+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7ajb | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
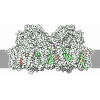
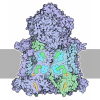
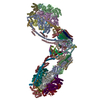
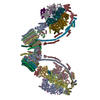
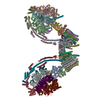
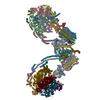
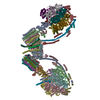
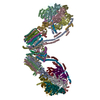
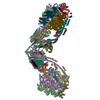
| Title | bovine ATP synthase dimer state1:state1 | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE / ATP synthase / mitochondria / mammalian / complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled proton transport / angiostatin binding / Formation of ATP by chemiosmotic coupling / Cristae formation / negative regulation of hydrolase activity / ATPase inhibitor activity / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex assembly / mitochondrial envelope / proton channel activity / heme biosynthetic process ...negative regulation of mitochondrial ATP synthesis coupled proton transport / angiostatin binding / Formation of ATP by chemiosmotic coupling / Cristae formation / negative regulation of hydrolase activity / ATPase inhibitor activity / mitochondrial proton-transporting ATP synthase complex assembly / mitochondrial envelope / proton channel activity / heme biosynthetic process / Mitochondrial protein degradation / negative regulation of endothelial cell proliferation / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex, proton-transporting domain / proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / proton transmembrane transport / aerobic respiration / erythrocyte differentiation / ADP binding / mitochondrial membrane / ATPase binding / protein homotetramerization / calmodulin binding / mitochondrial inner membrane / lipid binding / structural molecule activity / cell surface / protein homodimerization activity / ATP hydrolysis activity / protein-containing complex / mitochondrion / ATP binding / identical protein binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 9.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Spikes, T.E. / Montgomery, M.G. / Walker, J.E. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2items United Kingdom, 2items
| |||||||||
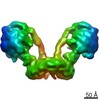
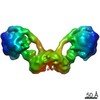
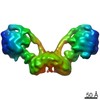
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021Title: Interface mobility between monomers in dimeric bovine ATP synthase participates in the ultrastructure of inner mitochondrial membranes. Authors: Tobias E Spikes / Martin G Montgomery / John E Walker /  Abstract: The ATP synthase complexes in mitochondria make the ATP required to sustain life by a rotary mechanism. Their membrane domains are embedded in the inner membranes of the organelle, and they dimerize ...The ATP synthase complexes in mitochondria make the ATP required to sustain life by a rotary mechanism. Their membrane domains are embedded in the inner membranes of the organelle, and they dimerize via interactions between their membrane domains. The dimers form extensive chains along the tips of the cristae with the two rows of monomeric catalytic domains extending into the mitochondrial matrix at an angle to each other. Disruption of the interface between dimers by mutation affects the morphology of the cristae severely. By analysis of particles of purified dimeric bovine ATP synthase by cryo-electron microscopy, we have shown that the angle between the central rotatory axes of the monomeric complexes varies between ca. 76 and 95°. These particles represent active dimeric ATP synthase. Some angular variations arise directly from the catalytic mechanism of the enzyme, and others are independent of catalysis. The monomer-monomer interaction is mediated mainly by j subunits attached to the surface of wedge-shaped protein-lipid structures in the membrane domain of the complex, and the angular variation arises from rotational and translational changes in this interaction, and combinations of both. The structures also suggest how the dimeric ATP synthases might be interacting with each other to form the characteristic rows along the tips of the cristae via other interwedge contacts, molding themselves to the range of oligomeric arrangements observed by tomography of mitochondrial membranes, and at the same time allowing the ATP synthase to operate under the range of physiological conditions that influence the structure of the cristae. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7ajb.cif.gz 7ajb.cif.gz | 1.3 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7ajb.ent.gz pdb7ajb.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7ajb.json.gz 7ajb.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/aj/7ajb https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/aj/7ajb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/aj/7ajb ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/aj/7ajb | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  11428MC  7ajcC  7ajdC  7ajeC  7ajfC  7ajgC  7ajhC  7ajiC  7ajjC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 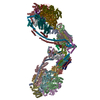
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-ATP synthase ... , 16 types, 54 molecules 8A8ABCAAABACDEFADAEAFGAGHAHIAIKLMNOPQRAKAL...
| #1: Protein | Mass: 7944.523 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | Mass: 55302.191 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: Residue 1 of chains A, B, C. The uniprot database is misleading stating that GLN is the first residue. The DNA sequence for this protein encodes GLU. The actual residue is pyroGLU. However ...Details: Residue 1 of chains A, B, C. The uniprot database is misleading stating that GLN is the first residue. The DNA sequence for this protein encodes GLU. The actual residue is pyroGLU. However pyroGLU and pyroGLN are the same. Residue 481 in chains A, B, and C can be Gly or SER. e.g. in this structure should be GLY. We have seen SER in some of our previous structures of bovine F1-ATPase. We have used the following REMARK in other PDB files: Microhetrogeneity REMARK 999 SER 481 GLY IN CHAINS A, B AND C REMARK 999 WAS IDENTIFIED AS A GLY FROM THE PROTEIN REMARK 999 SEQUENCE. IN THE CDNA SEQUENCE, THE CODON FOR THIS REMARK 999 RESIDUE WAS AGC SER IN THREE CLONES WHILE IN TWO REMARK 999 OTHERS IT WAS GGC GLY. THE DIFFERENCE WAS THOUGHT TO REMARK 999 BE DUE TO A MUTATION OCCURRING DURING EITHER PROPAGATION REMARK 999 OF THE CLONES IN THE LIBRARY OR SUBCLONING INTO M13 REMARK 999 VECTORS. THE ELECTRON DENSITY SUGGESTS A GLY IN REMARK 999 THIS POSITION. Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | Mass: 51757.836 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: P00829, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #4: Protein | Mass: 30300.760 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #5: Protein | Mass: 15074.813 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #6: Protein/peptide | Mass: 5662.693 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #8: Protein | Mass: 7653.034 Da / Num. of mol.: 16 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Details: Residue 43 is post translationally modified to tri-methyl-lysine Source: (natural)  #9: Protein | Mass: 20959.777 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #10: Protein | Mass: 24801.785 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #11: Protein | Mass: 24702.709 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #12: Protein | Mass: 18588.256 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #13: Protein | Mass: 8205.492 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #14: Protein | Mass: 10184.011 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #15: Protein | Mass: 11298.196 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #17: Protein | Mass: 6846.093 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #18: Protein | Mass: 6312.383 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Protein , 2 types, 4 molecules JAJhAh
| #7: Protein | Mass: 7462.098 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: Residues 1-60 of IF1 with a 6 His tag / Source: (gene. exp.)   #16: Protein | Mass: 8971.079 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 10 molecules 
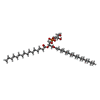

| #19: Chemical | ChemComp-CDL / #20: Chemical | ChemComp-LHG / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 1.18 MDa / Experimental value: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 4.5 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Grid material: GOLD / Grid type: UltrAuFoil | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 55 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: UCSF ChimeraX / Version: 1.1/v9 / Classification: model building / URL: https://www.rbvi.ucsf.edu/chimerax/ / Os: macOS / Type: package |
|---|---|
| EM software | Name:  UCSF Chimera / Version: 1.1 / Category: model fitting / Details: ChimeraX UCSF Chimera / Version: 1.1 / Category: model fitting / Details: ChimeraX |
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 9.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 15567 / Symmetry type: POINT |
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6ZPO Accession code: 6ZPO / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






































































 PDBj
PDBj