[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6smh: Cryo-electron microscopy structure of a RbcL-Raf1 supercomplex fr... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6smh | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
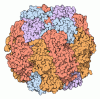
| Title | Cryo-electron microscopy structure of a RbcL-Raf1 supercomplex from Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PHOTOSYNTHESIS / Rubisco / Rubisco accumulation factor1 / Raf1 / Synechococcus elongatus 7942 / Cyanobacteria | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationribulose bisphosphate carboxylase complex assembly / photorespiration / carboxysome / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle / carbon fixation / photosynthesis / monooxygenase activity / magnesium ion binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.3 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Huang, F. / Kong, W.-W. / Sun, Y. / Chen, T. / Dykes, G.F. / Jiang, Y.L. / Liu, L.N. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 4items United Kingdom, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020Title: Rubisco accumulation factor 1 (Raf1) plays essential roles in mediating Rubisco assembly and carboxysome biogenesis. Authors: Fang Huang / Wen-Wen Kong / Yaqi Sun / Taiyu Chen / Gregory F Dykes / Yong-Liang Jiang / Lu-Ning Liu /   Abstract: Carboxysomes are membrane-free organelles for carbon assimilation in cyanobacteria. The carboxysome consists of a proteinaceous shell that structurally resembles virus capsids and internal enzymes ...Carboxysomes are membrane-free organelles for carbon assimilation in cyanobacteria. The carboxysome consists of a proteinaceous shell that structurally resembles virus capsids and internal enzymes including ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco), the primary carbon-fixing enzyme in photosynthesis. The formation of carboxysomes requires hierarchical self-assembly of thousands of protein subunits, initiated from Rubisco assembly and packaging to shell encapsulation. Here we study the role of Rubisco assembly factor 1 (Raf1) in Rubisco assembly and carboxysome formation in a model cyanobacterium, PCC7942 (Syn7942). Cryo-electron microscopy reveals that Raf1 facilitates Rubisco assembly by mediating RbcL dimer formation and dimer-dimer interactions. Syn7942 cells lacking Raf1 are unable to form canonical intact carboxysomes but generate a large number of intermediate assemblies comprising Rubisco, CcaA, CcmM, and CcmN without shell encapsulation and a low abundance of carboxysome-like structures with reduced dimensions and irregular shell shapes and internal organization. As a consequence, the Raf1-depleted cells exhibit reduced Rubisco content, CO-fixing activity, and cell growth. Our results provide mechanistic insight into the chaperone-assisted Rubisco assembly and biogenesis of carboxysomes. Advanced understanding of the biogenesis and stepwise formation process of the biogeochemically important organelle may inform strategies for heterologous engineering of functional CO-fixing modules to improve photosynthesis. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6smh.cif.gz 6smh.cif.gz | 849.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6smh.ent.gz pdb6smh.ent.gz | 711.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6smh.json.gz 6smh.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sm/6smh https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sm/6smh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sm/6smh ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/sm/6smh | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  10235MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 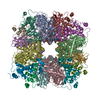
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 49641.219 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942 / FACHB-805) (bacteria) Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942 / FACHB-805) (bacteria)Gene: cbbL, rbcL, Synpcc7942_1426 / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q31NB3, ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase #2: Protein | Mass: 21676.561 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942 / FACHB-805) (bacteria) Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942 / FACHB-805) (bacteria)Gene: Synpcc7942_0833 / Production host:  |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: RbcL-Raf1 supercomplex of Synechococcus elongatus 7942 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942 / FACHB-805) (bacteria) Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942 / FACHB-805) (bacteria) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NITROGEN |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI F20 |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 200 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 25 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 16022 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj