemComp-LDP / |
|---|---|
| #7: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / |
| #8: Chemical | ChemComp-GDP / |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Cryo-EM structure of the GDP-bound dopamine receptor 1 and mini-Gs complex with Nb35 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#5 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 64000 X |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 601 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.16_3549: / Classification: refinement | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 973906 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.13 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 317029 / Num. of class averages: 2 / Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj


























