[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6tz9: CryoEM reconstruction of membrane-bound ESCRT-III filament compos... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6tz9 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
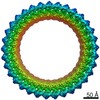
| Title | CryoEM reconstruction of membrane-bound ESCRT-III filament composed of CHMP1B only | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Charged multivesicular body protein 1b | ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIPID BINDING PROTEIN / membrane remodeling / membrane-bound protein filament / ESCRT-III | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationMIT domain binding / multivesicular body-lysosome fusion / amphisome membrane / vesicle fusion with vacuole / ESCRT III complex disassembly / late endosome to lysosome transport / ESCRT III complex / kinetochore microtubule / endosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway / membrane coat ...MIT domain binding / multivesicular body-lysosome fusion / amphisome membrane / vesicle fusion with vacuole / ESCRT III complex disassembly / late endosome to lysosome transport / ESCRT III complex / kinetochore microtubule / endosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway / membrane coat / nuclear membrane reassembly / multivesicular body sorting pathway / regulation of centrosome duplication / midbody abscission / membrane fission / plasma membrane repair / late endosome to vacuole transport / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway / multivesicular body assembly / multivesicular body membrane / regulation of mitotic spindle assembly / mitotic metaphase chromosome alignment / nucleus organization / viral budding via host ESCRT complex / autophagosome membrane / autophagosome maturation / nuclear pore / multivesicular body / viral budding from plasma membrane / establishment of protein localization / kinetochore / autophagy / protein transport / midbody / endosome membrane / protein domain specific binding / cell division / lysosomal membrane / extracellular exosome / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Nguyen, H.C. / Frost, A. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 5items United States, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2020Title: Membrane constriction and thinning by sequential ESCRT-III polymerization. Authors: Henry C Nguyen / Nathaniel Talledge / John McCullough / Abhimanyu Sharma / Frank R Moss / Janet H Iwasa / Michael D Vershinin / Wesley I Sundquist / Adam Frost /  Abstract: The endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRTs) mediate diverse membrane remodeling events. These typically require ESCRT-III proteins to stabilize negatively curved membranes; ...The endosomal sorting complexes required for transport (ESCRTs) mediate diverse membrane remodeling events. These typically require ESCRT-III proteins to stabilize negatively curved membranes; however, recent work has indicated that certain ESCRT-IIIs also participate in positive-curvature membrane-shaping reactions. ESCRT-IIIs polymerize into membrane-binding filaments, but the structural basis for negative versus positive membrane remodeling by these proteins remains poorly understood. To learn how certain ESCRT-IIIs shape positively curved membranes, we determined structures of human membrane-bound CHMP1B-only, membrane-bound CHMP1B + IST1, and IST1-only filaments by cryo-EM. Our structures show how CHMP1B first polymerizes into a single-stranded helical filament, shaping membranes into moderate-curvature tubules. Subsequently, IST1 assembles a second strand on CHMP1B, further constricting the membrane tube and reducing its diameter nearly to the fission point. Each step of constriction thins the underlying bilayer, lowering the barrier to membrane fission. Our structures reveal how a two-component, sequential polymerization mechanism drives membrane tubulation, constriction and bilayer thinning. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6tz9.cif.gz 6tz9.cif.gz | 708.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6tz9.ent.gz pdb6tz9.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6tz9.json.gz 6tz9.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tz/6tz9 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tz/6tz9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tz/6tz9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/tz/6tz9 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  20590MC  6tz4C  6tz5C  6tzaC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10397 (Title: CryoEM reconstruction of membrane-bound ESCRT-III filament composed of CHMP1B only EMPIAR-10397 (Title: CryoEM reconstruction of membrane-bound ESCRT-III filament composed of CHMP1B onlyData size: 3.8 Data #1: Processed particle stack and metadata for a cryoEM helical reconstruction of membrane-bound ESCRT-III filament composed of CHMP1B only [picked particles - multiframe - processed]) |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
| Symmetry | Helical symmetry: (Circular symmetry: 1 / Dyad axis: no / N subunits divisor: 1 / Num. of operations: 26 / Rise per n subunits: 1.86 Å / Rotation per n subunits: 13.86 °) |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 22140.354 Da / Num. of mol.: 26 / Mutation: K37E Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CHMP1B, C18orf2 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CHMP1B, C18orf2 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: HELICAL ARRAY / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: membrane-bound ESCRT-III copolymer filament composed of CHMP1B only Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 292 K Details: Grids were blotted with Whatman No. 1 filter paper for 4-8 seconds with a 0 mm offset at 19C and 100 percent humidity before plunging into liquid ethane |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 45 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 13.86 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 1.86 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 9661 / Symmetry type: HELICAL |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj